Lakhmir Singh & Manjit Kaur: Metals and Non-metals, Solutions- 4 | Science Class 10 PDF Download
(Page No - 191)
Question 1:
A zinc ore gave CO2 on treatment with a dilute add. Identify the ore and write its chemical formula.
Solution :
Calamine, ZnCO3
Question 2:
What chemical process is used for obtaining a metal from its oxide ?
Solution :
Reduction .
Question 3:
State two ways to prevent the rusting of iron.
Solution :
Rusting of iron can be prevented:
(i) By painting.
(ii) By applying grease or oil.
Question 4:
What is meant by galvanisation ? Why is it done ?
Solution :
The process of depositing a thin layer of zinc metal on iron objects is called galvanisation; It prevents iron from rusting.
Question 5:
Name the metal which is used for galvanising iron.
Solution :
Zinc is used for galvanising iron.
Question 6:
Explain why, iron sheets are coated with zinc.
Solution :
Zinc is a quite reactive metal. The action of air on zinc metal forms a very thin coating of zinc oxide all over it, which is hard and impervious to air and hence prevents the further corrosion of zinc metal as well as the iron below it.
Question 7:
Why do we apply paint on iron articles ?
Solution :
Iron objects are painted so that air and moisture can not come in contact with the iron objects and hence no rusting takes place.
Question 8:
Give reason for the following :
Carbonate and sulphide ores are usually converted into oxides during the process of extraction of metals.
Solution :
Carbonate and sulphide ores are usually converted into oxides because it is easier to obtain metals from their oxides (by reduction) than from carbonates or sulphides.
Question 9:
Name a reducing agent that may be used to obtain manganese from manganese dioxide.
Solution :
Aluminium powder is used as the reducing agent for the extraction of manganese from its oxide.
Question 10:
Name an alloy of lead and tin.
Solution :
Solder is an alloy of lead and tin.
Question 11:
Give the composition of an alloy called solder. State its one property and one use.
Solution :
Solder is an alloy of lead (Pb) and tin (Sn). It contains both the elements in 50-50 ratio. It has a low melting point and is used for soldering electrical wires together.
Question 12:
What is an amalgam ?
Solution :
An alloy of mercury metal with one or more other metals is known as an amalgam.
Question 13:
How many carats is pure gold ? Why is pure gold not suitable for making ornaments ?
Solution :
Pure gold is said to be of 24 carats. It is not suitable for making ornaments because it is very soft.
Question 14:
Name one method for the refining of metals.
Solution :
Electrolytic refining.
Question 15:
State two conditions for the rusting of iron.
Solution :
(i) Presence of air (oxygen).
(ii) Presence of water (or moisture).
Question 16:
In one method of rust prevention, the iron is not coated with anything. Which is this method ?
Solution :
Rusting of iron can be prevented by alloying iron with chromium and nickel to make stainless steel.
Question 17:
Name two alloys of iron. What elements are present in these alloys ?
Solution :
Steel – Iron and carbon.
Stainless steel – Iron, chromium and nickel.
Question 18:
Give reason for the following :
Silver, gold and platinum are used to make jewellery.
Solution :
Silver, gold and platinum are used to make jewellery b ecause all of these metals have a bright shiny surface and are resistant to corrosion.
Question 19:
Which metal becomes black in the presence of hydrogen sulphide gas in air ?
Solution :
Silver metal becomes black in the presence of hydrogen sulphide gas in air .
Question 20:
Name the gas in air which tarnishes silver articles slowly.
Solution :
Hydrogen sulphide gas tarnishes silver articles .
Question 21:
Silver metal does not combine easily with oxygen but silver jewellery tarnishes after some time. How ?
Solution :
The silver articles combine slowly with the hydrogen sulphide gas present in air to form a black coating of silver sulphide. The tarnishing of the silver objects is due to this silver sulphide coating on the object’s surface.
Question 22:
Write the composition of the alloy called bronze. Give two uses of bronze.
Solution :
Bronze is an alloy of copper and tin; 90% copper and 10% tin. It is used for making statues and coins.
Question 23:
Why does a new aluminium vessel lose shine so soon after use ?
Solution :
A new aluminium vessel lose shine so soon after use due to the corrosion of aluminium metal when exposed to moist air. This happens because the oxygen of air reacts with aluminium to form a thin, dull layer of aluminium oxide all over the vessel.
Question 24:
Why do gold ornaments look new even after several years of use ?
Solution :
Gold ornaments look new even after several years of use because gold does not corrode when exposed to atmosphere. It is a highly unreactive metal which remains unaffected by air, water vapour and other gases in the atmosphere.
