Strategic Alliances | Management Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
In the management field, a strategic alliance refers to an agreement between two or more companies to collaborate on a specific business activity. This collaboration allows each party to leverage the strengths of the other, leading to mutual benefits and a competitive advantage (Mockler, 1999). The emergence of strategic alliances is seen as a response to the challenges posed by globalization and the increasing complexity of the business environment.
Strategic alliances involve the exchange of knowledge and expertise among partners, along with a reduction in risks and costs, particularly in areas like supplier relationships, and the development of new products and technologies. While strategic alliances are sometimes compared to joint ventures, it's important to note that alliances may involve competitors and generally have a shorter lifespan. These alliances have evolved as formalized relationships between organizations, especially among companies operating in international business systems. The objective of these cooperative arrangements is to achieve organizational goals more effectively through collaboration than through competition. However, it's essential to acknowledge that alliances also pose challenges at various levels of analysis.
Theoretical Framework
Strategic alliance is when businesses willingly adjust their basic practices to work together efficiently, reducing repetition and waste for better overall performance (Frankel, Whipple, and Frayer, 1996).
Purpose of Strategic Alliances:
- A strategic alliance needs to align with the overall strategic plan of the involved parties, requiring strategic intent.
- Executive leadership support and formation at the highest level of management are crucial for a successful alliance.
Simplified Description:
- Essentially, a strategic alliance is like a "partnership" that allows businesses to team up for mutual benefits and a lasting competitive edge (Yi Wei, 2007).
Alternative Definitions:
- Buttery et.al. (1994) views strategic alliances as relationships between separate entities that maintain their corporate independence.
- Cauley De La Sierra (1995) introduces an international perspective, using "competitive alliance" to highlight that such partnerships involve strong international companies that remain competitors outside the alliance.
- Wheelan and Hunger (2000) describe strategic alliances as agreements between firms to do business together in a way that goes beyond regular dealings but stops short of a full partnership or merger.
Reasons for Strategic Alliances:
- Increased manufacturing and technological capabilities.
- Access to specific markets.
- Reduction of financial and political risks.
- Ensuring a competitive advantage.
Importance of Strategic Alliances:
- Organic growth is often not enough to meet organizations' required growth rates.
- Partnerships speed up the time it takes to bring products or services to the market.
- With increasing complexity, no single organization has all the expertise needed to serve customers effectively.
- Alliances help organizations share the rising costs of research and development.
- Strategic alliances provide access to global markets.
Forms of Strategic Alliances:
- Alliances can take the form of mutual services or consortia, partnerships between similar companies and industries to gain cost-effective benefits.
- When legal mergers are not possible, companies combine strengths for mutual value.
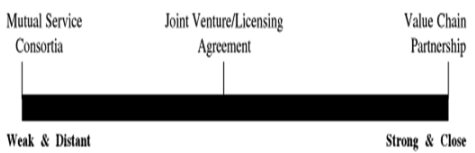
Types of Alliances:
- Licensing agreements involve one company granting rights to another in a different country or market to produce or sell a product.
- Value chain partnerships are strong alliances where companies form long-term arrangements with key suppliers or distributors for mutual benefits.
Historical Evolution of Strategic Alliances:
- In the 1970s, alliances focused on obtaining the best raw materials, lowest prices, advanced technology, and global market penetration.
- The 1980s saw alliances aimed at strengthening a company's position in the sector, utilizing economies of scale and scope.
- Examples include Boeing's alliance with Japanese companies and Kodak's partnership with Canon.
Shift in the 1990s:
- In the 1990s, collapsing barriers between geographical markets and sectors emphasized the expansion of capabilities and competencies.
- Companies needed continuous innovation to outpace competitors and maintain a competitive advantage (Harbison and Pekar, 1998).
