Cheat Sheet: Socio-Religious Reform Movements: General Features | History for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
The document aims to chronicle the significant milestones in the social reform movement in India during British rule. It highlights the various factors that contributed to the need for reform, the actions taken, and the influential figures who led these changes. The chronology is divided into distinct topics, each represented in a separate table for clarity and coherence.
Impact of British Rule and Social Conditions
This section examines the contrast between British-ruled India and the progressive Europe of the 18th century, emphasizing the stagnant nature of Indian society and the ripe conditions for reform.

The period marked a critical juncture, setting the stage for a transformative era in Indian society, necessitating reform.
Key Social Issues and Reforms
This table outlines the major social issues plaguing Indian society in the 19th century, including the treatment of women, caste problems, and the opposition to Western culture.
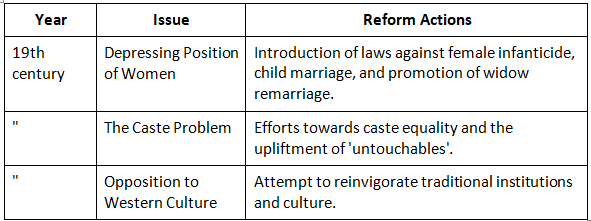
The social reform movements were a response to deeply entrenched societal issues, aiming to align Indian society with more progressive and humane values.
Educational and Women's Reforms
This section highlights the efforts made in the field of women's education and health, marking significant strides towards gender equality.

These reforms were crucial in elevating the status of women in Indian society, providing them with opportunities for education and better health.
Struggle Against Caste-Based Exploitation
This table focuses on the efforts to mitigate caste-based discrimination, a deeply rooted social issue in Indian society.
 The struggle against caste-based exploitation was a pivotal aspect of the social reform movement, leading to significant legislative and societal changes.
The struggle against caste-based exploitation was a pivotal aspect of the social reform movement, leading to significant legislative and societal changes.
|
111 videos|495 docs|173 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Socio-Religious Reform Movements: General Features - History for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are socio-religious reform movements? |  |
| 2. What were the general features of socio-religious reform movements? |  |
| 3. Who were some prominent leaders of socio-religious reform movements in India? |  |
| 4. What were the main goals of socio-religious reform movements in India? |  |
| 5. How did socio-religious reform movements contribute to the Indian independence movement? |  |

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|

















