Sluice Gate Uses, Types and Location | Civil Engineering Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Sluice Gate Uses and Types
Sluice gates are essential structures in water conservancy projects, including irrigation and waterlogging control. They function to regulate water flow and adjust water levels using sluice gate hoists.Classified according to the purpose of the sluice gate
Intake Sluice Gate
- Purpose: Built on the banks of rivers, reservoirs, or lakes, and at the head of irrigation diversion channels.
- Function: Ensures and controls the flow into the canal.
- Also Known As: Headgate.
Divide Sluice Gate
- Purpose: Introduces flow from the upper-level channel into the next-level channel as needed.
- Function: Acts as the inlet gate for the next-level channel.
- Location-Based Names: Branch canal inlet (for branch canals), Doumen (for agricultural canals).
Control Sluice Gate
- Purpose: Built across trunk and branch canals to control water levels and meet the requirements of branch and bucket channels.
- Function: Uses gate opening and closing to regulate water levels and flow. Also helps in generating electricity in canal sections with drops.
- Combined Functionality: Can be paired with discharge gates to control flow and ensure safety.

Sluicing Gate
- Purpose: Built in critical canal sections or structures to discharge water into a designated area during emergencies.
- Function: Drains flood or canal water to ensure the safety of important sections or buildings.
- Alternate Use: Drains remaining water at the end of irrigation channels or removes runoff from slopes.
Drain Sluice Gate
- Purpose: Built at the end of drainage channels to discharge floodwater into rivers or lakes.
- Function: Prevents waterlogging and stores water for irrigation when river levels are low.
- Special Feature: Can block tides, drain waterlogging, and facilitate shipping during low tide by drawing freshwater.
Rinse Sand Sluice Gate
- Purpose: Built at the end of sedimentation basins in diversion hubs or canal systems on sediment-laden rivers.
- Function: Opens to release water and wash away sediment deposited in upstream sections.
- Additional Functionality: Can be used with control sluice gates for sediment management.
Key Points
- Multiple Functions: Sluice gates are versatile and can serve various functions such as intake, division, control, sluicing, draining, and rinsing sand.
- Safety and Efficiency: They play a critical role in ensuring the safety of water management structures and efficient distribution and use of water resources.
- Customization: The type and location of sluice gates are customized based on the specific needs and functions required in different sections of water management systems.
Classified according to the structure of the sluice chamber
Sluice gates can be classified based on the structure of the sluice chamber. The primary types include open sluices and culvert sluices.1. Open Sluice
Description:
- Open sluices are characterized by having no soil filling over the sluice chamber.
- Widely used in situations where the water level in front of the canal headgate, control gate, or drainage gate does not change significantly.
- Commonly employed in low dike areas with large diversion flows.


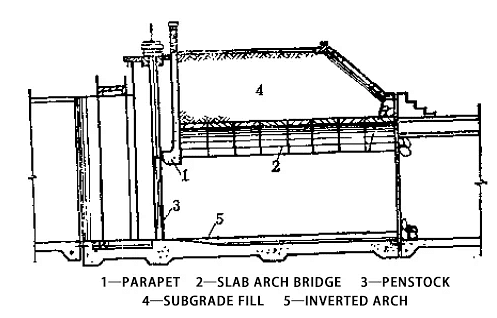
Types:
- Without Parapets: Used when there is minimal variation in upstream water levels and the flow through the sluice is considerable.
- With Parapets: Utilized when upstream water levels vary greatly but the flow is not substantial. This type reduces the gate height and the working bridge height, thus minimizing the gate opening force.
- Semi-Closed Sluice Chamber: Features a partially filled section behind the parapet wall to increase the anti-sliding stability. This configuration uses soil weight to enhance stability but requires a foundation with higher bearing capacity and a longer sluice chamber.
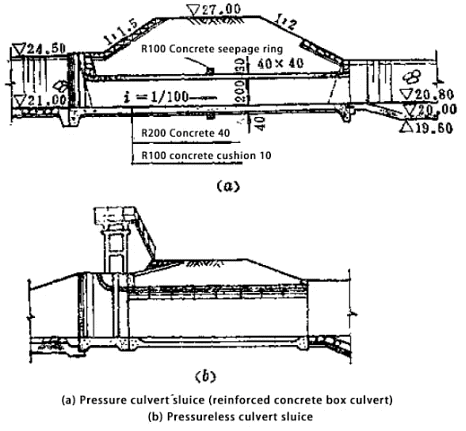
2. Culvert Sluice Gate
Description:
- Built on channels with high dikes and small diversion flows.
- The culvert sluice gate has soil filling over the cave body, often serving as a roadbed, making the structure of the connecting buildings simpler and more economical than open sluices.
Types:
- Pressure Culvert: Designed for specific hydraulic conditions where the water flows under pressure.
- Non-Pressure Culvert: Typically used in small drainage sluices, discharge sluices, and irrigation projects. Small sluice gates like buckets and agricultural gates often fall under this category.
Characteristics:
- Water Retention: Relies on the soil filling over the cave body.
- Flow Pattern Variability: The flow pattern inside the culvert changes with the water level in front of the sluice, accommodating different flow patterns such as pressure-flow.
- Anti-Seepage: The gate foundation and embankment anti-seepage measures are integrated.
- Load Distribution: The height of the filling varies, leading to uneven load distribution along the tunnel body. Proper segmentation with settlement joints and water-stop equipment is essential to prevent uneven settlement.

