NEET Previous Year Questions (2016-2024): Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production (Old NCERT) PDF Download
Q1: Which one of the following is NOT an advantage of inbreeding?
(a) It decreases homozygosity.
(b) It exposes harmful recessive genes but are eliminated by selection.
(c) Elimination of less desirable genes and accumulation of superior genes takes place due to it.
(d) It decreases the productivity of inbred population, after continuous inbreeding.
Ans: (d)
Inbreeding refers to the mating of individuals who are closely related by blood. While inbreeding can have some advantages, such as increasing uniformity and concentrating desirable traits, it also has several disadvantages. One of the disadvantages is a decrease in productivity of the inbred population over time.Continuous inbreeding leads to a phenomenon known as inbreeding depression. Inbreeding depression is the reduced fitness or vigor of a population due to increased expression of harmful recessive genes. As a result, inbred populations may experience reduced fertility, lower growth rates, and decreased overall productivity compared to outbred populations.
Q2: Breedings crops with higher levels of vitamins and minerals or higher proteins and healthier fats is called: (2022)
(a) Bio-remediation
(b) Bio-fortification
(c) Bio-accumulation
(d) Bio-magnification
Ans: (b)
- Bio-fortification is the process of breeding crops to increase their nutritional value by enhancing the levels of essential vitamins, minerals, and other important nutrients in the food. This is achieved through conventional breeding techniques or genetic engineering.

- By bio-fortifying crops, it is possible to address the problem of malnutrition and nutrient deficiencies in many parts of the world, particularly in developing countries. For example, breeding crops with higher levels of iron and zinc can help combat anemia and other health problems associated with nutrient deficiencies.
- On the other hand, bio-remediation refers to the use of living organisms to clean up polluted soil or water, while bio-accumulation and bio-magnification refer to the buildup of toxins in the food chain. These concepts are not related to breeding crops with higher nutritional value.
Q3: Match List - I with List - II (2021)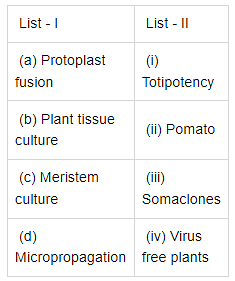
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
(a) (b) (c) (d)
(a) (iii) (iv) (i) (ii)
(b) (iv) (iii) (ii) (i)
(c) (iii) (iv) (ii) (i)
(d) (ii) (i) (iv) (iii)
Ans. (d)
- This capacity to generate a whole plant from any cell/explant is called totipotency.
- Each of these plants will be genetically identical to the original plant from which they were grown, i.e., they are somaclones.
- Hence, one can remove the meristem and grow it in vitro to obtain virus-free plants.
- Imagine a situation when a protoplast of tomato is fused with that of potato, and then they are grown – to form new hybrid plants combining tomato and potato characteristics. Well, this has been achieved – resulting in formation of pomato; unfortunately this plant did not have all the desired combination of characteristics for its commercial utilisation.
Q4: Mutations in plant cells can be induced by: (2021)
(a) Gamma rays
(b) Zeatin
(c) Kinetin
(d) Infrared rays
Ans. (a)
- Mutations are sudden changes or alterations in the DNA sequence of an organism that can lead to the formation of new traits or variations. These mutations can be induced artificially using different methods, such as exposure to radiation or chemicals. In the case of plants, mutations can be induced through the use of radiation sources, such as X-rays or gamma rays.
- Gamma rays are a type of high-energy radiation that can penetrate deeply into plant tissues and cause damage to the DNA molecule, leading to the formation of mutations. Gamma rays can cause changes in the nucleotide sequence of DNA, such as base substitutions, deletions, insertions, and rearrangements, which can result in changes in the phenotype of the plant.
- Zeatin and kinetin are two types of plant growth hormones that play a role in regulating plant growth and development. They do not induce mutations in plant cells, but they can promote cell division and differentiation, which can lead to changes in plant structure and function. Infrared rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation that can also affect plant growth and development, but they do not induce mutations in plant cells.
Q5: Which of the following is not an objective of Biofortification in crops? (2021)
(a) Improve vitamin content
(b) Improve micronutrient and mineral content
(c) Improve protein content
(d) Improve resistance to diseases
Ans. (d)
- Biofortification is the process of increasing the nutritional content of food crops by breeding or genetic engineering. It aims to address the problem of malnutrition and nutrient deficiencies in many parts of the world, particularly in developing countries.
- The objectives of biofortification are to improve the vitamin content, micronutrient and mineral content, and protein content of food crops. This can be achieved through conventional breeding or genetic engineering techniques.
- However, improving resistance to diseases is not an objective of biofortification. Disease resistance is a different trait that can be bred into crops using other methods, such as conventional breeding or genetic engineering.