Question 25:
Name two metals which are highly resistant to corrosion.
Solution :
Gold and platinum are highly resistant to corrosion.
Question 26:
Which property of ‘solder’ alloy makes it suitable for welding electrical wires ?
Solution :
Low melting point of solder makes it sutaible for welding electrical wires .
Question 27:
Explain why, carbon cannot reduce oxides of sodium or magnesium.
Solution :
Carbon cannot reduce oxides of sodium or magnesium because carbon is less reactive than magnesium or sodium. Carbon, which is a non-metal, is more reactive than zinc and can be placed just above Zn in the reactivity series. Hence, carbon can reduce the oxides of zinc and all other metals below zinc to form metals.
Question 28:
Why are the metals like Na, K, Ca and Mg never found in their free state in nature ?
Solution :
The metals like Na, K, Ca and Mg never found in their free state in nature because of the reason that all of these metals are high-up in the reactivity series. And just because they are so reactive, they are never found in nature as free elements.
Question 29:
Name one metal each which is extracted by :
(a) reduction with carbon. (b) electrolytic reduction.
(c) reduction with aluminium (d) reduction with heat alone.
Solution :
(a) Zinc
(b) Sodium
(c) Manganese
(d) Mercury
Question 30:
Fill in the following blanks with suitable words :
(a) The corrosion of iron is called…………………
(b) …………….and………………. are necessary for the rusting of iron.
(c) The process of depositing a thin layer of zinc on iron articles is called…………………………..
(d) Tiffin boxes are electroplated with…………………… but car bumpers are electroplated with………………………. to protect them from rusting.
(e) The corrosion of copper produces a…………………. coating of basic copper carbonate on its surface.
(f) Brass is an alloy of copper and……………………..
(g) Bronze is an alloy of copper and………………..
(h) The non-metal present in steel is…………………
(i) The alloy in which one of the metals is mercury is called an………………………..
(j) The electrical conductivity and melting point of an alloy is…………………………. than that of pure metals.
(k) The rocky material found with ores is called……………………
Solution :
(a) rusting
(b) air; water
(c) galvanisation
(d) tin; chromium
(e) green
(j) zinc
(g) tin
(h) carbon
(i) amalgam
(j) less
(k) gangue
(Page No - 192)
Question 31:
How is manganese extracted from manganese dioxide, MnO2 ? Explain with the help of an equation.
Solution :
Manganese metal is extracted by the reduction of its oxide with aluminium powder as the reducing agent. Thus, when manganese dioxide is heated with aluminium powder, then manganese metal is formed.
Question 32:
What is a thermite reaction ? Explain with the help of an equation. State one use of this reaction.
Solution :
The reduction of a metal oxide to form metal by using aluminium powder as a reducing agent is called a thermite reaction.
This property of reduction by aluminium is made use of in thermite welding for joining the broken pieces of heavy iron objects like girders etc.
A mixture of Iron (III) oxide and aluminium powder is ignited with a burning magnesium ribbon. Aluminium reduces iron oxide to produce iron metal with the evolution of a lot of heat. Due to this heat, iron metal is produced in the molten state. This molten iron is then poured between the broken iron pieces to weld them (to join them).
Question 33:
Which one of the methods given in column I is applied for the extraction of each of the metals given in column II :
Column I | Column II |
Electrolytic Reduction | Aluminium |
Reduction with carbon | Zinc |
Reduction with Aluminium | Sodium |
Iron | |
Manganese | |
Tin |
Solution :
Electrolytic reduction: Aluminium and Sodium;
Reduction with carbon : Zinc, Iron and Tin;
Reduction with aluminium: Manganese
Question 34:
(a) Give reason why copper is used to make hot water tanks but steel (an alloy of iron) is not.
(b) Explain why, the surface of some metals acquires a dull appearance when exposed to air for a long time.
Solution :
(a) Copper does not corrode easily in the presence of water but steel rusts in the presence of water.
(b) The surface of some metals acquires a dull appearance when exposed to air b ecause of the formation of an oxide layer on the surface of the metal.
Question 35:
(a) Why does aluminium not corrode right through ?
(b) What is meant by ‘anodising’ ? Why is it done ?
Solution :
(a) Aluminium does not corrode right through because aluminium is more reactive than iron and it forms a layer of aluminium oxide as soon as it comes in contact with moist air. This aluminium oxide layer is very tough and prevents the aluminium underneath from corroding.
(b) The process of thickening of aluminium oxide layer on the surface of aluminium objects by electrolysis is called anodizing. It is done to provide more protection to the aluminium object from corrosion.