There are three major types of international strategic alliances (Lorange and Roos, 1992)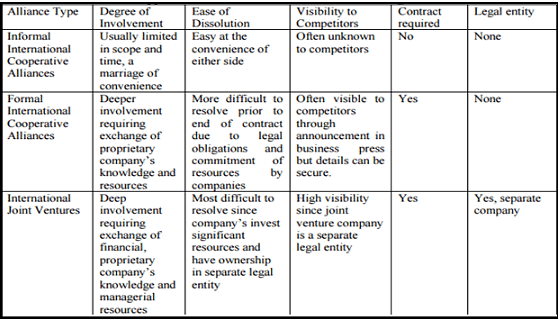
Managing Strategic Alliance
Complex Nature of Strategic Alliances:
- Managing strategic alliances can be challenging and intricate (Kazmi, 2008).
Management Principles for Strategic Alliances:
- Walters, et. al., suggested four principles for effective alliance management:
- Clearly define strategy and assign responsibility.
- Gradually develop the relationship between partners.
- Merge the cultures of partnering organizations.
- Plan for a possible exit strategy.
- Walters, et. al., suggested four principles for effective alliance management:
Success of Strategic Alliances in India:
- In the Indian context, strategic alliances outperform other organizational forms.
- These alliances have transformed competition patterns from traditional firm-to-firm to network-vs-network competition in both domestic and international markets.
Purpose of Strategic Alliances:
- Companies form alliances not just to access resources, technologies, and new markets but also to gain knowledge, processes, and insights for long-term competitive advantage.
Implementation of Strategic Plans:
- A strategic alliance plays a crucial role in successfully implementing a strategic plan.
- It needs to be strategic in nature, led by executive leadership, and formed by lower management at the highest level.
Adaptation in Complex Environments:
- To achieve efficiency, speed, and quality in diverse products within a complex environment, companies focus on core competencies and seek external sources for complementary resources, technical competences, and knowledge (Plake and Somers, 1998).
Categories of Strategic Alliances
There are many forms of strategic alliances which are mentioned below:
Joint Ventures:
- When two or more companies team up to work on a specific project, forming a single entity.
- Each business invests in the project, sharing costs, revenues, and profits.
- Joint ventures between small firms are rare due to commitment and cost challenges.
Outsourcing:
- Emerged in the 1980s and continued into the 1990s and beyond.
- Involves hiring external companies to handle specific tasks or functions.
Affiliate Marketing:
- A growing trend, especially online.
- Successful retailers use affiliate marketing for precise tracking of referrals throughout the order process.
Technology Licensing:
- Involves licensing trademarks, intellectual property, and trade secrets to an external firm.
- Often used as a cost-effective way to enter foreign markets.
- Disadvantage: Loss of control over technology once it's in others' hands.
Product Licensing:
- Similar to technology licensing but focuses on licensing the manufacture and sale of a specific product.
- Licensees usually get an exclusive geographic area for sales.
- Lower-risk way to expand product reach compared to building manufacturing and distribution.
Franchising:
- An effective nationwide success strategy.
- Franchisees pay a setup fee and ongoing payments.
- Disadvantage: Loss of control over how franchisees run their businesses.
R&D Alliances:
- Often falls into the joint venture category.
- Businesses collaborate on research ventures by forming a new entity.
strategic alliance
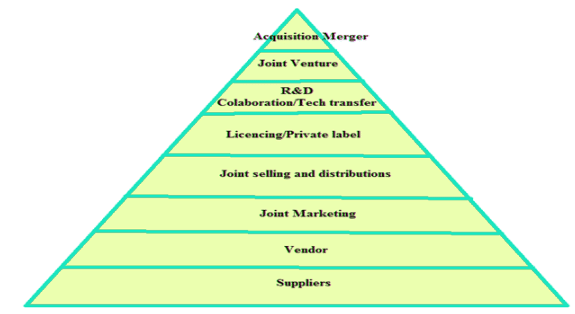
Stages of strategic alliance formation
Traditional Steps in Forming Strategic Alliances:
1. Strategy Development:
- Evaluate the alliance's feasibility, objectives, and reasons, aligning them with the overall corporate strategy.
- Focus on key issues and challenges, and develop resource strategies for production, technology, and personnel.
2. Partner Assessment:
- Analyze potential partner's strengths and weaknesses.
- Adapt strategies to accommodate different management styles.
- Establish selection criteria, understand partner motivations, and address any resource gaps.
