Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Question Answers - Transportation in Animals and Plants
Short Answer Questions
Q1: What do you mean by dialysis? Explain.
Ans: Dialysis is an artificial method used to remove waste and excess water from the blood when the kidneys are not functioning properly. It involves the following steps:
- The patient's blood is drawn into a dialysis machine.
- The blood passes through a tank containing a special solution of water, glucose, and salt.
- This solution helps to filter out waste products.
- The cleaned blood is then pumped back into the patient's vein.
- This process continues until all the blood has been purified.
Q2: Write the two functions of kidneys.
Ans: The two main functions of the kidneys are:
- Excretion: This is the process of removing harmful metabolic waste products from the body.
- Osmoregulation: This function regulates the osmotic pressure of body fluids by controlling the levels of water and salts.
Q3: State one function of the following:
- Arteries
- Vein
- Capillaries
Ans:
- Arteries: They carry blood from the heart to various parts of the body.
- Veins: They transport blood from different parts of the body back to the heart.
- Capillaries: They facilitate the exchange of materials between blood and surrounding cells.
Q4: Why is heart known as the pumping organ of the human body?
Ans: The heart is known as the pumping organ of the human body because it:
- Continuously beats to transport blood throughout the body.
- Pumps oxygen-rich blood to various body parts.
- Delivers carbon dioxide-rich blood to the lungs for removal.
This constant action is vital for maintaining the body's overall health and function.
Q5: What is the significance of dividing heart into different chambers?
Ans: The division of the heart into different chambers plays a crucial role in maintaining efficient blood circulation. Here are the key points:
- It prevents the mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
- This separation enhances the efficiency of blood circulation.
- It allows for effective transportation of oxygen to the body's tissues.
Q6: Explain pulse and pulse rate.
Ans: The pulse is the throbbing sensation felt in the arteries when blood flows through them. It is a direct result of the heart's activity. The number of times the heart beats in a minute is known as the pulse rate. Key points about pulse and pulse rate:
- A normal pulse rate for a resting person is typically between 72 and 80 beats per minute.
- The pulse can be felt in various parts of the body, such as the wrist and neck.
- A stethoscope is used by doctors to listen to the heartbeat and assess heart health.
Q7: Why walls of veins are thinner than the walls of arteries?
Ans: Veins have thinner walls than arteries for several reasons:
- The blood in veins is under lower pressure compared to blood in arteries.
- Arteries carry blood directly from the heart, which is pumped at high pressure.
- As a result, arteries need thicker, elastic walls to withstand this pressure.
In contrast, veins return blood to the heart and do not require such thick walls.
Q8: How do plants absorb water and minerals from soil?
Ans: Plants absorb water and minerals from the soil through their roots. This process involves:
- Root hairs increase the surface area for absorption.
- Water and dissolved minerals are taken in from the soil.
- The roots are in contact with underground water.
- Absorbed water moves up the plant through xylem vessels.
Overall, this system allows plants to efficiently gather the resources they need for growth and survival.
Q9: Differentiate between arteries and veins.
Ans: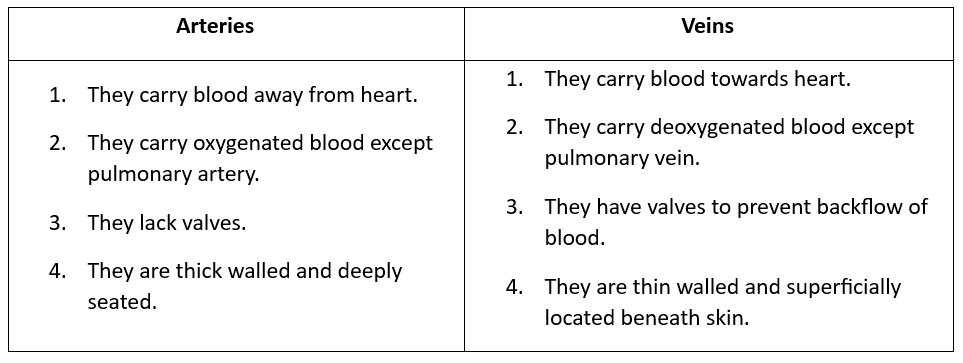
Q10: Differentiate between atrium and Ventricle.