Question 36:
(a) Why is an iron grill painted frequently ?
(b) Explain why, though aluminium is more reactive than iron, yet there is less corrosion of aluminium when both are exposed to air.
Solution :
(a) An iron grill is painted frequently to prevent its rusting .
(b)There is less corrosion of aluminium than iron when both are exposed to air because aluminium forms a layer of aluminium oxide on its surface as soon as it comes in contact with moist air. This aluminium oxide is very tough and prevents it from corroding right through.
Question 37:
(a) Name the method by which aluminium metal is extracted.
(b) Give the name and chemical formula of one ore of copper.
(c) How is zinc extracted from its carbonate ore (calamine) ? Explain with equations.
Solution :
(a) Electrolytic reduction .
(b)Copper glance (Cu2 S)
(c) When calamine ore is heated strongly in the absence of air i.e. calcined, it decomposes to form zinc oxide and carbon dioxide.
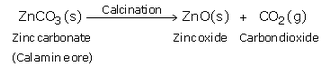
Then, zinc oxide is heated with carbon and zinc metal is produced.
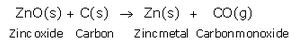
Question 38:
(a) Name two metals which occur in nature in free state as well as in combined state.
(b) Name one ore of manganese. Which compound of manganese is present in this ore ? Also write its chemical formula.
(c) A zinc ore on heating in air forms sulphur dioxide. Describe briefly any two stages involved in the conversion of this concentrated ore into zinc metal.
Solution :
(a) Copper and Silver occur in nature in free state as well as in combined state.
(b) Pyrolusite; Manganese dioxide; MnO2
(c) (i) Roasting: When zinc sulphide (zinc blende ore) is strongly heated in air (roasted), it forms zinc oxide and sulphur dioxide.
(ii) Reduction: Zinc oxide obtained is heated with carbon to form zinc metal.
Question 39:
How does the method used for extracting a metal from its ore depend on the metal’s position in the reactivity series ? Explain with examples.
Solution :
Different methods are used for extracting metals belonging to category of highly reactive metals, moderately reactive metals and less reactive metals. This is because the extraction of a metal from its concentrated ore is essentially a process of reduction of the metal compound present in the ore. For example: Manganese metal is obtained by the reduction of its oxide with aluminium powder and not carbon. This is because carbon is less reactive than manganese. Carbon, which is a non-metal, is more reactive than zinc and it can be placed just above Zn in the reactivity series. Hence, carbon can reduce the oxides of zinc and all other metals below zinc to form metals
Question 40:
Explain giving one example, how highly reactive metals (which are high up in the reactivity series) are extracted.
Solution :
The highly reactive metals are extracted by the electrolytic reduction of their molten chlorides or oxides.
Example: Sodium metal is extracted by the electrolytic reduction of molten sodium chloride. When electric current is passed through molten sodium chloride, it decomposes to form sodium metal and chlorine gas.
Question 41:
Describe with one example, how moderately reactive metals (which are in the middle of reactivity series) are extracted.
Solution :
The moderately reactive metals are extracted by the reduction of their oxides with carbon, aluminium, sodium or calcium.
Example: When zinc sulphide (zinc blende ore) is strongly heated in air (roasted), it forms zinc oxide and sulphur dioxide. This process is called roasting. Then, zinc oxide is heated with carbon to form zinc metal. This process is termed as reduction.
Question 42:
How are the less reactive metals (which are quite low in the reactivity series) extracted ? Explain with the help of an example.
Solution :
The less reactive metals are extracted by the reduction of their oxides by heat alone.
Example: Mercury (II) sulphide ore is roasted in air when mercury (II) oxide is formed. When this mercury (II) oxide is heated to about 300oC, it decomposes to form mercury metal.
Question 43:
What is meant by refining of a metal ? Name the most widely used method for the refining of impure metals obtained by various reduction processes. Describe this method with the help of a labelled diagram by taking the example of any metal.
Solution :
The process of purifying impure metals is called refining of metals.
Electrolytic refining is the most widely used method for the refining of impure metals obtained by various reduction processes.
In an electrolytic tank, acidified copper sulphate (CuSO4+ dilute H2O4) solution forms the electrolyte. A block of impure copper is made into an anode by connecting the positive terminal of a power supply (battery). A thin strip of highly pure copper metal is the cathode of the cell. The negative terminal of the power supply is connected to it.