3. Contract Negotiation:
- Ensure realistic objectives for all parties.
- Form high-quality negotiation teams.
- Define each partner's contributions, rewards, and protect proprietary information.
- Address termination clauses, penalties for poor performance, and clarify arbitration procedures.
4. Alliance Operation:
- Secure senior management commitment.
- Evaluate resources dedicated to the alliance.
- Align budgets and resources with strategic priorities.
- Measure and reward alliance performance.
- Assess the overall performance and results of the alliance.
5. Alliance Termination:
- Wind down the alliance when objectives are met, cannot be achieved, or when partners shift priorities or reallocate resources.
Number of alliances made by some large and medium scale firms (Schreiner, 2009)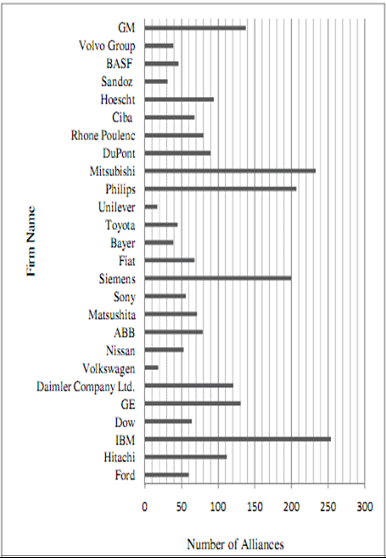
Definition of Strategic Alliances:
- Strategic alliances are ongoing agreements, beyond formal structures, where organizations collaborate to use resources and plan structures toward shared goals.
- Achieving the goals of independent organizations is connected to the business objectives of supporting organizations.
Inter-Firm Assistance and Challenges:
- Inter-firm assistance aims to strategically align and overcome critical hurdles in alliance formation.
- Research efforts sometimes fall short in identifying specific structural aspects that can support better performance in forming positive strategic alliances (Michael, et al., 1995).
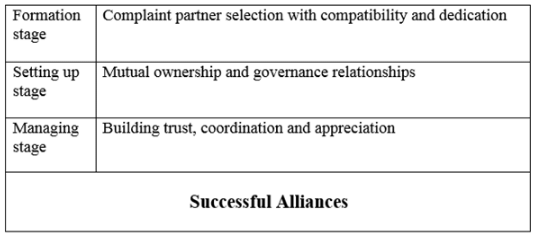
Success in Strategic Alliance
A strategic alliance is a partnership between independent companies, where they work together to achieve common goals like business growth, resource sharing, and expanding their capabilities. Key factors influence each stage of alliance development, contributing to its success (Gulati, 1998).
Factors for Alliance Success:
1. Selecting the Right Partner:
- Choosing a suitable and trustworthy partner is crucial in the initial stage of alliance formation.
2. Setting Up the Alliance:
- Designing the alliance, establishing roles and responsibilities, and ensuring proper control and authority at each level are essential in the second stage.
3. Managing and Evaluating:
- Proper management and ongoing evaluation are crucial in the third stage.
- This includes monitoring the alliance regularly to assess its perceived value.
Mutual Commitment for Success:
- Collaborators need to be committed to achieving success through:
- Financial success.
- Consistent company approaches aligned with the partnership.
- Clearly communicated and agreed-upon company goals.
- Fulfilling expected contributions and expectations.
Organizational Compatibility:
- Partner organizations should have:
- Compatible goals and vision.
- A shared need for collaboration.
- Shared values and corporate culture, with trust being crucial.
- Effective communication and a history of successful partnerships.
Biggs (2006) recognized some critical factors that determine the success of a strategic alliance:
Critical Success Factors affecting Strategic Alliances (Biggs, 2006)
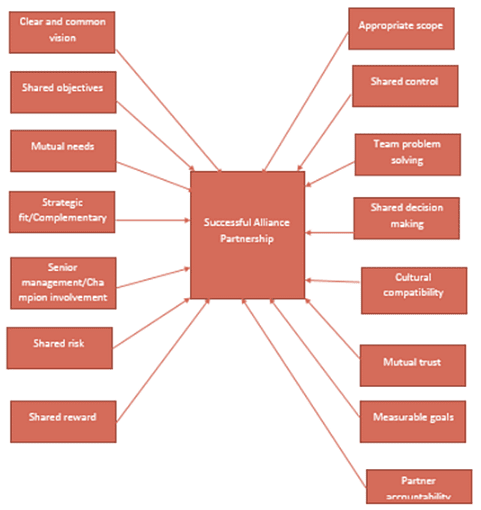
Determinants of Success:
- Key factors at each stage, from choosing the right partner to proper management and evaluation, contribute to the overall success of strategic alliances.
