Solutions: Mixtures & Types of Solutions | Chemistry Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is a Solution? |

|
| Different Types of Solutions |

|
| Properties of a Solution |

|
| Gaseous, Liquid, and Solid Solutions |

|
| What are Mixtures? |

|
| Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Mixtures |

|
What is a Solution?
A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more components in which the particle size is smaller than 1 nm.
Common examples of solutions are: sugar solution, salt solution, soda water, etc. In a solution, all the components appear as a single phase. There is particle homogeneity, i.e., particles are evenly distributed. This is why a whole bottle of soft drink has the same taste throughout.
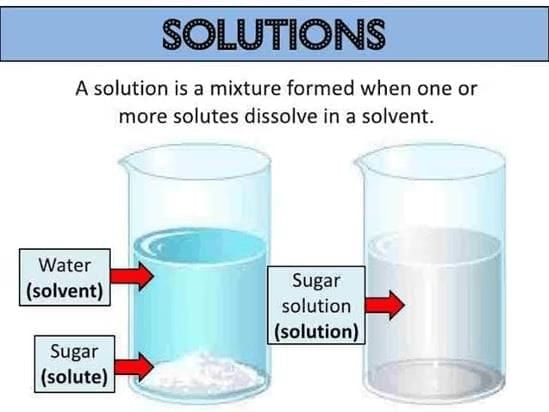
Solute and Solvent
- Solvent: The substance present in the largest quantity in a solution is generally referred to as the solvent.
Example: In a salt solution, since water is present in larger quantity, water is called the solvent. It is the solvent that determines the phase of a solution. - Solute: The substance present in lesser quantity in a solution is generally called the solute.
In other words, one or more components present in a solution other than the solvent are called the solutes.
Example: In a salt solution, salt is the solute. The solute may be more than one.
Note: The physical state of the solvent and solution is the same.
Different Types of Solutions
Solutions can be classified on various bases.
1. On the basis of the number of components dissolved:
- Binary Solution: Solutions that contain only two components are called binary solutions. For example, a salt solution is a binary solution, as it contains only two components.
Binary Solution = Solute + Solvent
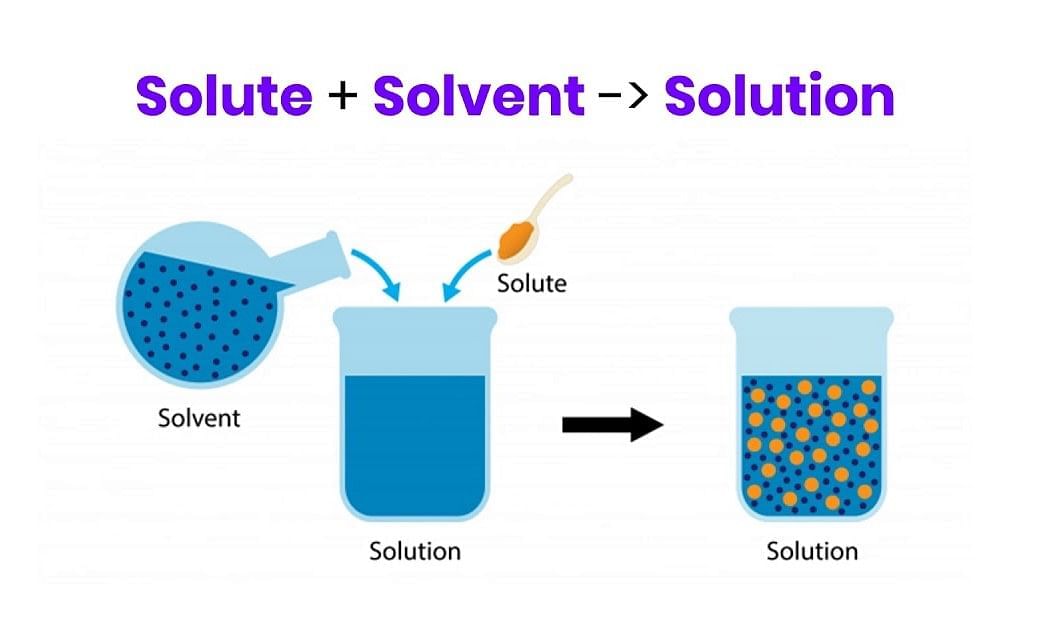 Binary SolutionSimilarly, solutions are called ternary or quaternary if composed of three or four components, respectively.
Binary SolutionSimilarly, solutions are called ternary or quaternary if composed of three or four components, respectively.
Thus, a solution may be regarded as a single phase containing more than one component.
- Ternary Solution: A ternary solution consists of three different components mixed together. These solutions are more complex than binary solutions due to interactions among three substances.
For example, an alcohol-water-acetone mixture is a ternary solution, where each component may have its own concentration. - Quaternary Solution:
