Soil Erosion and its Management - 2 | NABARD Grade A & Grade B Preparation - Bank Exams PDF Download
Soil Management
Soil conservation constitutes a systematic approach with the aim of preserving soil fertility, preventing soil erosion, and restoring soil health. It encompasses a range of agricultural techniques and management strategies designed to manage soil erosion by reducing the detachment and transportation of soil particles through air or water.
- To counteract soil erosion, various corrective measures have been put into practice, which include contour bunding, contour terracing, controlled grazing, regulated forestry, cover cropping, mixed farming, and crop rotation.
- Afforestation, the process of planting trees, has a vital role in mitigating soil erosion. Simultaneously, preventing the indiscriminate cutting down of trees is essential to avoid exacerbating erosion.
- Soil erosion is intricately connected to flooding, which is more frequent during the wet season. Therefore, it is crucial to focus efforts on storing floodwater and diverting rainwater. Projects like the Ganga-Kaveri Link Canal Project, which seeks to interlink rivers, are particularly significant in addressing this concern.
- Tackling the issue of soil erosion necessitates the reclamation of gullies and ravines. Various programs are in place, involving actions such as plugging gully mouths, constructing bunds across gullies, leveling gullies, and planting cover vegetation, especially in the Chambal ravines of Madhya Pradesh.
- In regions like northeastern India, the Western Ghats, and the Eastern Ghats, shifting cultivation (slash and burn) stands out as a primary cause of soil erosion. Encouraging farmers to adopt terraced farming practices is of utmost importance. Initiatives have been launched in seven northeastern states to address shifting cultivation, with a focus on rehabilitating families engaged in this practice, known as Jhumming. The objective is to replace shifting cultivation with more sustainable sedentary farming methods.
Example
A case of improper practice can be seen in the incorrect application of fertilizers. In India, the recommended fertilizer ratio of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (NPK) is 4 : 2 : 1. However, the actual usage frequently differs from this ratio, sometimes being as imbalanced as 10 : 4 : 1. This lack of balance can have adverse consequences on soil health and requires correction.
Additionally, agricultural land with a slope gradient ranging from 15 to 25 percent is not suitable for cultivation. If there is a necessity to use such land for farming, it is essential to implement careful terracing measures to prevent soil erosion and deterioration.
Government Initiatives
The Government of India has set up the Central Soil Conservation Board, which has devised multiple strategies for soil conservation, taking into account factors like climate, land characteristics, and societal practices. Among these initiatives is the "National project on management of soil health and fertility (NPMSF)," which is financially supported by the central government and focuses on advocating Integrated Nutrient Management (INM) while enhancing soil testing infrastructure. In addition to this project, there are other programs like the National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA) and the promotion of organic farming, all of which play a role in managing soil quality across India.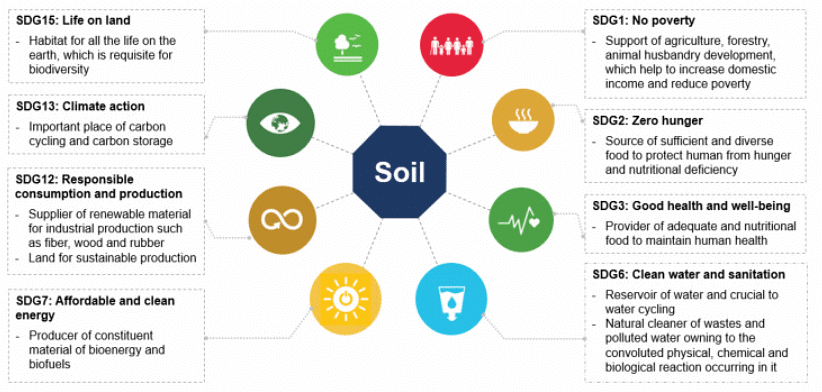
|
847 videos|1297 docs|420 tests
|
















