Small Satellites | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
The small satellite project is envisaged to provide platform for stand-alone payloads for earth imaging and science missions within a quick turn around time. For making the versatile platform for different kinds of payloads, two kinds of buses have been configured and developed.
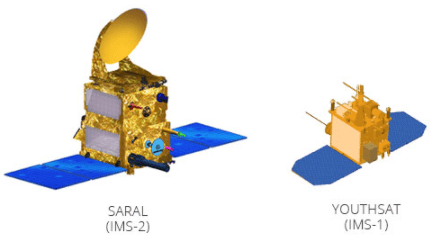
Indian Mini Satellite -1 (IMS-1)
IMS-1 bus has been developed as a versatile bus of 100 kg class which includes a payload capability of around 30 kg. The bus has been developed using various miniaturization techniques. The first mission of the IMS-1 series was launched successfully on April 28th 2008 as a co-passenger along with Cartosat 2A. Youthsat is second mission in this series and was launched successfully along with Resourcesat 2 on 20th April 2011.
Indian Mini Satellite -2 (IMS-2) Bus
IMS-2 Bus is evolved as a standard bus of 400 kg class which includes a payload capability of around 200kg. IMS-2 development is an important milestone as it is envisaged to be a work horse for different types of remote sensing applications. The first mission of IMS-2 is SARAL. SARAL is a co-operative mission between ISRO and CNES with payloads from CNES and spacecraft bus from ISRO.
Recently, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) chairman has mentioned the launch of an “SSLV-D1 Micro SAT in April 2022”.
- The SSLV (Small Satellite Launch Vehicle) aims to cater to the market for the launch of small satellites into Earth’s low orbits that has emerged in recent years to cater to the needs of developing countries, universities for small satellites, and private corporations.
Key Points
About:
- It is the smallest vehicle weighing only 110-tonne. It will take only 72 hours to integrate, unlike the 70 days taken now for a launch vehicle.
- It can carry satellites weighing up to 500 kg to a low earth orbit while the tried and tested Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) can launch satellites weighing in the range of 1000 kg.
- SSLV is a three-stage all solid vehicle and has a capability to launch up to 500 kg satellite mass into 500 km Low Earth Orbit (LEO) and 300 kg to Sun Synchronous Orbit (SSO).
- It is perfectly suited for launching multiple microsatellites at a time and supports multiple orbital drop-offs.
- The key features of SSLV are low cost, with low turn-around time, flexibility in accommodating multiple satellites, launch on demand feasibility, minimal launch infrastructure requirements, etc.
- The Government has sanctioned a total cost of Rs. 169 Crores for the development project including the development & qualification of the vehicle systems and the flight demonstration through three development flights (SSLV-D1, SSLV-D2 & SSLV-D3).
- ISRO’s new chairman Dr. Somanath is credited with designing and developing the SSLV during his tenure as director of the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre in Thiruvananthapuram since 2018.
- The maiden flight of the SSLV was scheduled to launch in July 2019 but that has since been delayed due to setbacks from Covid-19 and other issues.
Significance of SSLV
- The development and manufacture of the SSLV are expected to create greater synergy between the space sector and private Indian industries – a key aim of the space ministry.
- Indian industry has a consortium for the production of PSLV and should come together to produce the SSLV as well once it is tested.
- One of the mandates of the newly-created ISRO commercial arm, New Space India Limited (NSIL) is to mass-produce and manufacture the SSLV and the more powerful PSLV in partnership with the private sector in India through technology transfers.
- Its aim is to use research and development carried out by ISRO over the years for commercial purposes through Indian industry partners.
- Small satellite launches have so far depended on ‘piggy-back’ rides with big satellite launches on the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) — ISRO’s work-horse with more than 50 successful launches. As a result, small satellite launches have relied on ISRO finalising launch contracts for larger satellites.
|
146 videos|358 docs|249 tests
|
FAQs on Small Satellites - Science & Technology for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are small satellites? |  |
| 2. How do small satellites differ from larger satellites? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of using small satellites? |  |
| 4. How are small satellites launched into space? |  |
| 5. What are some challenges associated with small satellites? |  |
|
146 videos|358 docs|249 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|

















