Structure & Physiography Class 11 Geography
Introduction
- The Earth is approximately 460 million years old.
- Over these long years, it has undergone many changes brought about primarily by the endogenic and exogenic forces.
- These forces have played a significant role in giving shape to various surface and subsurface features of the earth.
- The Indian plate, which was to the south of the equator millions of years ago, was much larger in size, and the Australian plate was a part of it.
- Over millions of years, this plate broke into many parts, and the Australian plate moved towards the southeastern direction and the Indian plate to the north.
- This northward movement of the Indian plate is still continuing, and it has significant consequences on the physical environment of the Indian subcontinent.
- It is primarily through the interplay of these endogenic and exogenic forces and lateral movements of the plates that the present geological structure and geomorphologic processes active in the Indian subcontinent came into existence.
- India can be classified into three main geological divisions based on its geological structure and formations:
(i) The Peninsular Block
(ii) The Himalayas and other Peninsular Mountains
(iii) The Indo-Ganga-Brahmaputra Plain
The Peninsular Block
- The northern boundary of the Peninsular Block - line running from Kachchh along the western flank of the Aravali Range near Delhi and then roughly parallel to the Yamuna and the Ganga as far as the Rajmahal Hills and the Ganga delta.
- Karbi Anglong and the Meghalaya Plateau in the northeast and Rajasthan in the west are also extensions of this block.
- The northeastern parts are separated by the Malda fault in West Bengal from the Chotanagpur plateau.
- In Rajasthan, the desert and other desert-like features overlay this block.
- The Peninsula is formed by a great complex of very ancient gneisses and granites, which constitutes a major part of it.
- As a part of the Indo-Australian Plate, it has been subjected to various vertical movements and block faulting.
- The rift valleys of the Narmada, the Tapi, and the Mahanadi, and the Satpura block mountains are some examples of it.
- The Peninsula mostly consists of relict and residual mountains like the Aravali hills, the Nallamala hills, the Javadi hills, the Veliconda hills, the Palkonda range, and the Mahendragiri hills etc.
- The river valleys here are shallow with low gradients.
- Most of the east-flowing rivers form deltas before entering the Bay of Bengal.
- The deltas formed by the Mahanadi, the Krishna, the Kaveri, and the Godavari are important examples.
The Himalayas And Other Peninsular Mountains
- The Himalayas and other Peninsular mountains are young, weak, and flexible in their geological structure, contrasting with the rigid and stable Peninsular Block.
- These mountains continue to be influenced by both exogenic (external) and endogenic (internal) forces, leading to the formation of geological features such as faults, folds, and thrust plains.
- The mountains are of tectonic origin and are characterised by fast-flowing rivers that are still in their youthful stage.
- Common landforms associated with this stage include:
(i) Gorges
(ii) V-shaped valleys
(iii) Rapids
(iv) Waterfalls
Indo-Ganga-Brahmaputra Plain
- The third geological division of India consists of the plains formed by the Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra rivers.
- This region was originally a geosynclinal depression that reached its maximum development during the third phase of the Himalayan mountain formation, approximately 64 million years ago.
- Since that time, the depression has been gradually filled with sediments carried by both the Himalayan and the Peninsular rivers. The average depth of alluvial deposits in these plains ranges from 1,000 to 2,000 meters.
- The relief and physiography of India have been profoundly shaped by the geological and geomorphological processes active within the subcontinent.
Physiography
The physiography of an area results from its structure, process, and stage of development.- Diversity of Physical Features:
India exhibits great diversity in its physical landscape:
(i) North India: Characterised by rugged topography, including a series of mountain ranges with varied peaks, beautiful valleys, and deep gorges.
(ii) South India: Features stable tablelands with highly dissected plateaus, denuded rocks, and developed scarps.
