Short Questions: Our Country India | NCERT Summary: UPSC PDF Download
Q1: Describe the boundaries of India.
Ans: Boundaries of India.
- India is a country of vast geographical expanse.
- It is bounded by the mighty Himalayas in the north.
- Arabian sea bounds it in the west.
- Bay of Bengal forms its boundary in the east.
- Indian ocean bounds it in the south.
Q2: How does unity in diversity exist in India?
Ans:
- There is a great variety in climate, vegetation, wildlife as well as language and culture in India.
- In this diversity there is unity. It is reflected in traditions that bind us as one nation.
- India has a population of 122 crore according to Census of 2011.
- It is the second most populous country of the world after China.
Q3: Define delta. Which delta is the world’s largest delta? Where is it situated?
Ans: Delta: Delta is triangular deposition of the debris brought and deposited by rivers at their mouth. The Ganga and the Brahmaputra form the world’s largest delta.
 The Sunderban delta is situated at the mouth of the Ganga and Brahmaputra rivers at the head of the Bay of Bengal.
The Sunderban delta is situated at the mouth of the Ganga and Brahmaputra rivers at the head of the Bay of Bengal.
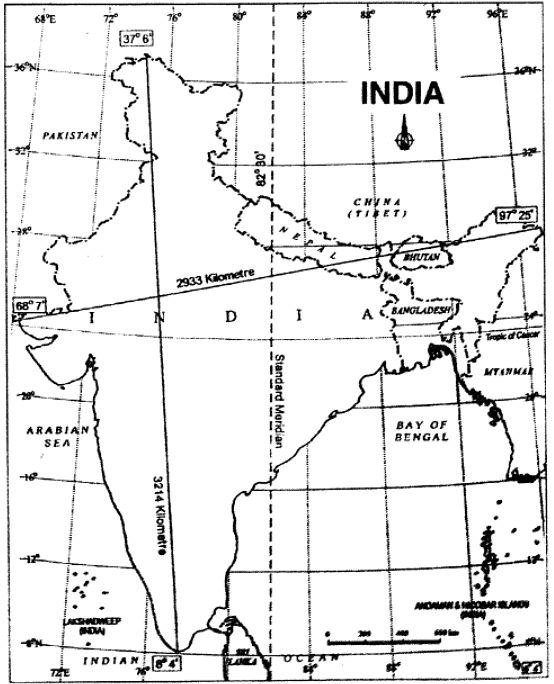
Q4: What is the locational extent of India? State the effect of East-West extent of India on time.
Ans: Location:
- India is located in the Northern hemisphere in respect of latitudes and the Eastern hemisphere in respect of longitudes.
- Tropic of Cancer (23°30′ N) passes almost through the middle of the country.
- From South to North, India is located between 6°4′ N latitudes and 37°6′ N latitudes.
- From West to East, India extends between 68°7′ E and 97°25′ E longitudes.
Effect of East-West extent on Time:
- The west to east extent leads to difference in local time from meridian to meridian.
- The local time changes by 4 minutes for every 1° difference in longitude (meridian).
- The time difference between the two extreme west and east points (Gujarat and Arunachal Pradesh) of India is about 2 hours.
- The sun rises 2 hours earlier in the east than in the west.
- The local time of 82°30′ E longitude is taken as the Indian Standard Time.
- This longitude is known as the Standard Meridian of India.
- Its time is taken as standard throughout the country.
- All watches in the country run according to the time of this meridian.
- Its time is called as 1ST.
Q5: Enumerate the physical divisions of India.
Ans: Physical Divisions of India:
- The Himalayan Mountains
- The North Indian Plains
- The Pennisular Plateau
- The Islands
- The Coastal Plains.
Q6: How is India a country of vast geographical expanse?
Ans:
- India has an area of about 32.8 crore hectares.
- Its north-south extent from Kashmir to Kanyakumari is about 3200 kms.
- It extends east-west from Arunachal Pradesh to Kuchchh over 2900 kms.
- The lofty mountains, the Thar desert, the Northern plains, Peninsular Plateau, east and west coasts and islands present a diversity of land forms.
Q7: Name any two south countries that share borders with India.
Ans: We have two neighbours to the south across the sea: the Maldives and Sri Lanka.
Q8: Which delta is formed by Ganga and Bramhputra?
Ans: The Sundarbans delta is formed by the Ganges and the Brahmaputra rivers.
Q9: Which place of India is known as coral reef?
Ans: Lakshadweep is regarded as India's coral reef. India owns the Lakshadweep Islands. The Arabian Sea is where it is located. These islands which are located off the coast of Kerala, have a lot of corals.
Q10: Give a briefing on the Himalayas.
Ans: One of India's physical divides is the mountains. The Himalayan Mountains can be found in the country's northwestern corner. They serve as northern sentinels. Three ranges run parallel to each other on this snow-capped peak. The Himachal, or intermediate Himalayas, is the range to the south of Himadri. There are numerous hill stations in this area. The Shiwalik range lies to the south of Himachal.
Q11: How useful are peninsular plateaus?
Ans: The peninsular plateau is a triangular-shaped plateau south of the northern plains. Coal, iron ore, and other minerals abound in this plateau region. There are various hill ranges and valleys in the plateau region. The Aravalli hills, one of the world's oldest ranges, are found on the peninsular plateau. They run along the peninsular plateau's north western edge.
Q12: Name two major rivers that fall in the Arabian sea.
Ans: The Arabian Sea is fed by two rivers that travel westward. Narmada and Tapi are the rivers.
Q13: Which are the new union territories of India?
Ans: India's two new union territories are Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh.
Q14: What is the position of India in latitude and longitude?
Ans: India is located in the earth's northern hemisphere. The Tropic of Cancer, which is 23 degrees and 30 minutes north of the equator, runs through the middle of the country. From south to north, Indian land stretches between latitudes 8 degrees 4 minutes north and 37 degrees 6 minutes north, and from west to east, between longitudes 68 degrees 7 minutes east and 97 degrees 25 minutes east.
Q15: What is the distance in India from north to south and east to west?
Ans: India is a massive country with a big geographical area. The massive Himalayas are to the north, and the Indian Ocean is to the south. The distance between Kashmir and Kanyakumari is approximately 3200 kilometres north-south. The distance between Kutch and Arunachal Pradesh, from west to east, is 2900 kilometres. The country's total area is around 3.28 million square kilometres.
Q16: Explains the regions around India.
Ans: Mountains, plateaus, plains, islands, and beaches abound throughout India. The mountains guard the northern part, while the plains guard the southern part. The peninsular plateau lies to the south of the plains. The Eastern and Western Ghats form a border to the east and west of these plateaus. Sahyadris is another name for the Western Ghats. The Eastern Ghats are uneven and fractured in several areas, unlike the Sahyadris, which are typically continuous.
|
666 docs
|

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
