Design Considerations:
- Flow Pattern: Aim to maintain a single flow pattern, especially in sediment-laden rivers, by adjusting the bottom slope to prevent sedimentation.
- Joint Quality: Ensure high-quality joints with effective water-stop facilities to prevent leakage.
- Reinforcement: Shorten gaps between joints and strengthen the longitudinal reinforcement.
- Settlement Management: Account for larger settlements in the middle of the culvert compared to the ends. Adjust the bottom elevation accordingly, potentially arching the middle part of the axis upwards.
By understanding these classifications and characteristics, engineers can design sluice gates that effectively manage water flow, maintain stability, and ensure the safety of water management structures.
Sluice gate location selection
The selection of the sluice gate site should be based on the characteristics and application requirements of the sluice, comprehensively considering the topography, geology, water flow, sediment content, construction and management, and other factors, and determined after comparing the schemes.When choosing a location for a sluice gate, several factors need to be considered:
Geological Conditions: The site should be on a natural foundation with uniform and compact soil, avoiding artificial foundation treatment. Consider the level of groundwater and the presence of confined water, as they affect construction drainage measures and foundation stability.
Water Flow Conditions: Choose a location that ensures uniform and smooth water flow, with straight river or canal sections before and after the gate. Avoid places where harmful erosion and sedimentation may occur.
Construction and Management Conditions: Ensure good construction diversion conditions, a wide construction site, and favorable transportation. Consider ease of management, operation, flood prevention, and emergency rescue. Combine with the layout of road bridges or agricultural bridges where possible.
These factors are crucial for the proper functioning and longevity of the sluice gate and to minimize the risk of accidents or failures.

Supplementary requirements
For the various sluices of the irrigation canal system, in addition to meeting the above common requirements, different supplementary requirements should be put forward for their work characteristics.Intake Sluice Gate:
- Select a site with a stable river bed and bank for perennial water diversion.
- Locate the sluice gate on the concave bank of a river bend for smoother water intake.
- Ensure the water diversion angle is between 30° and 60° to reduce sediment entering the canal.
- Consider the presence of other projects that control changes in the river course.
Headgate for Dam Intake:
- Choose a stable location on the river bank with moderate height to reduce excavation.
- Arrange the gate upstream or downstream of the end of the dam based on the river's width and bank steepness.
- Use tunnels or diversion canals for water diversion before arranging the intake gate on the upstream side.
Drain Sluice Gate:
- Select a site on the drainage channel from the lowest point of the flood control area to ensure effective drainage.
- Ensure the ground elevation at the sluice gate site is low.
- Locate the outlet of the drain on the concave bank of the river to avoid siltation.

Discharge (Retreat) Sluice Gate:
- Choose a location with larger drainage areas and short drainage canal lines for quick and smooth water discharge.
- Ensure the section between discharge structures is not too long to discharge floodwater into the canal in time.
Sluice Gates and Control Sluices:
- Arrange sluice gates at water distribution points from upper-level channels to lower-level channels.
- Ensure the entrance of the sluice gate does not protrude from the upper-level channel but is built backward on the canal bank.
- Consider building sluice gates and control gates together to reduce engineering and costs.

These considerations are essential for the efficient and effective operation of sluice gates in various water management and control scenarios.
|
350 videos|464 docs|2 tests
|
|
350 videos|464 docs|2 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|