Subordinate Courts in India - Indian Polity | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
INTRODUCTION
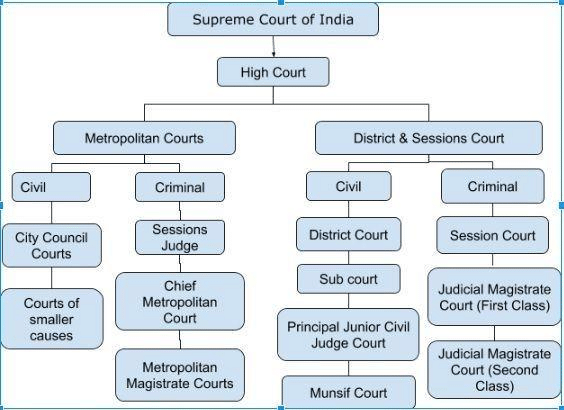
- These function below the high court’s at district or lower levels.
- In each district of India there are various types of Subordinate or lower Courts.
- The Structure and functions of Subordinate Courts are more or less uniform throughout the Country.
- Designations of courts Connote their functions. They are civil courts, Criminal Courts and revenue Courts.
Constitutional Provisions
The Articles 233 to 237 in the Constitution describe the provisions to regulate the organization of Subordinate Courts and to ensure their independence from the Executive.
Appointment of District Judges
- Appointments of District Judges in any State shall be made by the Governor of the State in consultation with the High Court exercising jurisdiction in relation to such State.
- A person not already in the service of the Union or of the State shall only be eligible to be appointed a District Judge if he has been for not less than seven years an advocate or a pleader and is recommended by the High Court for appointment.
Appointment of Other Judges
Appointment of other Judges (other than district judges) to the judicial service of a state is to be made by the Governor of the State after consultation with the State Public Service Commission and the High Court.
Control over Subordinate Courts
- The control over district courts and courts subordinate including the posting and promotion of, and the grant of leave to persons belonging to the judicial service of a State and holding any post inferior to the post of district judge shall be vested in the High Court,
- But nothing shall be construed as taking away from such persons any right of appeal which he may have under the law regulating the conditions of his service.
Interpretation
- The District Judge is the representative of the High Court in the District. He administers works distribution in the Subordinate Courts in the District. His is the most important post of the District.
- The subordinate courts covering the civil cases, in this aspect are considered as Junior Civil Judge Court, Principal Junior and Senior Civil Judge Court, which are also known as Sub Courts, Subordinate Courts.All these courts are treated with ascending orders.
- The subordinate courts covering the criminal cases are Second Class Judicial Magistrate Court, First Class Judicial Magistrate Court, and Chief Judicial Magistrate Court along with family courts which are founded to deal with the issues related to disputes of matrimonial issues only. The status of Principal Judge of family court is at par with the District Judge
1. Article 309 of the Constitution which occurs in chapter 1 of Part XIV deals with the recruitment and conditions of service of persons serving the Union or a State.
2. It empowers the appropriate Legislature to regulate the recruitment and conditions of service of persons appointed to public services and post in connection with the affairs of the Union or of any State.
3. The provision however says that until the appropriate Legislature shall make the rules, it shall be open to the President, in the case of services under the Union, and to the Governor, in respect of the services under the State, to make rules for the said purpose. Article 310, which incorporates pleasure clauses, is not relevant for the present purpose.
NATIONAL LEGAL SERVICES AUTHORITY

Article 39A of the Indian Constitution contains provisions for free legal aid to the weaker and poor sections of the society in order to ensure justice for all.
Also, Articles 14 and 22(1) of the Constitution make it obligatory for the State to ensure equality before law and a legal system which promotes justice on the basis of equal opportunity to all.
Therefore, the National Legal Services Authority (NALSA) was constituted under the Legal Services Authority Act, 1987 for the provision of free legal services to the weaker sections of the society (defined under section 12 of the Act) and to organize Lok Adalats for speedy and amicable resolution of cases, in 1995.
NALSA is also involved in monitoring & evaluating the implementation of legal aid programmes and laying down principles & policies for making legal services available under the Act.
To give effect to the directions of NALSA, State Legal Services Authority in every state, High Court Legal Services Authority in every High Court, Taluk Legal Services Authority in most of the Taluks and District Legal Services Authority in most of the Districts have been constituted.
Supreme Court Legal Services Authority has been constituted to implement and administer the legal services programme insofar as it relates to the Supreme Court.
NALSA lays down guidelines, principles, policies and is involved in framing effective and economical schemes for the State Legal Services Authorities to execute the Legal Services Programmes throughout the country. Primarily, all these authorities have been constituted to discharge the following functions regularly:
- Provision of free and competent legal services to eligible persons.
- Organization of Lok Adalats for speedy resolution of cases in an amicable manner.
- Organization of legal awareness camps in rural areas.
LOK ADALATS
 LOK ADALATS IN INDIA
LOK ADALATS IN INDIA
- The concept of Lok Adalat (People’s Court) is an innovative Indian contribution to the world jurisprudence. The introduction of Lok Adalats added a new chapter to the justice dispensation system of this country and succeeded in providing a supplementary forum to the victims for a satisfactory settlement of their disputes. This system is based on Gandhian principles.