A small electric curr ent is passed through the cell. Atoms from the anode enter the electrolyte. The copper from the anode gets converted into copper sulphide. An equal number of copper atoms from the solution get deposited on the cathode. This is to keep the concentration of the solution constant. Impurities from the anode block either remain in solution or collect below the anode, as they are unable to displace copper from the sulphate solution. The insoluble impurities remain in the electrolyte and are called anode mud.
Copper sulphate solution contains ions of Cu++ and SO4— . The following reactions take place at the anode and cathode when an electric current is passed.

Pure copper is scraped or removed from the cathode. Anode becomes thinner as the electrolysis process proceeds. Some important metals like gold and silver are present in the anode mud. These can be recovered separately.
Question 44:
(a) Define the terms (i) mineral (ii) ore, and (iii) gangue.
(b) What is meant by the ‘concentration of ore’ ?
(c) Name one ore of copper (other than cuprite). Which compound of copper is present in this ore ? Also, write its chemical formula.
Solution :
(a) (i) Minerals – The natural materials in which the metals or their compounds are found in earth are called minerals.
(ii) Ores – Those minerals from which the metals can be extracted conveniently and profitably are called ores.
(iii) Gangue – The unwanted impurities like sand, rocky material, earthy particles etc., present in an ore are called gangue.
(b) Before extracting metal from an ore, it is necessary to remove these impurities (gangue) from it. By removing the gangue, we get a concentrated ore containing a much higher percentage of metal. This is called concentration of ore; also known as enrichment of ore.
(c) Ore: Copper glance; Copper (I) sulphide, Cu2S.
(Page No - 193)
Question 45:
Explain how, a reduction reaction of aluminium can be used for welding cracked machine parts of iron. Write a chemical equation for the reaction involved.
Solution :
A mixture of Iron (III) oxide and aluminium powder is ignited with a burning magnesium ribbon. Aluminium reduces iron oxide to produce iron metal with the evolution of lot of heat. Due to this heat, iron metal is produced in the molten state. This molten iron is poured between broken iron parts of the machine to weld them (to join them).
Question 46:
(a) What is corrosion ?
(b) Name any two metals which do not corrode easily.
(c) What is the corrosion of iron known as ?
(d) Explain why, aluminium is a highly reactive metal, still it is used to make utensils for cooking.
Solution :
(a) The eating up of metals by the action of air, moisture or a chemical (such as an acid) on their surface is called corrosion.
(b) Gold and Platinum
(c) Rusting
(d) Aluminium begins to corrode quickly when it comes in contact with moist air. The action of moist air on aluminium metal forms a thin layer of aluminium oxide all over the metal. This aluminium oxide is very tough and prevents the metal underneath from further corrosion. Therefore, aluminium is used for making utensils irrespective of its highly reactive property as its corrosion leads to the non-corrosion of the metal in the longer run.
Question 47:
What is meant by ‘rusting of iron’ ? With the help of labelled diagrams, describe an activity to find out the conditions under which iron rusts.
Solution :
When an iron object is left in damp air (or water) for a considerable time, it gets covered with a red-brown flaky substance called rust. This is called rusting of iron .
Experiment to show that rusting of Iron requires both, air and water :
We take three test-tubes and put one clean iron nail in each of the three test-tubes:
1. In the first test-tube containing iron nail, we put some anhydrous calcium chloride and close its mouth with a tight cork . Anhydrous calcium chloride absorbs water moisture from the damp air present in the test-tube and make it dry. In this way, the iron nail in the first test-tube is kept in dry air (having no water vapour in it).
2. In the second test-tube containing iron nail , we put boiled distilled water. Boiled water does not contain any dissolved air (or oxygen) in it (this is because the process of boiling removes all the dissolved air from it). A layer of oil is put over boiled water in the test-tube to prevent the outside air from mixing with boiled water. In this way, the iron nail in the second test-tube is kept in air free boiled water.
3. In the third test-tube containing an iron nail, we put unboiled water so that about two-thirds of nail is immersed in water and the rest is above the water, exposed to damp air. In this way , the iron nail in the third test-tube has been placed in air and water together.
The mouth of all three test tube s is closed with a cork and it is kept aside for about one week.
After one week, we observe the iron nails kept in all the three test-tubes, one by one. We find that (i) No rust is seen on the surface of iron nail kept in dry air (water-free air) in the first test-tube. This tells us that rusting of iron does not take place in air alone.
(ii) No rust is seen on the surface of iron nail kept in air-free, boiled water in the second test-tube. This tells us that rusting of iron does not take place in water alone.
(iii) Red-brown rust is seen on the surface of iron nail kept in the presence of both air and water together the third test-tube. This tells us that rusting of iron takes place in the presence of both air and water together.