Benefits of Strategic Alliances
Ease of Market Entry:
- Advancements in technology make it easier for businesses to enter foreign markets.
- Strategic alliances provide a cost-effective way to enter new markets quickly.
- Overcoming challenges like competition and government regulations is easier with the support of an alliance.
Shared Risks:
- In uncertain markets, sharing risks becomes crucial.
- Strategic alliances help reduce or control a company's risks when entering new markets or launching new products.
Shared Knowledge and Expertise:
- Alliances allow access to knowledge and expertise that a company may lack.
- Information gained can be used not only in the joint venture but also for other projects and purposes.
Synergy and Competitive Advantage:
- Collaboration between partners creates synergy, making competition more effective.
- Additional benefits include entering new markets, protecting the home market, expanding distribution networks, reducing costs, and gaining access to hidden assets.
Broadening Product Line and Services:
- Alliances help in expanding product lines, services, and filling gaps in existing products.
- Companies collaborate to enter new markets, attract customers, and broaden their market share.
Increasing Performance and Capacity:
- Strategic alliances enhance performance, increase productive capacity, and improve existing products and services through joint manufacturing and development.
Resource Augmentation:
- Alliances lead to resource augmentation as all partners contribute resources.
- Firms with fewer resources can benefit from creating strategic alliances.
Gaining New Skills and Knowledge:
- Strategic alliances are formed to gain new skills and knowledge.
- Partners learn from each other's skills, technology, and technical standards.
Enhanced Market Presence:
- Alliances help companies enter new markets and attract potential customers, expanding their market share.
- Especially beneficial for companies operating in stagnant industries looking to grow in emerging businesses.
Reducing Future Competition:
- By forming alliances, companies reduce the risk of future competition.
- Demonstrates opportunities for future collaborations and allows firms to gain proficiency and economies of scale.
Causes of Unsuccessful Strategic Alliances
Control of Strategy Implementation:
- Alliance failure can occur when there are issues related to the control of strategy implementation.
Dependency on Partners for Skills:
- Companies may face challenges if they depend too much on partners for specific skills.
Unequal Gains Perception:
- If partners feel they are gaining less from the alliance than others, it can lead to problems and ultimately cause failure.
Poor Project Management:
- Improper planning and monitoring of the alliance's development can create problems.
Conflicts in Objectives and Plans:
- Conflicts between allies in deciding objectives and plans can impact the feasibility and relationship of the alliance.
Cultural Differences:
- Clashes in cultural values and thinking can lead to conflicts and failure of strategic alliances.
Role Ambiguity and Uncertainty:
- Changes in job positions and role ambiguity can hinder organizations from fulfilling their obligations in the alliance.
Multiple Alliances with Competitors:
- A partner forming alliances with competing organizations may affect the success of the alliance.
Antitrust Procedures:
- Involvement of antitrust procedures can limit the benefits of an alliance by inviting government intervention.
In conclusion, strategic alliances are crucial tools in a competitive business environment. These partnerships help companies gain a competitive edge, access skills and resources, share facilities, and enter new markets. Forming strategic alliances allows companies to develop a portfolio of partnerships, focusing on various dimensions of their business operations and addressing current and potential markets.
FAQs on Strategic Alliances - Management Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. How can companies effectively manage strategic alliances? |  |
| 2. What are the different categories of strategic alliances? |  |
| 3. What are the stages of strategic alliance formation? |  |
| 4. What are some key factors that contribute to success in strategic alliances? |  |
| 5. What are some common causes of unsuccessful strategic alliances? |  |




