A quaternary solution contains four different components dissolved in one another, making it more complex due to increased interactions.
An example is a mixture of ethanol, water, acetone, and acetic acid.
2. On the basis of the dissolving capacity of the solvent:
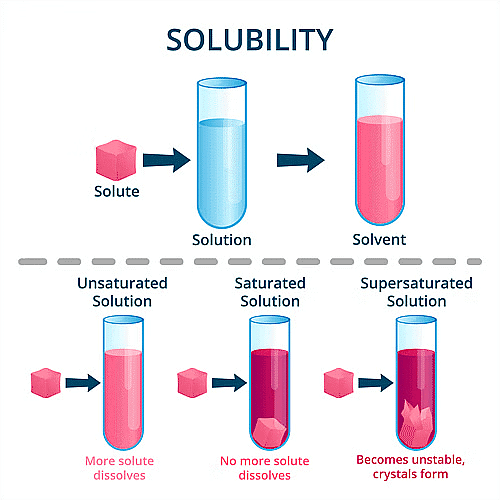
- Supersaturated Solution: A solution is supersaturated when it contains more solute than can normally dissolve at a given temperature. The excess solute separates as crystals at the bottom.
- Saturated Solution: A solution is saturated when it cannot dissolve any more solute at a given temperature.
- Unsaturated Solution: A solution is unsaturated when more solute can still dissolve in the solvent at a given temperature.
3. On the basis of the amount of solute added to the solvent:
- Dilute Solution: A solution with a relatively small amount of solute dissolved in a large amount of solvent is called a dilute solution.
- Concentrated Solution: A solution with a relatively large amount of solute is called a concentrated solution.
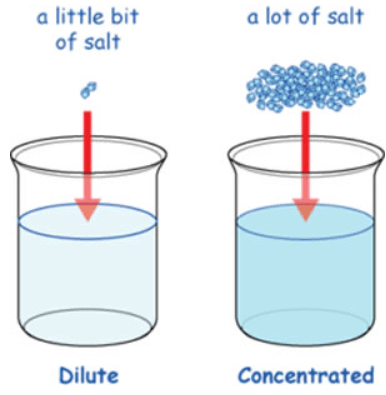 Dilute and Concentrated Solution
Dilute and Concentrated Solution
4. On the basis of the type of solvent:
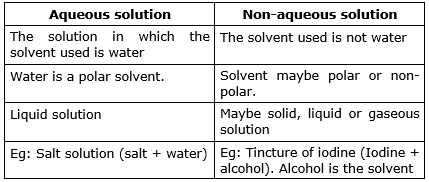
- Aqueous Solution: A solution where the solvent is water is called an aqueous solution.
- Non-Aqueous Solution: A solution where the solvent is not water, such as alcohols or benzene, is called a non-aqueous solution.
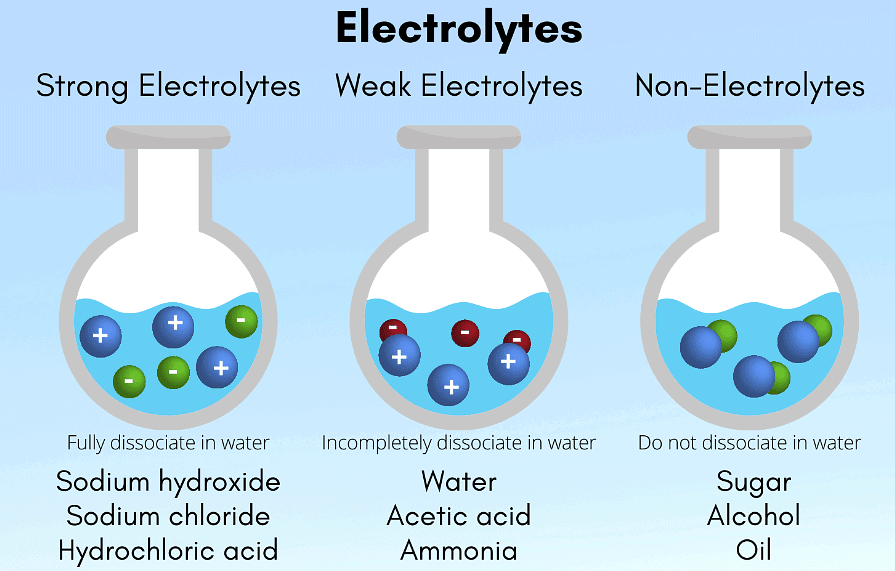
5. On the basis of the ability to conduct electricity:
Solutions that conduct electricity due to the presence of free ions are called electrolytic solutions. This ion formation depends on the component’s ability to dissociate into ions.
- Strong Electrolyte
- Weak Electrolyte
Properties of a Solution
- A solution consists of a single phase, i.e., it is a monophasic system.
- A solution is uniform throughout and shows consistent properties such as density, refractive index, etc.
- The components of a solution cannot be easily separated by physical methods.
- The composition of a solution is not definite but can vary within certain limits.
- Certain properties of a solution, such as density, viscosity, surface tension, boiling point, and freezing point, vary with its composition.
In a solution, components may be solid, liquid, or gas.
Gaseous, Liquid, and Solid Solutions
Gaseous, liquid, and solid solutions are homogeneous mixtures where the components are evenly distributed at a molecular level. The difference lies in the physical state of the solvent and solute.
