Solved Examples: The Solid State | Chemistry Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
SOLVED SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS
Example 1. A face-centred cubic solid of an element A has a largest sized guest atom B at the body centre octahedral hole if insertion of B doesn't affect the original unit cell dimension; determine the packing fraction of the solid.
Sol. In the given solid, there is one B and four A per unit cell.
Also, under the condition of largest possible size of B, it will be in contact of A present at the face centres only and the following relationship will exist: and 2(rA + rB) = a
and 2(rA + rB) = a
solving,
Now, packing fraction



Example 2. An element A has BCC structure and another guest atom B, of largest possible size are present at each edge centres of unit cell of A but without disturbing the original unit cell dimension. Determining the void percentage of this solid.

Sol. Since B is closer to corner than to face centre, in close contact,
2(rA + rB) = a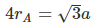
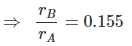
In a unit cell, there are two A and 12 × = 3B
Packing fraction (f) = 

⇒ Void space = 31.6%
Example 3. An element A has a BCC structure and another guest atoms B, of largest possible size, are present at the face centres, but without disturbing the unit cell dimension. Determine the packing fraction of this solid.

Sol. In the above solid, face centres are closer to body centre, therefore, the relationship.
2(rA rB) = 0
⇒ 
Now, packing fraction (f) = 
 = 0.684
= 0.684
Example 4. Calcium has face-centred cubic lattice and radius of calcium atom is 195.6 picometre. Determine the number of Ca atoms present on surfaces of a mm3 block of calcium metal assuming that atoms in the closest packing calcium metal assuming that atoms are in the closest packing.
Sol. In FCC, the relation is


⇒ 
= 553.24 × 10-9 mm.
⇒ Area of a face of unit cell = a3 = 3.06 × 10-13 mm2
⇒ Surface area of metal block = 6 mm2
⇒ Total number of faces of unit cells present on surface
=  = 1.96 × 1013
= 1.96 × 1013
Each face contributes two Ca atoms on surface as shown in diagram.
⇒ Total number of Ca atoms present on surface
= 2 × 1.96 × 1013 = 3.92 × 1013
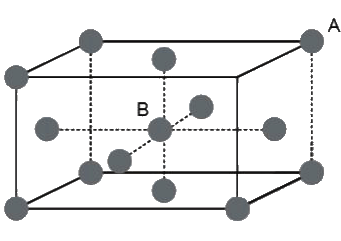
Example 5. An atom crystallizes in hexagonal closed packed arrangement. Determine dimensions (radius and length) of a large cylindrical atom that can be accommodated in the centre of HCP, in terms of radius of host atom.
Sol. The cylinder will pass through centre of middle layer and will lie between the face centres.

Therefore,
Height of cylinder (h) = height of hexagon (h) = 2r
Since, in HCP :  ,
,
where r = radius of atoms.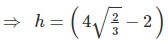
r = 1.266 r
Also, if R is the radius of cylinder, then in the case of closet contact :
⇒ R = 0.155 r,
⇒ h = 1.266 r
Example 6. A uniform cylindrical, polymer molecule crystallizes in body centred cubic array. Determine the packing fraction of this polymer in solid state assuming that molecules are in their closest contact.
Sol. The arrangement of molecules can be represented as follows :

Here,

⇒ 
Packing fraction (f) = 
= 
Example 7. Show the following arrays of atoms on a plane in an atomic FCC.
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Sol.
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Example 8. Cesium bromide crystallizes in cubic arrangement like CsCl. Given the ionic radii of Cs and Br- are 1.88 Å and 1.82 Å respectively, determine the packing fraction.
Sol. Here Cs ion is at body centre and Br- at the corners, therefore the relationship is
2(r++ r-) = 
= 2 (1.88 1.82) Å,
⇒ a = 4.27 Å
Packing fraction (f) = 

Example 9. Titanium metal crystallizes in a BCC arrangement and radius of an atom is 142 picometre. Determine the atomic weight of titanium if the density is 16.6 g/cm3. Also determine the number of unit cells present in a 5 cm3 block of titanium metals.
Sol. In BCC arrangement of atoms, the relationship between edge length radius of the atom is
Density (r) = 
Where, N = Number of atoms per unit cell,
M = Molar mass, NA = Avogadro's number
V = Volume of unit cell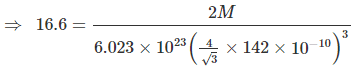
Here, the radius is taken in cm unit since, density is in g/cm3 unit.
Solving : M = 176. Also mass of 5 cm3 block = 5 × 16.6 = 83 g
⇒ Number of atoms is 5 cm3 block 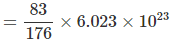
⇒ Number of unit cells 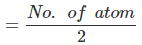 =
=  = 1.42 × 1023
= 1.42 × 1023
Example 10. Copper metal crystallizes in face-centred cubic arrangement and surface of adjacent atoms along the edge of the unit cell are 106 picometres apart. Determine the density of metal. Atomic mass of copper metal is 63.5 u.
Sol. According to the given information, a view of one face of the unit cell will be as shown below.
In FCC; 4√2a

The given distance is a - 2r = a - 

⇒ a = 362 pm = 3.62 × 10-8 cm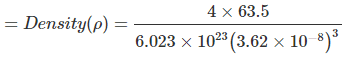 = 8.89 g/cm3
= 8.89 g/cm3
Example 11. Potassium crystallizes in "body centred cubic" arrangement and the surfaces of the adjacent atoms along the edges of unit cells are 71.4 picometre apart. Determine the density of metal. Atomic weight of K = 39. ?
Sol. In BCC, the relationship between edge length and radius of atom is
Also, given a - 2r = 71.4 × 10-10 cm
⇒ 
⇒ 71.4 × 10-10 cm
⇒ a = 5.329 × 10-10 cm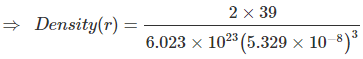
= 0.855 g/cm3
|
108 videos|286 docs|123 tests
|
FAQs on Solved Examples: The Solid State - Chemistry Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is the Solid State in NEET? |  |
| 2. What are some important topics to study in the Solid State for NEET? |  |
| 3. How can I prepare for the Solid State section in NEET? |  |
| 4. What are some common mistakes students make in the Solid State section of NEET? |  |
| 5. How much weightage does the Solid State section carry in NEET? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|


















