Short & Long Answer Questions: The p-Block Elements - 2 | Inorganic Chemistry for NEET PDF Download
Q.1 Complete and Balance-
a) P4 + 8SICl2 →
b) 3CH3CooH + PCl3 →
c) P4 + 10SO2Cl2 →
d) POCl3 + 3H2O →
e) Sn + PCl5 →
f) 4AgNO3 + 2H2O +H3PO2 →
Ans. Complete and Balance
a) P4 + 8SOCl2 → 4PCl3 + 4SO2 + 2S2Cl2
b) 3CH3COOH + PCI3 → 3CH3COCI + H3PO3
c) P4 + 10SO2CI2 → 4PCI5 + 10SO2
d) POCI3 + 3H2O → H3PO4 + 3HCI
e) Sn + PCI5 → SnCl4 + 2PCI3
f) 4AgNO3 + 2H2O + H3PO2 → 4Ag + 4HNO3 + H3PO4
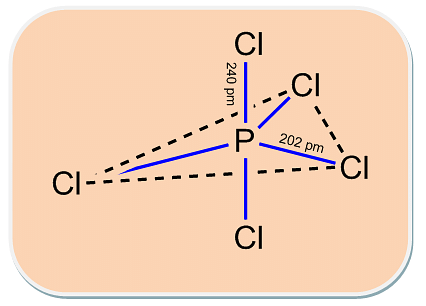
Q.2 All five bonds in PCI3 are not equal. Give an equation in support of this statement.
Ans. When heated, PCI5 loses a chlorine molecule this shows that two P- CL bonds are weaker and hence longer than others. 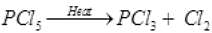
 Q.4 Explain the chemistry behind brown ring test for detection of nitrate ions.
Q.4 Explain the chemistry behind brown ring test for detection of nitrate ions.
Ans. The brown ring test for nitrate ions depends on the ability of Fe2+ to reduce nitrates to nitric oxide, which reacts with Fe2+ to form a brown coloured complex.
NO-3 +3Fe2+ + 4H+ → NO + 3Fe3+ + 2H2O
[Fe(H2O)6]2+ + NO → [Fe(H2O)5 NO]2++ H2O
Q.5 Write the various steps for preparation of sulphuric acid by contact process?
Ans. Contact process for sulphuric acid:-
Step 1: Burning of sulphur in air to give SO2
S+O2SO2
Step 2: Conversion of SO2 to SO3 by reacting it with oxygen in presence of V2O5 .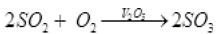
Step 3: Absorption of SO3 in H2SO4 to give of oleum (H2S2O7)
SO3 + H2SO4 → H2S2O7(oleum)
Step 4: Dilution of oleum with water to get H2SO4 of desired concentration
H2S2O7 + H2O → 2H2SO4
Q.6 Name different sulphates formed by sulphuric acid?
Ans. The two type of sulphates are –
(i) Normal sulphate eg. Na2SO4 , CuSO4
(ii) acid sulphate eg.NaHSO4.
Q.7.Why are pentahalides more covalent than trihalides?
Ans. In pentahalides, the oxidation state is +5 and in trihalides, the oxidation state is +3. Since the metal ion with a high charge has more polarizing power, pentahalides are more covalent than trihalides.
Q.8 Why is BiH3 the strongest reducing agent amongst all the hydrides of Group 15 elements?
Ans. As we move down a group, the atomic size increases and the stability of the hydrides of group 15 elements decreases. Since the stability of hydrides decreases on moving from NH3 to BiH3 , the reducing character of the hydrides increases on moving from NH3 to BiH3 .
Q.9 Why is N2 less reactive at room temperature?
Ans. The two N atoms in N2 are bonded to each other by very strong triple covalent bonds. The bond dissociation energy of this bond is very high. As a result, N2 is less reactive at room temperature.
Q.10 How does ammonia react with a solution of Cu2+?
Ans. NH3 acts as a Lewis base. It donates its electron pair and forms a linkage with metal ion.
Q.11 What happens when white phosphorus is heated with concentrated NaOH solution in an inert atmosphere of CO2?
Ans. White phosphorous dissolves in boiling NaOH solution (in a CO2 atmosphere) to give phosphine,PH3 . 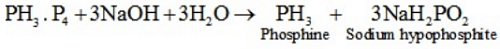
Q.12 Write a balanced equation for the hydrolytic reaction of PCI5 in heavy water.
Ans. All the bonds that are present in PCI5 are not similar. It has three equatorial and two axial bonds. The equatorial bonds are stronger are stronger than the axial ones. Therefore, when PCI5 is heated strongly, it decomposes to form PCI3 .
Q.13 What happens when PCI5 is heated ?
Ans. PCI5 + D2O → POCI3 + 2DCI2
POCI3 + 3D2O → D3PO4 + 3DCI
Therefore, the net reaction can be written as
PCI5 + 4D2O → D3PO4 + 5DCI
Q.14 List the important sources of sulphur.