Question 48:
(a) What is an alloy ? How is an alloy made ?
(b) What elements are present in steel ? How are the properties of steel different from those of pure iron ?
(c) Give the constituents and one use of brass.
Solution :
(a) An alloy is a homogeneous mixture of two or more metals (or a metal and small amount of non-metals). An alloy is prepared by mixing the various metals in molten state in required proportions, and then cooling their mixture to the room temperature.
(b) Steel contains iron and carbon.
This alloy of iron (steel) is hard and strong. It also rusts less readily than pure iron.
(c) Brass contains copper and zinc.
Brass is used for making cooking utensils.
Question 49:
(a) Name two metals which resist corrosion due to the formation of a thin, hard and impervious layer of oxide on their surface.
(b) Name five methods of preventing rusting of iron.
(c) What are the constituents of stainless steel ? What are the special properties of stainless steel ?
Solution :
(a) Aluminium and Zinc resist corrosion due to the formation of a thin, hard and impervious layer of oxide on their surface.
(b)(i) Painting (ii) Applying grease or oil (iii) Galvanisation (iv) Tin and chromium plating (v) Alloying to form stainless steel.
(c)Stainless steel contains iron, chromium and nickel.
Stainless steel does not rust at all and is strong and tough.
Question 50:
(a) Name an alloy of copper. State its chemical composition and any one use.
(b) Explain why, when a copper object remains in damp air for a considerable time, a green coating is formed on its surface. What is this process known as ?
Solution :
(a) Brass:It contains Copper (Cu)-80% and Zinc(Zn) – 20%. It is used for making cooking utensils.
(b) When a copper object remains in damp air for a considerable time, then copper reacts slowly with the carbon dioxide and water of air to form a green coating of basic copper carbonate on the surface of the object. The formation of this green coating of basic copper carbonate corrodes it. This process is known as corrosion of copper.
Question 51:
(a) How does the painting of an iron object prevent its rusting ?
(b) How does the electrical conductivity of copper alloys, brass and bronze, differ from that of pure copper ?
(c) What is meant by 22 carat gold ? Name the metals which are usually alloyed with gold to make it harder.
Solution :
(a) When a coat of paint is applied to the surface of an iron object, it prevents air and moisture to come in contact with the object; hence no rusting takes place.
(b) The electrical conductivity of copper alloys like brass and bronze is less than that of pure copper.
(c) It means that 22 parts pure gold is alloyed with 2 parts of either silver or copper for making ornaments; Silver and copper are usually alloyed with gold to make it harder .
Question 52:
Explain giving equation, what happens when :
(a) ZnCO3 is heated in the absence of air ?
(b) a mixture of CU2O and CU2S is heated ?
Solution :
(a) When zinc carbonate is heated strongly in the absence of air, it decomposes to form zinc oxide and carbon dioxide.
(b) When copper (I) oxide reacts with copper (I) sulphide, it forms copper metal and sulphur dioxide.
Question 53:
(a) For the reduction of a metal oxide, suggest a reducing agent other than carbon.
(b) Explain why, an aqueous solution of sodium chloride is not used for the electrolytic extraction of sodium metal.
Solution :
(a) Aluminium can be used a reducing agent other than carbon.
(b) We cannot use an aqueous solution of sodium chloride to obtain sodium metal because if we electrolyse an aqueous solution of sodium chloride, then as soon as sodium metal is produced at cathode, it will react with water present in the aqueous solution to form sodium hydroxide. Hence, electrolysis of an aqueous solution of sodium chloride will produce sodium hydroxide and not sodium metal.
Question 54:
How are metals refined by the electrolytic process ? Describe the electrolytic refining of copper with the help of a neat labelled diagram.
Solution :
For the refining of an impure metal by the process of electrolysis, a thick block of impure metal is made anode (connected to +ve terminal of the battery) and a thin strip of the pure metal is made cathode (connected to -ve terminal of battery). A water soluble salt (of the metal to be refined) is taken as electrolyte. On passing current, impure metal dissolves from the anode and goes into the electrolyte solution. And pure metal from the electrolyte deposits on the cathode.
Electrolytic refining of copper: In an electrolytic tank, acidified copper sulphate (CuSO4+ dilute H2O4) solution forms the electrolyte. A block of impure copper is made into an anode by connecting the positive terminal of a power supply (battery). A thin strip of highly pure copper metal is the cathode of the cell. The negative terminal of the power supply is connected to it.