(iii) Central Region: Contains the vast North Indian Plain, situated between the northern mountains and southern plateaus. - Physiographic Divisions of India:
(i) The Northern and North-eastern Mountains
(ii) The Northern Plain
(iii) The Peninsular Plateau
(iv) The Indian Desert
(v) The Coastal Plains
(vi) The Islands
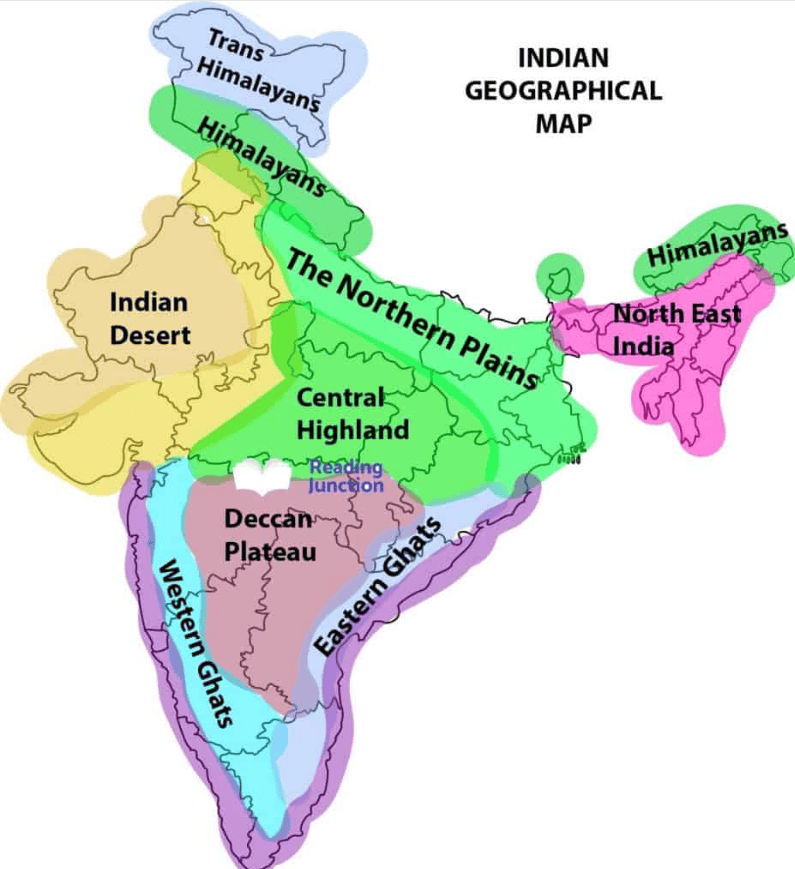
The North and Northeastern Mountains
- The North and Northeastern Mountains are comprised of the Himalayas and the Northeastern hills.
- Some of the important ranges are the Greater Himalayan range, which includes the Great Himalayas and the Trans-Himalayan range, the Middle Himalayas, and the Shiwalik.
- The general orientation of these ranges in northwestern India is from northwest to southeast.
- In the Darjeeling and Sikkim regions, the Himalayas run in an east-west direction, while in Arunachal Pradesh, they extend from southwest to northwest.
- In Nagaland, Manipur, and Mizoram, the ranges run in a north-south direction.
- The Great Himalayan Range (central axial range) is approximately 2,500 km long (east to west) and 160-400 km wide (north to south).
- The Himalayas act as a barrier, separating the Indian subcontinent from Central and East Asian countries.
- Beyond being a physical barrier, the Himalayas also serve as a climatic, drainage, and cultural divide.
The Northern Plains
- Alluvial deposits from the Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra rivers create the northern plains.
- They stretch about 3,200 km from east to west, with an average width of 150-300 km.
- Alluvial deposits can reach depths of 1,000-2,000 m.
- Zoning of the Plains
(a) Bhabar
(i) A narrow belt (8-10 km) parallel to the Shiwalik foothills.
(ii) Streams from the mountains deposit rocks and boulders; rivers may disappear here.
(b) Tarai
(i) Located south of Bhabar, approximately 10-20 km wide.
(ii) Streams re-emerge, creating marshy areas with rich natural vegetation and diverse wildlife.
(c) Alluvial Plains
(i) Bhangar - Older alluvial deposits.
(ii) Khadar - Newer alluvial deposits. - The plains exhibit features like sand bars, meanders, oxbow lakes, and braided channels.
- The Brahmaputra plains are noted for riverine islands and sand bars, often subject to flooding and shifting courses.
- The river mouths form significant deltas, such as the Sunderbans delta.
- The plains are generally flat, with an elevation of 50-150 m above sea level.
- Haryana and Delhi serve as a water divide between the Indus and Ganga river systems.
- The Brahmaputra flows from northeast to southwest, turning sharply southward at Dhubri before entering Bangladesh.
- The fertile alluvial soil supports crops like wheat, rice, sugarcane, and jute, sustaining a large population.