Ans: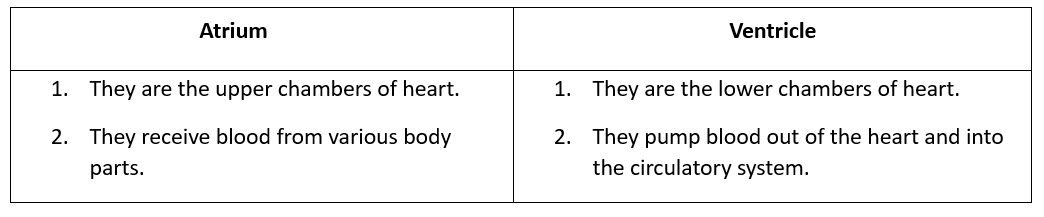
Q11: Why do sponges and hydra not have blood?
Ans: Sponges and hydra do not have blood because they lack a circulatory system. Instead, they rely on the surrounding water for essential functions:
- The water brings food and oxygen into their bodies.
- As the water exits, it carries away waste materials and carbon dioxide.
Thus, these animals do not require a circulatory fluid like blood.
Q12: Enlist the functions of blood.
Ans:
- Blood transports substances like digested food from the small intestine to other parts of the body.
- It carries oxygen from the lungs to the cells and carbon dioxide back to the lungs.
- Blood also transports waste products for removal from the body.
Q13: Differentiate between xylem and phloem.
Ans: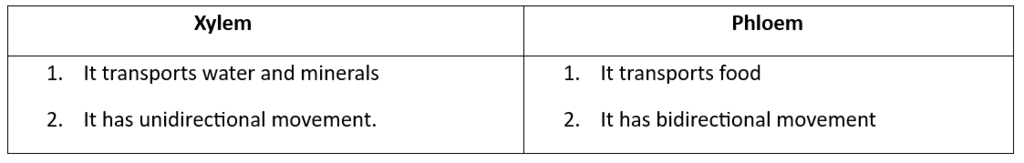
Q14: Differentiate between RBC and WBC.
Ans:
Q15: Why is blood needed by all the parts of the body?
Ans: The blood is essential for all parts of the body because it:
- Transports nutrients, such as digested food, from the small intestine to various body parts.
- Delivers oxygen from the lungs to the body's cells.
- Removes waste products for excretion from the body.
Q16: Why blood is red in colour?
Ans: The colour of blood is primarily due to the presence of haemoglobin, a red pigment found in red blood cells (RBCs). Here’s how it works:
- Haemoglobin binds with oxygen in the lungs.
- It transports oxygen to all parts of the body, reaching every cell.
- Without haemoglobin, delivering oxygen efficiently would be challenging.
Thus, the presence of haemoglobin is what makes blood appear red.
Q17: What is the function of RBCs?
Ans: Red Blood Cells (RBCs) contain a red pigment called haemoglobin. Their main functions include:
- Binding with oxygen in the lungs.
- Transporting oxygen to all parts of the body.
- Facilitating efficient oxygen delivery to cells.
- Giving blood its red colour due to the presence of haemoglobin.
Without haemoglobin, it would be challenging to supply oxygen effectively throughout the body.
Q18: Does transpiration serve any useful function in the plants? Explain.
Ans: Transpiration is an essential process in plants that serves several useful functions:
- Plants absorb water and minerals from the soil through their roots.
- Not all absorbed water is used; some evaporates through stomata on the leaves.
- This evaporation creates a suction pull that helps draw water up from the roots to the leaves, even in tall trees.
- Transpiration also helps to cool the plant, similar to how sweating cools the human body.
Q19: Explain stomata and its function in plants.
Ans: Stomata are tiny pores located on the surface of leaves, surrounded by special cells known as guard cells. Their main functions include:
- Carbon Dioxide Absorption: Stomata allow plants to take in carbon dioxide from the air, which is essential for the process of photosynthesis.
- Water Regulation: Stomata also play a role in the absorption of water and minerals from the soil. While not all absorbed water is used by the plant, much of it evaporates through the stomata in a process called transpiration. This evaporation creates a suction pull that helps draw water up from the roots to the leaves, especially in tall trees. Additionally, transpiration helps cool the plant.