Q6: Which of the following is not a step in Multiple Ovulation Embryo Transfer Technology (MOET)? (2021)
(a) Cow is fertilized by artificial insemination
(b) Fertilized eggs are transferred to surrogate mothers at 8-32 cell stage
(c) Cow is administered hormone having LH like activity for super ovulation
(d) Cow yields about 6-8 eggs at a time
Ans. (c)
- In this method, a cow is administered hormones, with FSH-like activity, to induce follicular maturation and super ovulation – instead of one egg, which they normally yield per cycle, they produce 6-8 eggs.
- The animal is either mated with an elite bull or artificially inseminated.
- The fertilised eggs at 8–32 cells stages, are recovered non-surgically and transferred to surrogate mothers.
Q7: By which method was a new breed ‘Hisardale’ of sheep formed by using Bikaneri ewes and Marino rams ? (2020)
(a) Cross breeding
(b) Inbreeding
(c) Out crossing
(d) Mutational breeding
Ans. (a)
Cross-breeding is the process where the breeding between the two individuals of different species takes place. “Hisardale" is a new breed of sheep developed by crossing Bikaneri ewes and Marino rams in Punjab.
Q8: Select the incorrect statement. (2019)
(a) Inbreeding helps in accumulation of superior genes and elimination of undesirable genes.
(b) Inbreeding increases homozygosity.
(c) Inbreeding is essential to evolve purelines, in any animal.
(d) Inbreeding selects harmful recessive gene that reduce fertility and productivity.
Ans: (d)
- Inbreeding strategies allow the desirable qualities of more closely related individuals to be continued within the same breed for 4-6 generations. It increases homozygosity and thus, is necessary for evolving a pureline.
- Inbreeding exposes harmful recessive genes that are eliminated by selection. It also helps in accumulation of superior genes and elimination of less desirable genes. Therefore, this approach where there is selection at each step, increases the productivity of inbred population. However, continued inbreeding, especially close inbreeding usually leads to reduce fertility and even productivity. This is called inbreeding depression.
Q9: Mad cow disease in cattle is caused by an organism which has : (2019)
(a) Inert crystalline structure
(b) Abnormally folded protein
(c) Free RNA without protein coat
(d) Free DNA without protein coat
Ans: (b)
- Mad cow disease, also known as bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE), is a fatal neurodegenerative disease that affects cattle. It is caused by an abnormally folded protein called prion.
- Prions are infectious agents that are composed entirely of protein and have no DNA or RNA. They are able to convert normal proteins into their abnormal form, leading to the accumulation of protein aggregates in the brain, which damages nerve cells and causes characteristic symptoms of the disease.
- Prions are unique infectious agents because they do not have any genetic material, such as DNA or RNA, and they are not destroyed by traditional methods of sterilization, such as heat or radiation.
- The abnormally folded protein is resistant to degradation by proteases, which are enzymes that normally break down proteins in the body. This resistance to degradation is due to the tight packing of the protein molecules, which makes it difficult for proteases to access the protein and break it down.
Q10: Homozygous purelines in cattle can be obtained by (2017)
(a) Mating of unrelated individuals of same breed
(b) Mating of individuals of different breed
(c) Mating of individuals of different species
(d) Mating of related individuals of same breed
Ans: (d)
When breeding is between animals of the same breed for 4-6 generation, it is called inbreeding. Inbreeding, as a rule, increases homozygosity. Thus, inbreeding is necessary if we want to obtain a pureline in any animal.
Q11: A true breeding plant is (2016)
(a) One that is able to breed on its own
(b) Produced due to cross-pollination among unrelated plants
(c) Near homozygous and produces offspring of its own kind
(d) Always homozygous recessive in its genetic constitution
Ans: (c)
- True breeding plants are those that, when self-fertilized or crossed with another true breeding plant of the same variety, produce offspring that are identical to the parents in terms of their genetic makeup. These plants are homozygous for a particular trait, meaning that they have two copies of the same allele for that trait.
- Option (a) is incorrect because the ability to self-pollinate or breed on its own does not necessarily make a plant true breeding.
- Option (b) is incorrect because true breeding plants are typically produced through self-pollination or controlled cross-pollination among related plants, not among unrelated plants.
- Option (d) is incorrect because not all true breeding plants are homozygous recessive in their genetic constitution. They may be homozygous dominant or heterozygous for a particular trait.
Therefore, the correct option is (c) near homozygous and produces offspring of its own kind, as true breeding plants are nearly homozygous for a particular trait and produce offspring that are genetically identical to themselves.
Q12: Interspecific hybridisation is the mating of (2016)
(a) Animals within same breed without having common ancestors
(b) Two different related species
(c) Superior males and females of different breeds
(d) More closely related individuals within same breed for 4-6 generations.
Ans: (b)
In interspecific hybridisation, a species is mated with a different related species of the same genus.
 Interspecific Hybridisation
Interspecific Hybridisation
Interspecific hybrids are generally difficult to produce, but they are important in plant breeding, particularly in breeding for disease resistance. This is also called intrageneric hybridisation.