A small electric curr ent is passed through the cell. Atoms from the anode enter the electrolyte. The copper from the anode gets converted into copper sulphide. An equal number of copper atoms from the solution get deposited on the cathode. This is to keep the concentration of the solution constant. Impurities from the anode block either remain in solution or collect below the anode, as they are unable to displace copper form the sulphate solution. The insoluble impurities remain in the electrolyte and are called anode mud.
Copper sulphate solution contains ions of Cu++ and SO4— . The following reactions take place at the anode and cathode when an electric current is passed.


Pure copper is scraped or removed from the cathode. Anode becomes thinner as the electrolysis process proceeds. Some important metals like gold and silver are present in the anode mud. These can be recovered separately.
Question 55:
(a) Name the chemical compound which is electrolysed in molten state to obtain aluminium metal. Which gas is evolved during this process ?
(b) Name the chemical compound which is electrolysed in molten state to obtain sodium metal. Which gas is produced in this process ?
(c) Name the gas produced when calamine ore is calcined.
(d) Name the gas evolved when cinnabar ore is roasted.
Solution :
(a) Aluminium oxide is electrolysed in molten state to obtain aluminium metal. Oxygen gas is evolved during the process.
(b) Sodium chloride is electrolysed in molten state to obtain sodium metal. Chlorine gas is evolved during this process.
(c) Carbon dioxide is produced when calamine ore is calcined.
(d) Sulphur dioxide gas is evolved when cinnabar ore is roasted.
Question 56:
(a) Name two metals which are found in nature mainly in the free state (as metallic elements).
(b) Name two metals which are always found in combined state.
(c) What iron compound is present in haematite ore ? Also write its chemical formula.
Solution :
(a) Gold and Platinum are found in nature mainly in the free state.
(b) Sodium and Magnesium are always found in combined state.
(c) Iron (III) oxide; Fe2O3 is present in haematite ore.
Question 57:
(a) What is the difference between a mineral and an ore ?
(b) Which metal is extracted from cinnabar ore ?
(c) Name one ore of sodium. Name the sodium compound present in this ore and write its chemical formula.
(d) How is sodium metal extracted ? Explain with the help of equation of the reaction involved.
(e) Name three other metals which are extracted in a manner similar to sodium.
Solution :
(a)The natural materials in which the metals or their compounds are found in earth are called minerals. Those minerals from which the metals can be extracted conveniently and profitably are called ores.
(b) Mercury.
(c)Rock salt – Sodium chloride, NaCl.
(d)Sodium metal is extracted by the electrolytic reduction of molten sodium chloride. When electric current is passed through molten sodium chloride, it decomposes to form sodium metal and chlorine gas.
(e) Potassium, Calcium and Magnesium .
Question 58:
(a) Name the metal which is extracted from haematite ore.
(b) Name one ore of aluminium. Name the aluminium compound present in this ore and write its chemical formula.
(c) How is aluminium metal extracted ? Explain with the help of an equation.
(d) Name the electrode at which aluminium metal is produced.
(e) Which gas is produced during the extraction of aluminium ? At which electrode is this gas produced ?
Solution :
(a)Iron is extracted from haematite ore .
(b)Bauxite; Aluminium oxide, Al2O3.2H2O
(c)Aluminium metal is extracted by the electrolytic reduction (electrolysis) of molten aluminium oxide. When electric current is passed through molten aluminium oxide, it decomposes to form aluminium metal and oxygen gas.
(d) A luminium metal is produced at Cathode (Negative electrode).
(e) Oxygen gas is produced; at anode (Positive electrode).
(Page No - 194)
Question 59:
(a) Which metal is extracted from bauxite ore ?
(b) Give the name of one ore of iron. Which iron compound is present in this ore ? Write its chemical formula.
(c) Describe the extraction of zinc metal from its sulphide ore (zinc blende). Write equations of the reactions involved.
(d) Explain why, the galvanised iron article is protected against rusting even if the zinc layer is broken.
(e) Name a common metal which is highly resistant to corrosion.
Solution :
(a) Aluminium.
(b) Haematite; Iron (III) oxide, Fe2O3
(c) Zinc sulphide (zinc blende ore) is strongly heated in air (roasted), it forms zinc oxide and sulphur dioxide. This process is called roasting.

Then, zinc oxide is heated with carbon to form zinc metal. This process is termed as reduction.
ZnO(s) + C(s) → Zn(s) + CO(g)
(d) The galvanized iron object remains protected against rusting even if a break occurs in the zinc layer because zinc is more easily oxidised than iron. Hence, the zinc continues to corrode but iron object does not corrode or rust.
(e) Aluminium .
Question 60:
(a) Name the metal which is extracted from the ore called ‘rock salt’.