Ans. Sulphur mainly exists in combined form in the earth's crust primarily as sulphates [gypsum (CaSO4. 2H2O ), Epsom salt (MgSO4. 7H2O), baryte (BaSO4)] and sulphides [galena (PbS), zinc blends (ZnS), copper pyrites (CuFeS2)].
Q.15 Why is H2O a liquid and H2S a gas?
Ans. H2O has oxygen as the central atom. Oxygen has smaller size and higher electronegativity as compared to sulphur. Therefore, there is extensive hydrogen bonding in H2O , which is absent in H2S . Molecules of H2S are held together only by weak Van der Waal's forces of attraction.
Hence, H2O exists as a liquid while H2S as a gas.
Q.16 Complete the following reactions:
(i) C2H4 + O2→
(ii) 4Al + 3O2 →
Ans. (i) 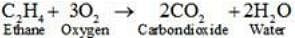
(ii) 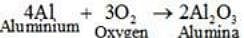
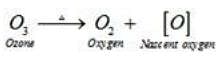
Therefore, ozone acts as a powerful oxidising agent.
Q.17 Why does O3 act as a powerful oxidizing agent?
Ans. Ozone is not a very stable compound under normal conditions and decomposes readily on heating to give a molecule of oxygen and nascent oxygen. Nascent oxygen, being a free radical, is very reactive.

Therefore, ozone acts as a powerful oxidizing agent.
Q.18 What happens when sulphur dioxide is passed through an aqueous solution of Fe(III) salt?
Ans. SO2 acts as a reducing agent when passed through an aqueous solution containing Fe(III) salt. It reduces Fe(III) to Fe(II) i.e., ferric ions to ferrous ions.
2Fe2+ + SO2 + 2H2O → 2Fe2+ + SO2-4 + 4H+
Q.19 Give two examples to show the anomalous behaviour of fluorine.
Ans. Anomalous behaviour of fluorine
(i) It forms only one oxoacid as compared to other halogens that form a number of oxoacids.
(ii) Ionisation enthalpy, electronegativity, and electrode potential of fluorine are much higher than expected.
Q.20 Sea is the greatest source of some halogens. Comment.
Ans. Sea water contains chlorides, bromides, and iodides of Na, K, Mg, and Ca. However, it primarily contains NaCl. The deposits of dried up sea beds contain sodium chloride and carnallite, KCL.MGCl2.6H2O . Marine life also contains iodine in their systems. For example, sea weeds contain upto 0.5% iodine as sodium iodide. Thus, sea is the greatest source of halogens.
Q.21 Give the reason for bleaching action of C12.
Ans. When chlorine reacts with water, it produces nascent oxygen. This nascent oxygen then combines with the coloured substances present in the organic matter to oxide them into colourless substances.
Cl2 + H2O → 2HCl+[O]
Coloured substances + [O]→Oxidized colourless substance
Q.22 Name two poisonous gases which can be prepared from chlorine gas.
Ans. Two poisonous gases that can be prepared from chlorine gas are
(i) Phosgene (COCI2)
(ii) Mustard gas (CICH2CH2SCH2CH2CI)
Q.23 Why has it been difficult to study the chemistry of radon?
Ans. It is difficult to study the chemistry of radon because it is a radioactive substance having a half-life of only 3.82 days. Also, compounds of radon such as RnF2 have not been isolated. They have only been identified.
Q.24 Why is helium used in diving apparatus?
Ans. Air contains a large amount of nitrogen and the solubility of gases in liquids increases with increase in pressure. When sea divers dive deep into the sea, large amount of nitrogen dissolves in their blood. When they come back to the surface, solubility of nitrogen decreases and it separates from the blood and forms small air bubbles. This leads to a dangerous medical condition called bends. Therefore, air in oxygen cylinders used for diving is diluted with helium gas. This is done as He is sparingly less soluble in blood.
Q.25 Why does the reactivity of nitrogen differ from phosphorus?
Ans. Nitrogen is chemically less reactive. This is because of the high stability of its molecule, N2. In, N2 the two nitrogen atoms form a triple bond. This triple bond has very high bond strength, which is very difficult to break. It is because of nitrogen's small size that it is able to form pπ-pπ bonds with itself. This property is not exhibited by atoms such as phosphorus. Thus, phosphorus is more reactive than nitrogen.
Q.26 Why does NX3 form hydrogen bond but PH3 does not?
Ans. Nitrogen is highly electronegative as compared to phosphorus. This causes a greater attraction of electrons towards nitrogen in NX3 than towards phosphorus in PH3 . Hence, the extent of hydrogen bonding in PH3 is very less as compared to NX3 .
Q.27 How is nitrogen prepared in the laboratory? Write the chemical equations of the reactions involved.