The Peninsular Plateau
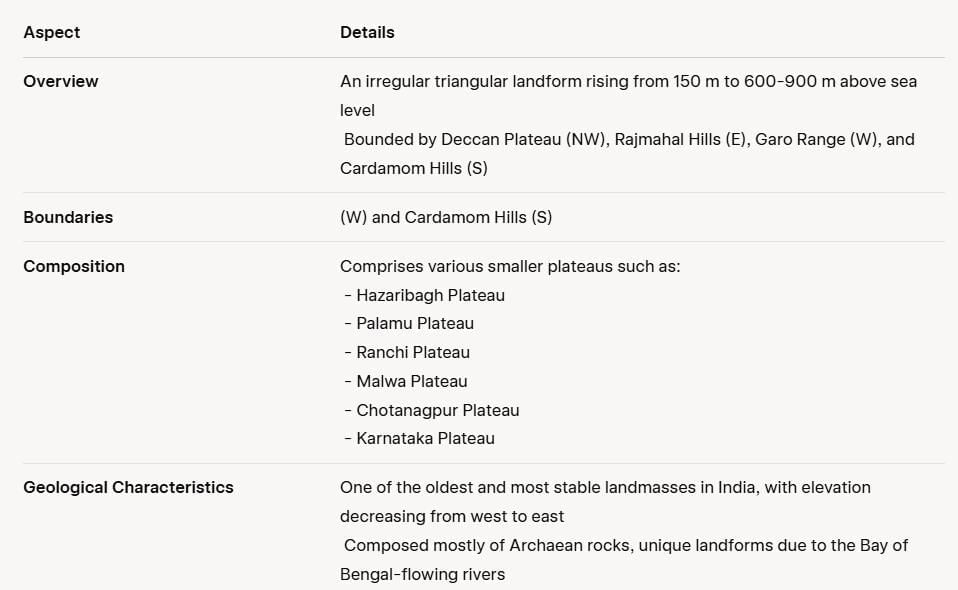
 The Structure and Physiology of the Peninsular Plateau
The Structure and Physiology of the Peninsular Plateau
The Deccan Plateau
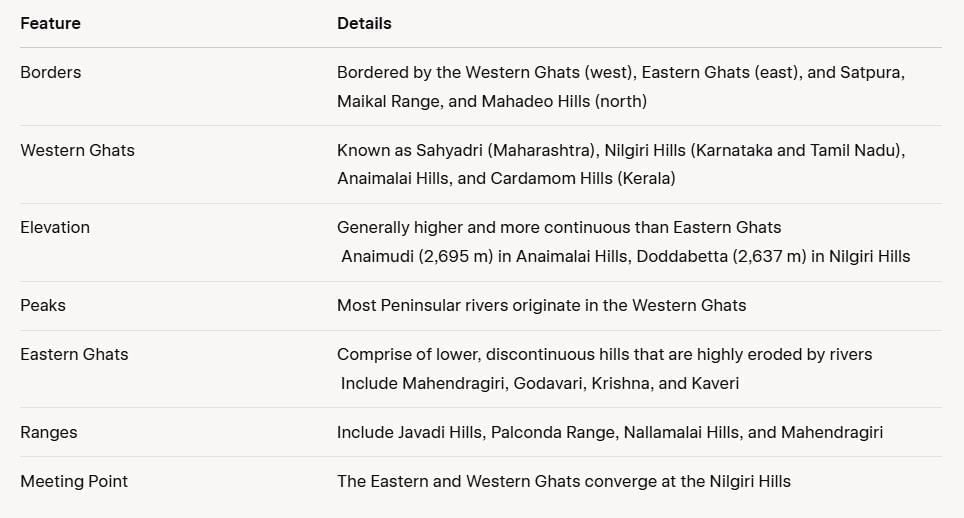
The Central Highlands
- The region is bounded to the west by the Aravali Range.
- The SATPURA Range consists of scarped plateaus at elevations ranging from 600-900 m above sea level, marking the northern boundary of the Deccan Plateau.
- This range is a classic example of relict mountains, characterised by significant erosion and discontinuous formations.
- The Peninsular Plateau extends to Jaisalmer in the west, where it features longitudinal sand ridges and crescent-shaped sand dunes known as barchans.
- The area has experienced metamorphic processes, indicated by the presence of metamorphic rocks such as marble, slate, and gneiss.
- The Central Highlands have an elevation between 700-1,000 m above sea level and slope towards the north and northeast.
- Most tributaries of the Yamuna River originate in the Vindhyan and Kaimur Ranges.
- The Banas River is the only significant tributary of the Chambal River that starts from the Aravali in the west.
- The Rajmahal Hills form an eastern extension of the Central Highlands, with a significant reserve of minerals located in the Chotanagpur Plateau.
The Northeastern Plateau
- The Meghalaya Plateau is an extension of the main Peninsular Plateau.
- A significant fault was created between the Rajmahal Hills and the Meghalaya Plateau due to the northeastward movement of the Indian plate during the Himalayan formation.
- This fault was later filled with sediment from various rivers.
- Currently, the Meghalaya and Karbi Anglong Plateaus are separated from the main Peninsular Block.