(b) Name two ores of zinc. Write the names of the chemical compounds present in them and give their chemical formulae.
(c) Explain how, mercury is extracted from its sulphide ore (cinnabar). Give equations of the reactions involved.
(d) In the electrolytic refining of a metal M, what would you take as anode, cathode and electrolyte ?
(e) Name any five metals which are purified by electrolytic refining method.
Solution :
(a) Sodium.
(b) (i) Calamine; Zinc carbonate, ZnCO3
(ii) Zinc blende; Zinc sulphide, ZnS
(c) Mercury (II) sulphide ore is roasted in air when mercury (II) oxide is formed.

When this mercury (II) oxide is heated to about 3000C, it decomposes to form mercury metal.

(d) Anode – Thick block of i mpure metal M
Cathode – Thin strip of p ure metal M
Electrolyte – Water soluble salt (of metal M).
(e) (i) Copper
(ii) Zinc
(iii) Nickel
(iv) Gold
(v) Silver
Question 61:
(a) Which metal is extracted from calamine ore ?
(b) Name one ore of mercury. Which mercury compound is present in this ore ? Write its chemical formula.
(c) How is copper extracted from its sulphide ore (copper glance), Cu2S ? Explain with equations of the reactions involved.
(d) What is an alloy ? Give two examples of alloys.
(e) How are the properties of an alloy different from those of the constitutent elements ?
Solution :
(a) Zinc
(b) Cinnabar; Mercury (II) sulphide, HgS
(c) The concentrated copper (I) sulphide ore (copper glance), Cu2S is roasted in air when a part of copper (I) sulphide is oxidised to copper (I) oxide.
When a good amount of copper (I) sulphide has been converted to copper (I) oxide, then the supply of air for roasting is stopped. In the absence of air, copper (I) oxide formed above reacts with remaining copper (I) sulphide to form copper metal and sulphur dioxide.
(d) An alloy is a homogeneous mixture of two or more metals (or a metal and small amounts of non-metals).
Steel and Brass are examples of alloys.
(e) (i) Alloys are stronger than the metals from which they are made.
(ii) Alloys are harder than the constituent metals.
(iii) Alloys are more resistant to corrosion.
(iv) Alloys have lower melting points than constituent metals.
(v) Alloys have lower electrical conductivity than pure metals.
(Page No - 195)
Question 92:
An element A which is a part of common salt and kept under kerosene reacts with another element B of atomic number 17 to give a product C. When an aqueous solution of product C is electrolysed then a compound D is formed and two gases are liberated.
(a) What are A and B ?
(b) Identify C and D.
(c) What will be the action of C on litmus solution ? Why ?
(d) State whether element B is a solid, liquid or gas at room temperature.
(e) Write formula of the compound formed when element B reacts with an element E having atomic number 5.
Solution :
(a) A is sodium and B is chlo rine
(b) C is sodium chloride and D is sodium hydroxide
(c) C will have no effect on litmus solution since it is neutral in nature.
(d) B is a gas at room temperature.
(e) EB3
Question 93:
A metal which exists as a liquid at room temperature is obtained by heating its sulphide ore in the presence of air.
(a) Name the metal and write its chemical symbol.
(b) Write the name and formula of the sulphide ore.
(c) Give the equations of chemical reactions involved in the production of metal from its sulphide ore.
(d) Name a common device in which this metal is used.
(e) Can this metal displace copper from copper sulphate solution ? Why ?
Solution :
(a) Mercury, Hg
(b) Cinnabar, HgS
(c)


(d) Thermometer
(e) No; Because it is less reactive than copper.
(Page No - 196)
Question 94:
No chemical reaction takes place when granules of a rusty-brown solid A are mixed with the powder of another solid B. However, when the mixture is heated, a reaction takes place between its components. One of the products C is a metal and settles down in the molten state while the other product D floats over it. It was observed that the reaction is highly exothermic.
(a) What could the solids A and B be ?
(b) What are the products C and D most likely to be ?
(c) Write the chemical equation for the reaction between A and B leading to the formation of C and D. Mention the physical sates of all the reactants and products in this equation and indicate the heat change which takes place.
(d) What is the special name of such a reaction ? State one use of such a reaction.
(e) Name any two types of chemical reactions under which the above reaction can be classified.
Solution :
(a) A is iron ( III ) oxide and B is aluminium powder.
(b) C is molten iron metal and D is aluminium oxide.
(c) 
(d) This reaction is called thermite reaction. It is used for welding of broken pieces of heavy iron objects like railway tracks, etc.