Q20: What will happen if there are no platelets in the blood?
Ans: Platelets are essential cells in the blood that help form clots to stop bleeding when we get injured. If there are no platelets in the blood:
- Even a small injury could lead to excessive bleeding.
- Without clots, the body cannot effectively seal wounds.
- This can result in serious health risks, including death.
In summary, absence of platelets severely impairs the body's ability to control bleeding.
Q21: What is the significance of transport of materials in plants and animals?
Ans: Transport of materials is crucial for both plants and animals, as all organisms require essential substances for survival. These include:
- Food: Provides energy; every cell needs it for vital functions.
- Water: Necessary for various biochemical processes.
- Oxygen: Essential for cellular respiration.
In animals, the transport system also removes waste products to maintain health. Key points include:
- Blood circulates nutrients and oxygen to cells.
- Waste products are transported to excretory organs for removal.
Overall, effective transport systems ensure that all parts of an organism receive what they need to function properly.
Q22: Why is it necessary to excrete waste products?
Ans: When our cells perform their functions, certain waste products are released. These waste products are toxic and hence need to be removed from the body. The process of removal of wastes produced in the cells of the living organisms is called excretion.
Q23: What is heartbeat? Name the instrument used to provide information about heartbeat.
Ans: Heartbeat refers to the rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the heart, which occurs continuously throughout life. Each complete cycle is known as one heartbeat. The instrument used to monitor the heartbeat is called an Electrocardiogram (ECG). It records the electrical activity of the heart, providing important information about its rhythm and health.
Q24: Sometimes doctor inject medicines directly in our bloodstream, where do they inject in artery or in vein?
Ans : Doctor inject medicines in vein because veins are superficial and are easily locatable, secondly medicines need to be transported to all parts of the body through vein medicines reach the heart and from heart it is pumped to all part of body.
Q25: Explain the role of platelets in blood clotting.
Ans: Doctors inject medicines into the vein for several reasons:
- Accessibility: Veins are closer to the surface of the skin, making them easier to locate.
- Distribution: Medicines injected into veins quickly enter the bloodstream, allowing them to reach the heart and be pumped to all parts of the body.
This method ensures that the medication is effectively delivered throughout the body.
Long Answer Questions
Q1: Describe the function of the heart and circulatory system.Ans : The heart is a vital organ that continuously beats to act as a pump for transporting blood, which carries essential substances throughout the body.
Key features of the heart include:
- Located in the chest cavity, tilted slightly to the left.
- Approximately the size of a fist.
- Contains four chambers to prevent the mixing of oxygen-rich and carbon dioxide-rich blood.
- Two upper chambers called the atria (singular: atrium). Two lower chambers called the ventricles.
The circulatory system functions as follows:
- Blood flows from the right side of the heart to the lungs to receive oxygen.
- It then returns to the heart, where it is pumped to the rest of the body.
The walls of the heart's chambers are made of muscle that contract and relax rhythmically, creating a heartbeat.
Q2: Explain the function and components of blood.
Ans : The main components of blood are:
- Plasma: The liquid part of blood.
- Red Blood Cells (RBC): These contain a red pigment called haemoglobin, which binds with oxygen and transports it to all body cells. Without haemoglobin, delivering oxygen efficiently would be challenging. This pigment gives blood its red colour.
- White Blood Cells (WBC): These cells defend the body against infections by fighting germs.
- Platelets: These are responsible for forming clots when blood comes into contact with air. They help prevent excessive bleeding by sealing cuts and injuries.
Blood also plays a crucial role in:
- Transporting nutrients, such as digested food, from the small intestine to other body parts.
- Carrying oxygen from the lungs to body cells.
- Removing waste products from the body.
|
111 videos|286 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Question Answers - Transportation in Animals and Plants
| 1. What are the main modes of transportation in animals? |  |
| 2. How do plants transport water and nutrients? |  |
| 3. What role do the heart and blood vessels play in animal transportation? |  |
| 4. How does transpiration assist in the transportation process in plants? |  |
| 5. What are the differences between open and closed circulatory systems in animals? |  |






