Ans. An aqueous solution of ammonium chloride is treated with sodium nitrite. 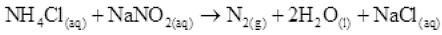
NO and HNO3are produced in small amounts. These are impurities that can be removed on passing nitrogen gas through aqueous sulphuric acid, containing potassium dichromate.
Q.28 Why does nitrogen show catenation properties less than phosphorus?
Ans. Catenation is much more common in phosphorous compounds than in nitrogen compounds. This is because of the relative weakness of the N-N single bond as compared to the P-P single bond. Since nitrogen atom is smaller, there is greater repulsion of electron density of two nitrogen atoms, thereby weakening the N-N single bond.
Q.29 . Give the disproportionation reaction of H3PO3.
Ans. On heating, orthophosphorus acid H3PO3 disproportionates to give orthophosphoric acid H3PO3 and phosphine (PH3) . The oxidation states of P in various species involved in the reaction are mentioned below. 
Q.30 Which aerosols deplete ozone?
Ans. Freons or chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are aerosols that accelerate the depletion of ozone. In the presence of ultraviolet radiations, molecules of CFCs break down to form chlorine-free radicals that combine with ozone to form oxygen.
Q.31 Explain why inspite of nearly the same electronegativity, oxygen forms hydrogen bonding while chlorine does not.
Ans. Both chlorine and oxygen have almost the same electronegativity values, but chlorine rarely forms hydrogen bonding. This is because in comparison to chlorine, oxygen has a smaller size and as a result, a higher electron density per unit volume.
Q.32 Write two uses of CIO2.
Ans. Uses of CIO2 :
(i) It is used for purifying water.
(ii) It is used as a bleaching agent.
Q.33 Why are halogens coloured?
Ans. Almost all halogens are coloured. This is because halogens absorb radiations in the visible region. This results in the excitation of valence electrons to a higher energy region. Since the amount of energy required for excitation differs for each halogen, each halogen displays a different colour.
Q.34 . Write the reactions of F2 and Cl2 with water.
Ans.(i)

(ii) 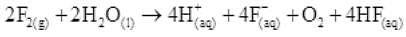
Q.35 How can you prepare Cl2 from HCl and HCl from Cl2 ? Write reactions only.
Ans.(i) Cl2can be prepared from HCl by Deacon's process.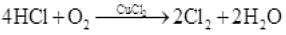
(ii) HCl can be prepared from Cl2 on treating it with water
Q.36 What inspired N. Bartlett for carrying out reaction between Xe and PtF6 .
Ans. Neil Bartlett initially carried out a reaction between oxygen and PtF6 . This resulted in the formation of a red compound, O+2[PtF5]-.
Later, he realized that the first ionization energy of oxygen (1175 kJ/mol) and Xe (1170 kJ/mol) is almost the same. Thus, he tried to prepare a compound with Xe and PtF6 . He was successful and a red-coloured compound,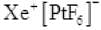 was formed.
was formed.
Q.37 Write balanced equations for the following:
(i) NaCl is heated with sulphuric acid in the presence of MnO2 .
(ii) Chlorine gas is passed into a solution of NaI in water.
Ans. (i) 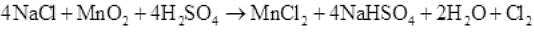
(ii) 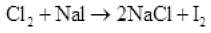
Q.38 With what neutral molecule is CIO- isoelectronic? Is that molecule a Lewis base?
Ans. CIO- is isoelectronic to ClF. Also, both species contain 26 electrons in all as shown. Total electrons CIO- = 17 + 8 + 1 = 26
In ClF = 17 + 9 = 26
ClF acts like a Lewis base as it accepts electrons from F to form CIf3.
Q.39 How XeO3 are and XeOF4 prepared?
Ans. (i) XeO3 can be prepared in two ways as shown.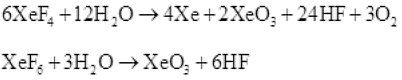
(ii) XeOF4 can be prepared using XeF6 .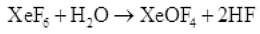
Q.40 Why do noble gases have comparatively large atomic sizes?
Ans. Noble gases do not form molecules. In case of noble gases, the atomic radii corresponds to van der Waal's radii. On the other hand, the atomic radii of other elements correspond to their covalent radii. By definition, van der Waal's radii are larger than covalent radii. It is for this reason that noble gases are very large in size as compared to other atoms belonging to the same period.
|
74 videos|106 docs|111 tests
|
FAQs on Short & Long Answer Questions: The p-Block Elements - 2 - Inorganic Chemistry for NEET
| 1. What are the p-block elements? |  |
| 2. What are the properties of the p-block elements? |  |
| 3. How are the p-block elements classified? |  |
| 4. What are some important compounds formed by p-block elements? |  |
| 5. How are the p-block elements used in everyday life? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|

















