Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Sound Waves
Sound Waves | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Describing Sound
- Sound waves are produced by vibrating sources.
- When a sound wave contacts a solid, it can transfer vibrations to the solid.
- For instance, sound waves can make a drinking glass vibrate. If the glass vibrates excessively, it can shatter.
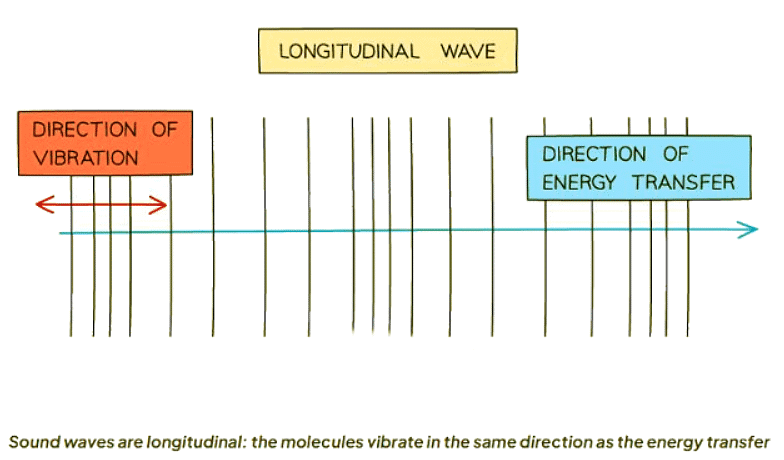
- Sound waves necessitate a medium for propagation. This implies that in the absence of molecules, as in a vacuum, sound cannot travel.
Compression & Rarefaction
- Longitudinal waves are composed of compression and rarefaction. Compression denotes a region of higher density, where molecules are closely packed, whereas rarefaction indicates a region of lower density, where molecules are more dispersed.
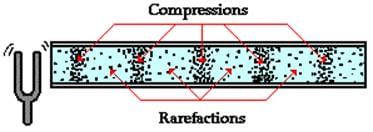 Sound is a longitudinal wave consisting of compressions and rarefactions - these are areas where the pressure of the air varies with the wave
Sound is a longitudinal wave consisting of compressions and rarefactions - these are areas where the pressure of the air varies with the wave
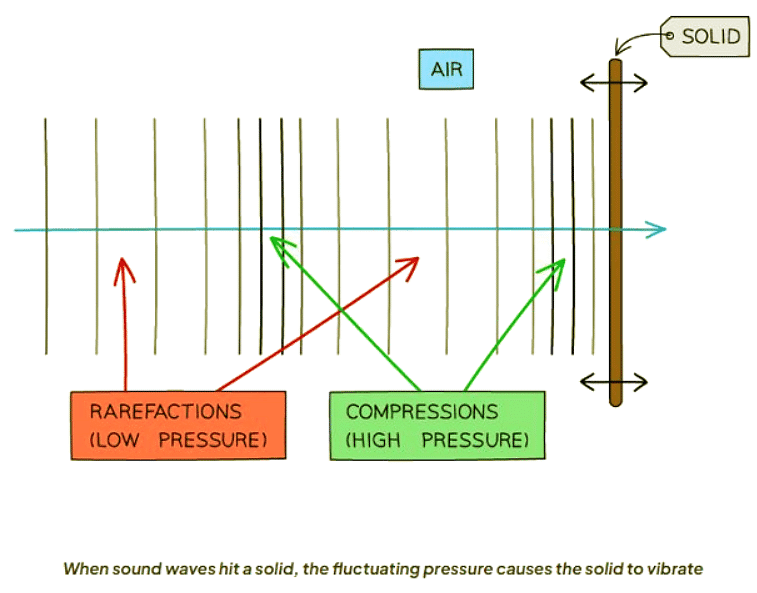
- These compressions and rarefactions result in fluctuations in pressure that change over time along with the wave.
- Consequently, sound constitutes a form of pressure wave.
- When these waves encounter a solid object, the pressure variations induce vibrations in the surface of the solid that synchronize with the sound wave.
Question for Sound WavesTry yourself: What are compression and rarefaction in sound waves?View Solution
The document Sound Waves | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
126 videos|194 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Sound Waves - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is sound compression and rarefaction? |  |
Ans. Sound compression is the region in a sound wave where air particles are pushed close together, creating an area of high pressure. Rarefaction, on the other hand, is the region in a sound wave where air particles are spread apart, creating an area of low pressure.
| 2. How do sound waves travel through a medium? |  |
Ans. Sound waves travel through a medium by causing particles in the medium to vibrate back and forth in the direction of the wave. This vibration creates areas of compression and rarefaction that propagate through the medium.
| 3. What is the relationship between the frequency of a sound wave and its pitch? |  |
Ans. The frequency of a sound wave is directly related to its pitch. Higher frequency sound waves have higher pitch, while lower frequency sound waves have lower pitch.
| 4. How does the amplitude of a sound wave affect its volume? |  |
Ans. The amplitude of a sound wave is directly related to its volume. Higher amplitude sound waves are perceived as louder, while lower amplitude sound waves are perceived as quieter.
| 5. Can sound waves travel through a vacuum? |  |
Ans. No, sound waves require a medium, such as air, water, or solids, to travel through. They cannot travel through a vacuum because there are no particles in a vacuum to transmit the vibrations of the sound wave.
Related Searches