Q13: Among the following edible fishes, which one is a marine fish having rich source of omega-3 fatty acids? (2016)
(a) Mystus
(b) Mangur
(c) Mrigala
(d) Mackerel
Ans: (d)
Mackerel is a marine fish, rich in omega- 3-fatty acids. Mystus, Mangur and Mrigala are freshwater fishes.
Q14: A system of rotating crops with legume or grass pasture to improve soil structure and fertility is called (2016)
(a) Strip farming
(b) Shifting agriculture
(c) Ley farming
(d) Contour farming
Ans: (c)
Ley farming is an agricultural system where the field is alternately seeded for grain and left fallow for growing hay or used for pasture. During the fallow/pasture period the soil is filled with roots of grasses and other plants. New ploughing mixes them in the soil and also increases the amount of nitrogen in the soil especially when legume forage are used. It also protects soil from erosion by maintaining constant soil coverage.
Q15: A system of rotating crops with legume or grass pasture to improve soil structure and fertility is called (2016)
(a) Ley farming
(b) Contour farming
(c) Strip farming
(d) Shifting agriculture
Ans: (a)
- The system of rotating crops with legume or grass pasture to improve soil structure and fertility is known as Ley farming.
- In this method, the cultivated land is divided into several parts, and the crops are grown in rotation with legumes or grasses.
- Legumes like peas and beans are beneficial as they fix atmospheric nitrogen into the soil. This enhances soil fertility and reduces the need for artificial fertilizers.
- The grasses also help to maintain the structure of the soil and prevent soil erosion. Overall, Ley farming is an effective method to maintain the health of the soil and increase crop productivity.
Q16: Which of the following enhances or induces fusion of protoplasts ? (2015)
(a) Polyethylene glycol and sodium nitrate
(b) IAA and kinetin
(c) IAA and gibberellins
(d) Sodium chloride and potassium chloride
Ans: (a)
Polyethylene glycol and sodium nitrate play an important role in the fusion of protoplasts from the same or different species. It is done for the formation of somatic hybrid cells. This process is adopted when normal sexual reproduction is not possible for the production of hybrids.
Q17: A technique of micropropagation is : (2015)
(a) Somatic embryogenesis
(b) Protoplast fusion
(c) Embryo rescue
(d) Somatic hybridization
Ans: (a)
- Micropropagation is a technique of plant propagation in which a small piece of plant tissue, such as a stem or leaf, is cultured in a nutrient medium under controlled conditions to produce multiple copies of the same plant. The answer to the question is option (a) somatic embryogenesis.
- In this technique, somatic cells are stimulated to develop into embryos, which are then grown into mature plants. It is a useful technique for propagating plants that are difficult or slow to grow by traditional methods.
- It is also used for the mass production of plants with desirable traits, such as disease resistance, improved yield, and faster growth.
Overall, micropropagation techniques like somatic embryogenesis have significant applications in horticulture and agriculture.
Q18: Outbreeding is an important strategy of animal husbandry because it: (2015)
(a) Is useful in producing purelines of animals.
(b) Is useful in overcoming inbreeding depression.
(c) Exposes harmful recessive genes that are eliminated by selection.
(d) Helps in accumulation of superior genes.
Ans: (b)
- Outbreeding is useful in the problem of inbreeding depression. Outbreeding is the breeding of unrelated individuals within a breed or between different breeds.
- It is an important strategy in animal husbandry because it helps to overcome inbreeding depression, which is the reduction in fitness or vigor of a population that occurs as a result of breeding closely related individuals.
- Inbreeding can lead to the expression of harmful recessive alleles and a decrease in genetic diversity, which can reduce the ability of a population to adapt to changing environments or resist diseases.
Q19: To obtain virus - free healthy plants from a diseased one by tissue culture technique, which part/parts of the diseased plant will be taken: (2014)
(a) Apical meristem only
(b) Palisade parenchyma
(c) Both apical and axillary meristems
(d) Epidermis only
Ans: (c)
- Even if the plant gets some viral infection still the meristematic region remains free. Hence, meristems are taken out from the plant and are grown in vitro to obtain a plant that is free from viruses. Therefore, both axillary and apical meristems are used for this purpose.
Option A: Along with the apical meristem, the axillary meristem is also utilized in tissue culture.
Option B: As parenchyma is not included in the meristem, it can be easily infected by viruses and hence, is not suitable for tissue culture.
Option D: The plant's epidermis is easily infected by the virus, making it inappropriate for use in tissue culture.
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2016-2024): Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production (Old NCERT)
| 1. What are some strategies for enhancing food production? |  |
| 2. How do high-yielding crop varieties contribute to enhancing food production? |  |
| 3. What is precision farming and how does it help in food production? |  |
| 4. How does crop rotation contribute to enhancing food production? |  |
| 5. What is integrated pest management (IPM) and how does it aid in food production? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|


