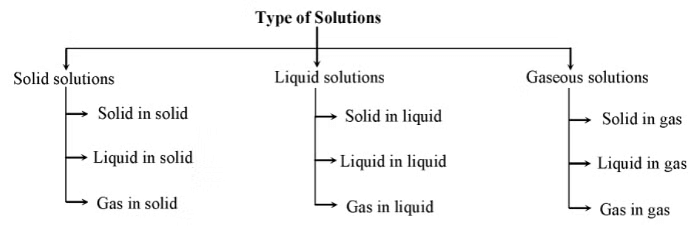
1. Gaseous Solutions
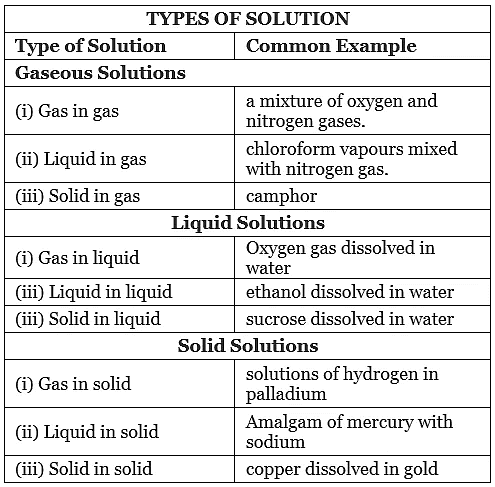
Solutions in which the solvent is in a gaseous state are called gaseous solutions. They can be divided into the following three types based on the phases of solute and solvent:
- Gas-Gas Solution: Solutions in which both solute and solvent are gases are called gas-gas solutions.
Example: Mixture of nitrogen and oxygen, mixture of carbon dioxide and nitrogen, mixture of carbon dioxide and oxygen, etc. - Liquid-Gas Solution: Solutions in which the solute is in a liquid state and the solvent is in a gaseous state are called liquid-gas solutions.
Example: Mixture of chloroform in nitrogen gas. - Solid-Gas Solution: Solutions in which the solute is in a solid state and the solvent is in a gaseous state are called solid-gas solutions.
Example: Mixture of camphor in nitrogen gas.
2. Liquid Solutions
Solutions in which the solvent is in a liquid state are called liquid solutions.
Liquid solutions can be classified into the following three types:
- Gas-Liquid Solution: Solutions with a gaseous solute and a liquid solvent are called gas-liquid solutions.
Example: Mixture of oxygen in water, mixture of carbon dioxide in water. Coca-Cola, a beverage, is an example of a gas-liquid solution, as it has carbon dioxide dissolved in water. - Liquid-Liquid Solution: Solutions in which both solute and solvent are in a liquid state are called liquid-liquid solutions.
Example: Vinegar solution, a mixture of ethanoic acid and water; ethanol in water, etc. - Solid-Liquid Solution: Solutions with a solid solute and a liquid solvent are called solid-liquid solutions.
Example: Solution of salt in water, solution of glucose in water, etc.
3. Solid Solutions
Solutions with a solvent in the solid state are called solid solutions.
Solid solutions can be divided into the following three categories:
- Gas-Solid Solution: Solutions with a solid solvent and a gaseous solute are called gas-solid solutions.
Example: Solution of Hydrogen in Palladium. - Liquid-Solid Solution: Solutions with a solid solvent and a liquid solute are called liquid-solid solutions.
Example: An amalgam of mercury with sodium. - Solid-Solid Solution: Solutions with both solvent and solute in the solid state are called solid-solid solutions.
Example: Solution of gold and copper.
What are Mixtures?
When two or more chemically non-reacting substances are mixed, they form mixtures, which may be homogeneous or heterogeneous.

