Strategy and Structure | Management Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Organization Structure
The structure of an organization encompasses two overarching dimensions:
1. Vertical Dimensions
Tall Structures:
- Think of tall structures as organizations with many layers of hierarchy, like a skyscraper.
- In these organizations, managers have more control over their subordinates, and there's a clear line of authority from top to bottom.
Best for Mass Production:
- Tall structures work well for companies that produce large quantities of standardized products or services using mass production methods.
- These organizations typically rely on well-established technologies and processes to achieve efficiency in production.
Characteristics:
- Specialization of Tasks: Each employee has a specific role and set of responsibilities within the organization.
- Chain of Command: There is a clear hierarchy of authority, where each level of management oversees the one below it.
- Formal Reporting Relationships: Employees report to their immediate supervisors through formal channels.
- Grouping into Departments: Employees are organized into departments based on their specialized functions or areas of expertise.
- Upward and Downward Communication: Communication flows both upward, from subordinates to superiors, and downward, from superiors to subordinates, following the chain of command.
2. Horizontal Dimensions
Flat Structures:
- Horizontal structures are characterized by fewer layers of management and a more decentralized decision-making process.
- In these organizations, there is less emphasis on hierarchy and more focus on collaboration and teamwork among employees.
Ideal for Different Products:
- Flat structures are suitable for companies that produce differentiated products or services and require flexibility and innovation.
- They are often found in medium-sized businesses, as well as non-profit organizations that provide specialized social services.
Characteristics:
- Sharing of Tasks: Employees in flat structures often have overlapping roles and responsibilities, allowing for greater flexibility and adaptability.
- Sharing of Information: There is a culture of openness and transparency, where information is shared freely among team members to facilitate collaboration.
- Decentralized Decision Making: Rather than decisions being made solely by top management, authority is distributed across different levels of the organization, empowering employees to make decisions within their areas of expertise.
- Focus on Learning: Flat structures encourage a culture of continuous learning and improvement, where employees are encouraged to share knowledge and skills to enhance the overall effectiveness of the organization.
Types of Organization Structure
The main types of organizational structures are given below:
1. Entrepreneurial Structure:
- This is the simplest type of structure where one person owns and manages the organization.
- It's typically found in small businesses that focus on a single product or service for a local market.
- Elementary form of structure
- Organization owned and managed by one person
- Serving single business, product or serve local markets
- Owner looks after all decisions, day to day operations of strategic nature.
2. Functional Structure:
- When a business grows and offers more products, tasks need to be specialized.
- Different areas like production, marketing, finance, and personnel have their own leaders.
- Suitable for businesses that are not too big, with a limited number of products.
- It's like dividing the work into building blocks based on functions performed (like making the product, selling it, managing money, and handling people).
- This structure can extend to different levels as the organization grows.
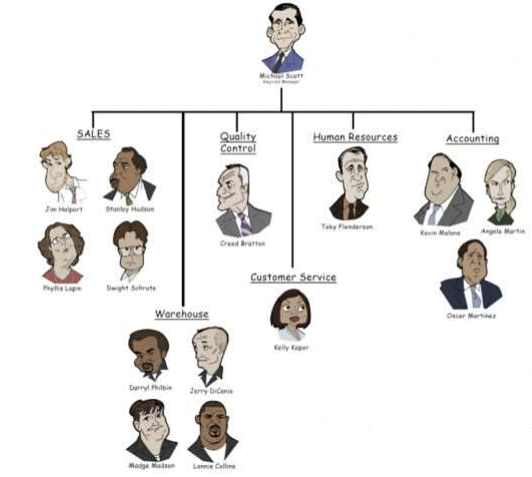
- Functional Structure seeks to distribute decision making and operational authority towards each.
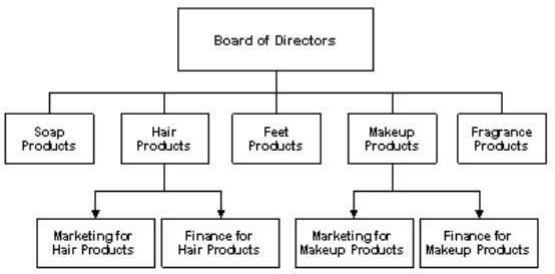
3. Divisional Structure:
- Work gets divided based on product lines, customer types, and geographical areas covered.
- Each division has its management at a higher level, and a functional structure might still be in place within each division.
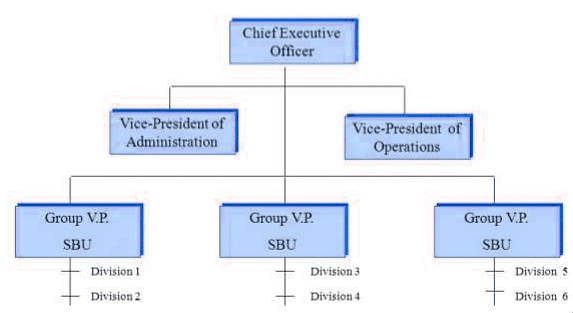
4. SBU Structure (Strategic Business Unit):
- Any part of a business organization is treated separately for strategic management purposes.
- SBUs are formed when top management finds it challenging to control a division strategically.
5. Matrix Structure:
- In large organizations dealing with multiple projects, a matrix structure is put in place.
- Functional specialists are assigned to specific projects, new products, or services.
- During the project duration, specialists from various areas create different groups, reporting to a team leader.
- These specialists work simultaneously under their project and in their original department.
Structural Considerations in Strategic Implementation
Before making changes, leaders check if the current structure supports the new strategy.They align the organizational hierarchy to back primary goals and gain a competitive edge.Weaknesses are identified, and plans are made to handle potential issues.
Structuring Activities:
- Managers outsource tasks not directly tied to strategic goals to experts at a lower cost.
- Employees can then focus on core tasks, like design and sales, while specialized work is done externally.
Aligning Functions to Objectives:
- Leaders ensure all staff have the skills and resources needed for the strategy.
- Clear processes with defined roles and responsibilities are established.
- The strategy must be consistent across all departments, adaptable to changes, and technically possible.
Establishing Authority:
- Managers clarify which decisions need executive approval and which employees can make independently.
- Decisions are ideally made by those closest to the situation to streamline operations and eliminate unnecessary tasks.
- Employees given decision flexibility are also held accountable.
Developing Partnerships:
- Teamwork is crucial for achieving specific goals.
- A balanced scorecard ensures departments work together instead of competing against each other.
- A cooperative environment encourages sharing resources, personnel, and knowledge among departments.
- The structure supports learning and development for sustainable growth.
FAQs on Strategy and Structure - Management Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What are the different types of organization structures? |  |
| 2. How do structural considerations impact strategic implementation? |  |
| 3. What is the relationship between strategy and structure in UPSC exams? |  |
| 4. How can organizations ensure that their strategy and structure are aligned for success? |  |
| 5. What role does organizational structure play in the success of strategic implementation in UPSC exams? |  |