- The Meghalaya Plateau is subdivided into three regions: Garo Hills, Khasi Hills, and Jaintia Hills.
- These hills are named after the tribal groups that inhabit the area.
- An extension of the Meghalaya Plateau is found in the Karbi Anglong Hills of Assam.
- Similar to the Chotanagpur Plateau, the Meghalaya Plateau is rich in minerals, including coal, iron ore, sillimanite, limestone, and uranium.
- This region receives heavy rainfall from the southwest monsoon, leading to a highly eroded surface.
- Cherrapunji features a rocky terrain with little to no permanent vegetation cover.
The Indian Desert
- The Great Indian Desert is located northwest of the Aravali Hills.
- Characterised by undulating terrain, it features longitudinal dunes and barchans.
- Receives low annual rainfall, below 150 mm, resulting in an arid climate and minimal vegetation cover.
- Due to these characteristics, it is also referred to as Marusthali.
- Geological evidence indicates that this region was underwater during the Mesozoic era, supported by findings at the Aakal Fossil Park and marine deposits near Brahmsar (wood fossils are approximately 180 million years old).
- While the desert's underlying rock structure is an extension of the Peninsular Plateau, extreme aridity has shaped its surface through physical weathering and wind action.
 The Indian desert
The Indian desert
- Notable desert features include mushroom rocks, shifting dunes, and oases (mainly in the southern region).
- The desert can be divided based on orientation: the northern part slopes towards Sindh, and the southern part towards the Rann of Kachchh.
- Most rivers in this area are ephemeral, with the Luni River being significant in the southern desert.
- The region experiences low precipitation and high evaporation, leading to water scarcity.
- Some streams disappear after a short distance, creating typical cases of inland drainage as they flow into lakes or playas.
- The lakes and playas contain brackish water, which serves as the main source for salt extraction.
The Coastal Plains
India has an extensive coastline, which can be divided into two main types based on location and geomorphological processes:
- Western Coastal Plains
- Eastern Coastal Plains
(i) Western Coastal Plains
- This area is an example of a submerged coast.
- The city of Dwaraka, once part of the mainland, is now underwater.
- The western coast is narrow and ideal for ports and harbours.
Important Ports:
1. Kandla
2. Mazagaon
3. JLN Port Navha Sheva
4. Marmagao
5. Mangalore
6. CochinGeographical Divisions:
1. Kachchh and Kathiawar coast (Gujarat)
2. Konkan coast (Maharashtra)
3. Goan coast (Goa)
4. Malabar coast (Karnataka and Kerala)The plains are narrow in the middle and wider towards the north and south.
Rivers here do not create deltas.
Known for 'Kayals' (backwaters) used for fishing, navigation, and tourism. The famous Nehru Trophy Vallamkali (boat race) occurs in Punnamada Kayal, Kerala.
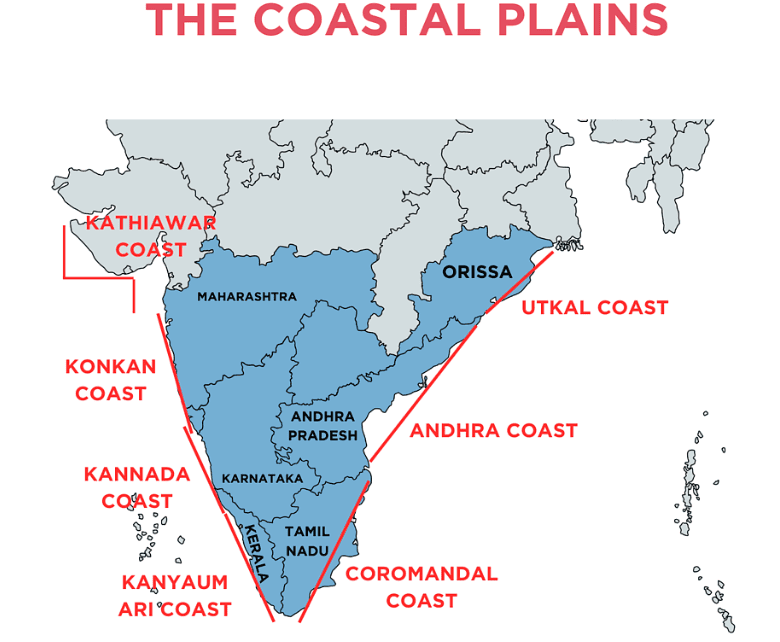
(ii) Eastern Coastal Plains
- Broader than the western coastal plains, classified as an emergent coast. Well-developed deltas formed by eastward-flowing rivers into the Bay of Bengal.
- Major Deltas are the Mahanadi, the Godavari, the Krishna, and the Kaveri.