- It is one of the components of ADR (Alternative Dispute Resolution) systems. In ancient times, the disputes were referred to “Panchayats”, which were established at the village level. Panchayats resolved the disputes through arbitration. It has proved to be a very effective alternative to litigation.
- This concept of the settlement of disputes through mediation, negotiation or arbitration is conceptualized and institutionalized in the philosophy of Lok Adalat. It involves people who are directly or indirectly affected by dispute resolution.
Origin of Lok Adalats
- The concept of Lok Adalats was pushed back into oblivion in last few centuries before independence and particularly during the British regime. Now, this concept has, once again, been rejuvenated. It has become very popular and familiar amongst litigants.
- This is the system, which has deep roots in Indian legal history and its close allegiance to the culture and perception of justice in Indian ethos. Experience has shown that it is one of the very efficient and important ADR mechanisms and most suited to the Indian environment, culture and societal interests.
- Camps of Lok Adalats were started initially in Gujarat in March 1982 and now it has been extended throughout the Country.
- The evolution of this movement was a part of the strategy to relieve heavy burden on the Courts with pending cases and to give relief to the litigants. The first Lok Adalat was held on March 14, 1982 at Junagarh in Gujarat.
Maharashtra commenced the Lok Nyayalaya in 1984.
- The advent of Legal Services Authorities Act, 1987 gave a statutory status to Lok Adalats, pursuant to the constitutional mandate in Article 39-A of the Constitution of India. It contains various provisions for settlement of disputes through Lok Adalat.
- This Act mandates constitution of legal services authorities to provide free and competent legal services to the weaker sections of the society and to ensure that opportunities for securing justice are not denied to any citizen by reason of economic or other disabilities.
- It also mandates organization of Lok Adalats to secure that the operation of the legal system promotes justice on the basis of equal opportunity. When statutory recognition had been given to Lok Adalat, it was specifically provided that the award passed by the Lok Adalat formulating the terms of compromise will have the force of decree of a court, which can be executed as a civil court decree.
- The evolution of movement called Lok Adalat was a part of the strategy to relieve heavy burden on the Courts with pending cases and to give relief to the litigants who were in a queue to get justice. It contains various provisions for settlement of disputes through Lok Adalat.
The parties are not allowed to be represented by the lawyers and encouraged to interact with judge who helps in arriving at amicable settlement. No fee is paid by the parties. Strict rule of Civil Procedural Court and evidence is not applied. Decision is by informal sitting and binding on the parties and no appeal lies against the order of the Lok Adalat.
Permanent Lok Adalats
In 2002, the Parliament brought about certain amendments to the Legal Services Authorities Act, 1987 to institutionalize the Lok Adalats by making them a permanent body to settle the disputes related to public utility services. The Central or State Authorities may, by notification, establish Permanent Lok Adalats at any Permanent Lok Adalats, for determining issues in connection to Public Utility Services.
Public Services include:
- Transport service
- Postal, telegraph or telephone services
- Supply of power, light and water to public
- System of public conservancy or sanitation
- Insurance services and such other services as notified by the Central or State Governments
Permanent Lok Adalats have the same powers that are vested in the Lok Adalats.
Jurisdiction of Lok Adalats
A Lok Adalat shall have jurisdiction to determine and to arrive at a compromise or settlement between the parties to a dispute in respect of:
- any case pending before; or
- any matter which is falling within the jurisdiction of, and is not brought before, any court for which the Lok Adalat is organized.
The Lok Adalat can compromise and settle even criminal cases, which are compoundable under the relevant laws.
Lok Adalats have the competence to deal with a number of cases like:
- Compoundable civil, revenue and criminal cases
- Motor accident compensation claims cases
- Partition Claims
- Damages Cases
- Matrimonial and family disputes
- Mutation of lands case
- Land Pattas cases
- Bonded Labour cases
- Land acquisition disputes
- Bank’s unpaid loan cases
- Arrears of retirement benefits cases
- Family Court cases
- Cases, which are not subjudiced
Powers of Lok Adalats
- The Lok Adalat shall have the powers of a civil court under the Code of Civil Procedure
- 1908, while trying a suit, in respect of the following matters:
- Power to summon and enforce the attendance of any witness and to examine him/her on oath.
- Power to enforce the discovery and production of any document.
- Power to receive evidence on affidavits,
- Power for requisitioning of any public record or document or copy thereof or from any court.
- Such other matters as may be prescribed
- Every Lok Adalat shall have the power to specify its own procedure for the determination of any dispute coming before it.
- All proceedings before a Lok Adalat shall be deemed to be judicial proceedings within the meaning of Sections 193, 219 and 228 of IPC.
- Every Lok Adalat shall be deemed to be a Civil Court for the purpose of Sec 195 and Chapter XXVI of Cr.P.C.
Advantages of Lok Adalats
- Speedy Justice
- Economical
- Unburdening of Courts and thus reducing the backlog of cases.
- Maintenance of Cordial Relations (since the main thrust is on compromise and not punishment.
|
142 videos|780 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on Subordinate Courts in India - Indian Polity - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are subordinate courts in India? |  |
| 2. What is the role of subordinate courts in the Indian legal system? |  |
| 3. How are judges appointed in subordinate courts in India? |  |
| 4. What is the hierarchy of subordinate courts in India? |  |
| 5. Can the decisions of subordinate courts be appealed? |  |
















