Seating Arrangement | Logical Reasoning for CLAT PDF Download
What is Seating Arrangement?
The seating arrangement is the logical arrangement of either objects or people in a logical manner. One has to either perform the arrangement to answer the questions or decode the predefined arrangement by applying the logical analysis.
- Seating arrangement questions are the most common problem types in all entrance exams containing the Logical Reasoning section.
- These concepts involve the arrangement of objects/ people in many possible ways.
The question based on sitting arrangement can be classified into the following types:
Type 1: Person Sitting in a Circle / Around a Table
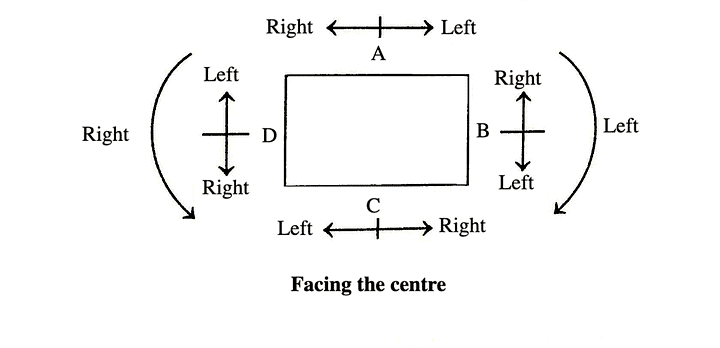
- In the questions of Type 1, the persons are sitting either around a table or circle. In either of the condition, the persons are facing the centre.

- The important point to be remembered is that the left side of the persons who is facingNorth, is just opposite of one, sitting opposite to him, who is facingSouth.


- From the diagram above, we observe that A is facing North and B is facing South. Also, the left side of A is just opposite to Right side of B. Similarly right side of A is just opposite of left side of B.
- Whenever we are presented with this kind of problem, the first step should be to locate the “Fulcrum,” i.e. the position around which we can locate the other positions.
- The next step is to draw the circle or the table and start the process of allocating the positions.
- In almost all the questions, the position of one person in relation to two other persons is given. We find that two different positions are possible.
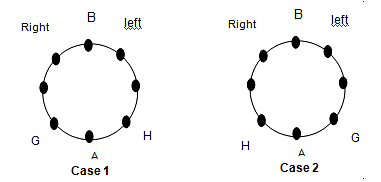
- Let us say, we are given that A is sitting between G and H, just opposite to B.
In such a case, following are the two possibilities:
In Case 1, G is to the left of A and in Case 2, G is to the right of A
- If we are further provided with the information that C is sitting second to the right of H.
- We note that this information can only be true in case 1, because in case 2, G is already second to the right of H. So we can reject case 2 and continue with case 1 only.
- In the next step, the other positions given can be allocated up very easily and we can answer the questions given to us.
- Generally based on one diagram, four to five questions are asked in the examinations. Once we have completed the diagram, all the questions can be answered.
Who is diagonally opposite to A?
Who is immediate neighbour of A?
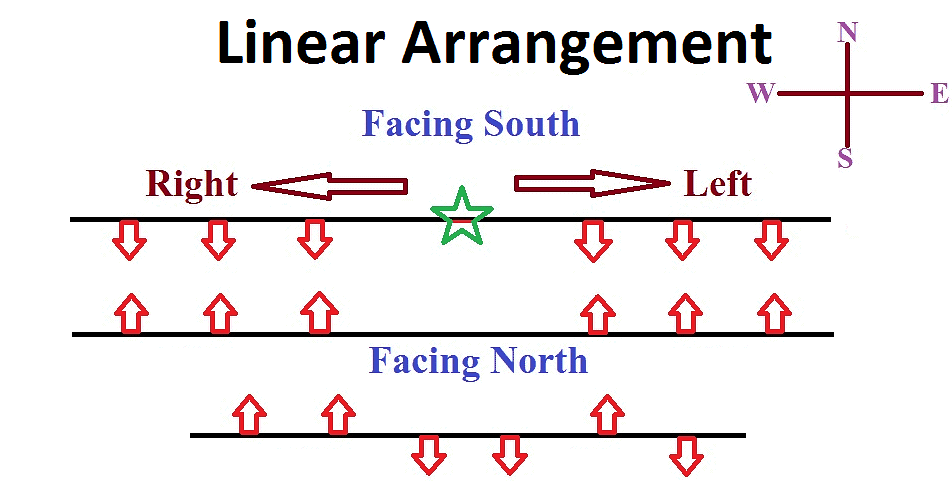
Type 2: Linear Arrangement
- Any logical arrangement of objects or people either horizontally or vertically or diagonally is known as Linear arrangement.
 Example: The row of the travellers in a train, students in a prayer hall, etc.
Example: The row of the travellers in a train, students in a prayer hall, etc.
1) F is to the immediate right of E. 2) E is 4th to the right of G. 3) C is the neighbour of B and D. 4) Person who is third to the left of D is at one of ends. What is the position of A ?
|
34 videos|85 docs|70 tests
|
FAQs on Seating Arrangement - Logical Reasoning for CLAT
| 1. What is a seating arrangement in examinations? |  |
| 2. Why is seating arrangement important in exams? |  |
| 3. What are the common types of seating arrangements used in exams? |  |
| 4. How can I prepare for seating arrangement questions in competitive exams? |  |
| 5. Are there any strategies to solve seating arrangement problems quickly? |  |

|
Explore Courses for CLAT exam
|

|