(e) Displacement reactions and oxidation-reduction reactions.
Question 95:
In an electrolytic tank, aluminium metal is being extracted by the electrolysis of molten aluminium oxide using carbon electrodes. It is observed that one of the carbon electrodes is gradually burnt away and has to be replaced.
(a) Which carbon electrode (cathode or anode) is burnt away ?
(b) Why is this carbon electrode burnt away ?
Solution :
(a) Positively charged carbon electrode (Anode)
(b) This carbon electrode is burnt away because oxygen produced during the electrolysis of molten aluminium oxide reacts gradually with the carbon of carbon anode to form carbon dioxide gas.
Question 96:
A metal X which is resistant to corrosion is produced by the electrolysis of its molten oxide whereas another metal Y which is also resistant to corrosion is produced by the reduction of its oxide with carbon. Metal X can be used in powder form in thermite welding whereas metal Y is used in making cathodes of ordinary dry cells.
(a) Name the metals X and Y.
(b) Which of the two metals is more reactive : X or Y ?
(c) Name one ore or metal X. Also write its chemical formula.
(d) Name one ore of metal Y. Also write its chemical formula.
(e) Name one alloy of metal X and one alloy of metal Y.
Solution :
(a) X is aluminium and Y is zinc.
(b) X is more reactiv e than Y.
(c) Bauxite; Al2 O3 .2H2O
(d) Calamine, ZnCO3
(e) Alloy of metal X : Duralumin ; Allo y of metal Y : Brass
Question 97:
When an object made of metal A is kept in air for a considerable time, it loses its shine and becomes almost black due to the formation of a layer of substance B. When an object made of another metal C is kept in damp air for a considerable time, it gets covered with a green layer of substance D. Metal A is the best conductor of electricity whereas metal C is the next best conductor of electricity.
(a) What is metal A ?
(b) What is metal C ?
(c) Name the substance B.
(d) Name the substance D.
What type of chemical can be used to remove the green layer from metal C and clean it ? Why ?
Solution :
(a) Silver
(b) Copper
(c) Silver sulphide
(d) Basic copper carbonate
(e) Dilute acid solution; The acid sol ution dissolves green coloured basic copper carbonate present on the corroded copper object makes it look shiny, red brown again.
Question 98:
Four metals P, Q, R and S are all obtained by the reduction of their oxides with carbon. Metal P is used to form a thin layer over the sheets of metal S to prevent its corrosion. Metal Q is used for electroplating tiffin boxes made of metal S whereas metal R is used in making car batteries. Metals Q and R form an alloy called solder. What are metals P, Q, R and S ? How have you arrived at this conclusion ?
Solution :
Metal P is zinc; Metal Q is tin; Metal R is lead; Metal S is iron.
Metal P (zinc) is used to form a thin layer on metal S (iron) by the process of galvanisation to prevent its corrosion.
Metal Q (tin) i s used for electroplating tiffin boxes made of metal S (iron).
Metal R (lead) is used in making car batteries.
Metals Q (tin) and R (lead) form an alloy called solder .
Question 99:
A black metal oxide XO2 is used as a catalyst in the preparation of oxygen gas from potassium chlorate. The oxide XO2 is also used in ordinary dry cells. The metal oxide XO2 cannot be reduced satisfactorily with carbon to form metal X.
(a) Name the metal X.
(b) Name the metal oxide XO2
(c) Which reducing agent can be used to reduce XO2 to obtain metal X ?
(d) Name another metal which can also be extracted by the reduction of its oxide with the above reducing agent.
Solution :
(a) Manganese
(b) Manganese dioxide
(c) Aluminium
(d) Chromium
Question 100:
Metals X and Y can be recovered from the anode mud left behind after the electrolytic refining of copper metal. The coins made of metal X look new even after several years of use but the coins made of metal Y lose their shine gradually and get blackened soon. When metal X is alloyed with a small amount of metal Y, it becomes hard and hence suitable for making ornaments. What are metals X and Y ? Also state the colour of metal X.
Solution :
Metal X is gold and Metal Y is silver; The colour of metal X (gold) is yellow.
|
85 videos|437 docs|75 tests
|
FAQs on Lakhmir Singh & Manjit Kaur: Metals and Non-metals, Solutions- 4 - Science Class 10
| 1. What are metals and non-metals? |  |
| 2. What are some examples of metals and non-metals? |  |
| 3. What are the physical properties of metals? |  |
| 4. What are the physical properties of non-metals? |  |
| 5. What are the uses of metals and non-metals? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|

