- Due to its emergent nature, fewer ports and harbours compared to the West. The continental shelf extends up to 500 km, complicating port development.
- Notable ports along the eastern coast include Chennai, Visakhapatnam, Kolkata and Paradip.
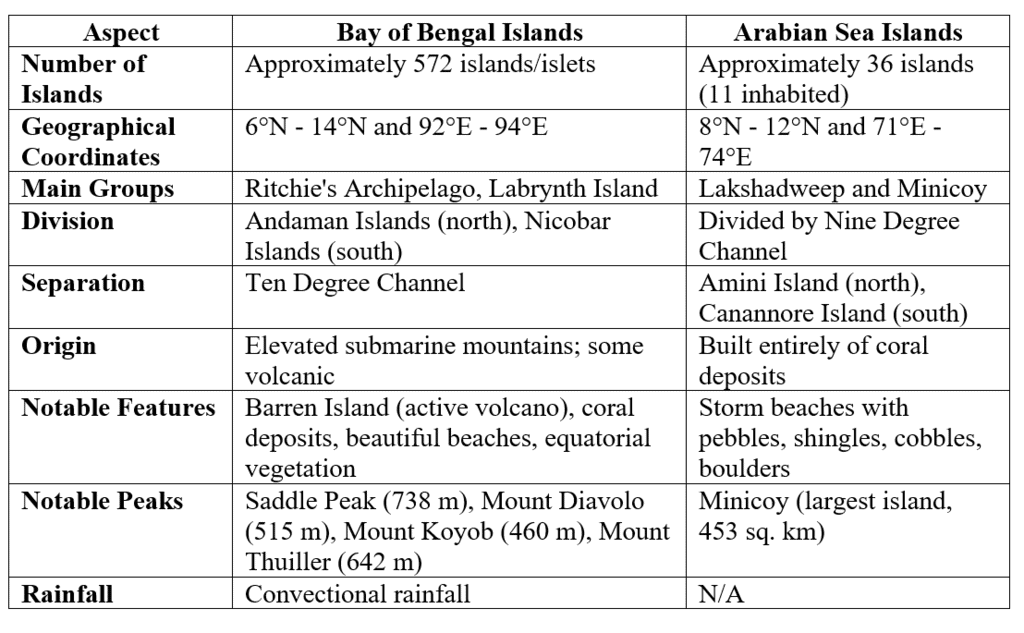
The Islands
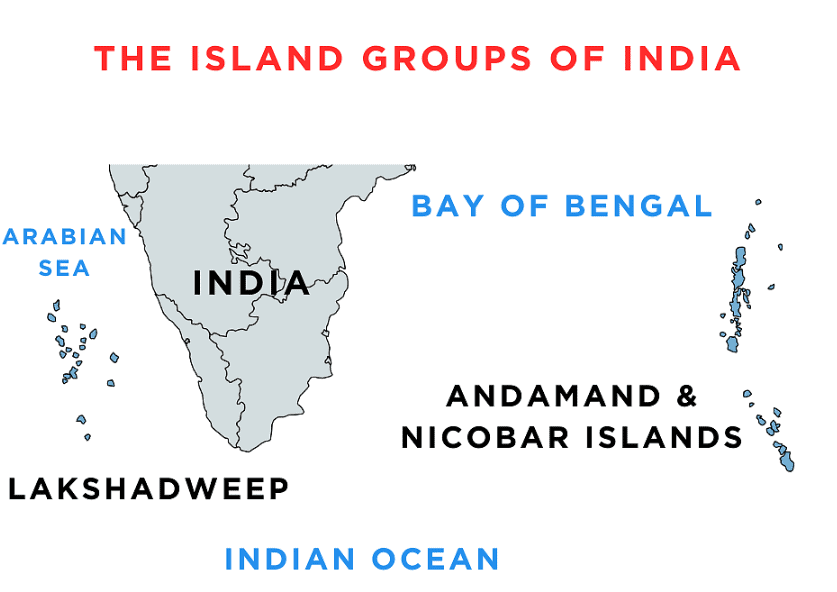
India has two significant island groups:
- Bay of Bengal Islands
- Arabian Sea Islands

|
70 videos|289 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Structure & Physiography Class 11 Geography
| 1. What are the major geological features of the Peninsular Block? |  |
| 2. How does the physiography of the Peninsular Block differ from that of the Himalayas? |  |
| 3. What are the main rivers originating from the Peninsular Block? |  |
| 4. What role does the Peninsular Block play in India’s climate? |  |
| 5. Why is the Peninsular Block considered a stable landform? |  |






