- A heterogeneous mixture consists of distinct phases, and the observed properties are the sum of the properties of individual phases. A homogeneous mixture consists of a single phase with properties that may differ significantly from those of the individual components.
- A homogeneous mixture whose composition can be varied within certain limits is termed a true solution.
- The constituents of a solution cannot be separated by filtration, settling, or centrifugal action. All solutions are characterized by
(i) Homogeneity
(ii) Absence of settling
(iii) The molecular or ionic state of subdivision of the components. When the solution is composed of only two chemical substances, it is termed a binary solution. - Similarly, it is called ternary or quaternary if composed of three or four components, respectively. Thus, a solution may be regarded as a single phase containing more than one component.
Examples
- A mixture of salt and sugar.
- A mixture of oxygen and nitrogen.
- A mixture of sugar in water.
Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Mixtures
1. Homogeneous Mixture
A mixture of two or more components with no distinct phase is called a homogeneous mixture. A homogeneous mixture is generally referred to as a solution.Example: When two spoons of salt are mixed in a glass of water, the resulting mixture has no distinct phase and is called a solution.
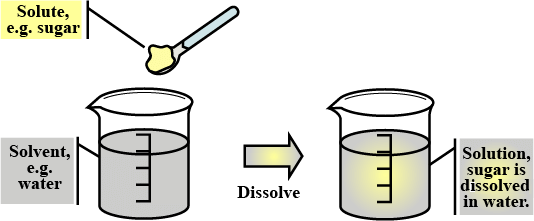 Sugar Solution
Sugar Solution
Air is a mixture of different gases with no distinct phase, thus often referred to as a solution.
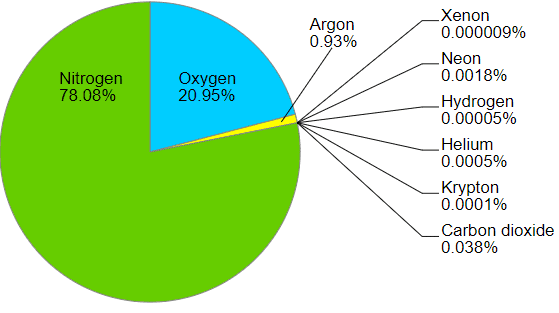 Air: Mixture of Gases
Air: Mixture of Gases
In a homogeneous mixture, i.e., a solution, the composition and properties are uniform throughout.
2. Heterogeneous Mixture
A mixture of two or more components with distinct phases is called a heterogeneous mixture.Example: In a mixture of mustard oil and water, the phases of water and mustard oil can be clearly distinguished, making it a heterogeneous mixture.
 Heterogeneous Mixture: Oil and Water
Heterogeneous Mixture: Oil and Water
Examples of Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Mixtures:
- Homogeneous: Sugar solution, air, salt solution.
- Heterogeneous: Oil and water, sand and water, salt and sugar.
|
75 videos|278 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Solutions: Mixtures & Types of Solutions - Chemistry Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What are the differences between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures? |  |
| 2. What is a solution in chemistry? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of solutions based on their states of matter? |  |
| 4. What are the properties of a solution? |  |
| 5. Can you give examples of gaseous, liquid, and solid solutions? |  |





















