Teeth: Alimentary Canal | Additional Study Material for NEET PDF Download
Teeth
- Teeth are ectomesodermal in origin. Major portion of teeth arises from Dermis. Part of tooth present outside the gums only is derived from ectoderm or Epidermis (Enamel part).
- In human teeth of upper jaw are attached to the maxilla bone. While teeth of lower jaw are attached to Mandible bone. But in rabbit upper incisors are attached to premaxilla. While upper pre molars and molars attached to the maxilla bone. While lower teeth are attached to dentary bone.
➢ Structure of Teeth
There are three parts of the tooth. These are:
1. Crown: It is the outer part of the tooth, exposed outside gums.
2. Neck: It is the middle part of the tooth which is embedded inside the gums.
3. Root: It is the part of tooth that is inserted inside the socket of jaw bone. (Alveoli)
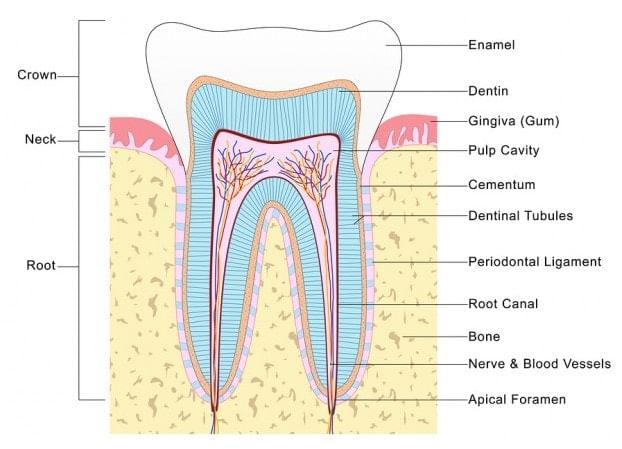 Structure of Tooth
Structure of Tooth
- The crown part of the tooth is made up of a very hard substance called Enamel. It is the hardest material in animal kingdom.
- Enamel is ectodermal. It is secreted by Ameloblast cells of the ectoderm. It has maximum amount of inorganic salt (96%) in it, Inorganic salt are mainly found in the form of phosphate and carbonate of Ca, Mg, Na and K. 3% of water is found in the enamel. Along with the keratin & ossein protein (1%) are also found in teeth. Ossein is a protein of bones. Remaining part of tooth develops from mesoderm of embryo.
- Dentine is the main part of tooth. Approximately 69% inorganic salts are present in dentine and 65% are present in cement. (62% inorganic salts are present in bones.)
- Dentine surrounds a cavity called pulp-cavity. This cavity contains soft connective tissue, blood capillaries, nerve fibres. Pulp cavity is necessary for the nutrition and survival of the teeth. At the base of pulp-cavity an aperture is present. Through this aperture, blood capillaries and nerve fibres enter inside the teeth. This aperture is called apical-foramen.
- A special type of cells form the lining of the pulp-cavity called the Odontoblast cells. These cells are the dentine secreting cells. Cytoplasmic process of odontoblasts are embedded into dentine in the form of fine tubule. These processes are called canaliculi. These canaliculi secretes dentine. The teeth continue to grow till the odontoblast cells remain active. In adults, the pulp-cavity shrinks and the odontoblasts become inactive so the teeth stop growing. The cement layer is made up of the cementocytes cells. Between the root and the bones of the teeth a periodontal membrane is present.
- In Rabbit and rat the pulp-cavity of the incisor remains wide throughout their life, so these teeth grow continuously throughout their life span.
- If one incisor of Rabbit & rat is broken then the opposite incisor grows continuously, finally the animal can neither close the mouth nor gnaw the food. So the animal dies due to starving.
➢ Types of Teeth Found in Mammals
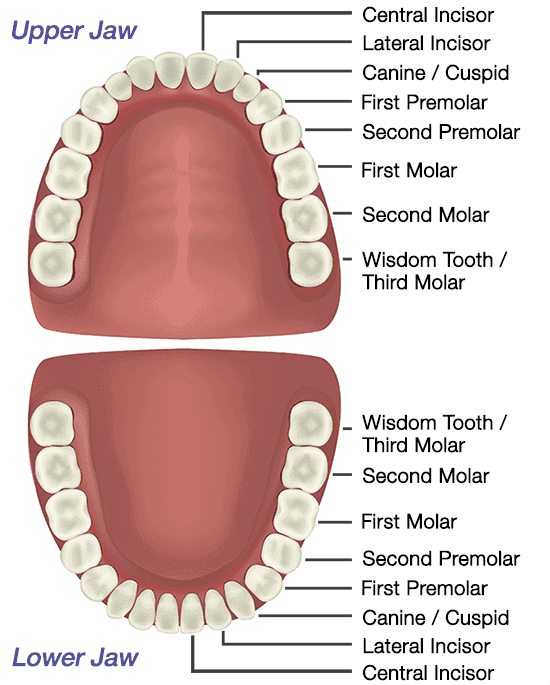 Tooth Chart
Tooth Chart
1. Incisor: These are long, chisel-like teeth for gnawing the food. They are more developed in gnawing animals.
Example: lagomorphs, rodents, tusk of elephant are modification of upper Incisor. Tusk is used to protect from enemies, attack on enemies (not for feeding purpose)
2. Canines: These are sharp-pointed teeth meant for tearing the food. Canines are most developed in carnivorous animals. canines are absent in herbivorous animals.
Example: Rabbits do not have canines. In herbivorous, the space of canine in gums is empty and this empty space is called diastema.
3. Pre Molar: These teeth are meant for chewing and crushing of food, they are triangular in shape.
4. Molars (Cheek teeth): These also meant for chewing & crushing of food. They are rectangular in shape. Premolar and molar help in the mastication of food. In human teeth of upper jaw are attached to the maxilla bone. While teeth of lower jaw are attached to the mandible bone.
- In mammals, except Premolar and Last molar, all type of teeth appear twice in life. Teeth which appear during childhood are called milk teeth or temporary teeth. Due to the activity of osteoclast cells. These milk teeth are shed, off then permanent teeth appear.
- When temporary molars shed, their socket are filled by premolar and new socket are formed for permanent molar. This occurs once in lifetime.
- In frog, only upper jaw has teeth.
- In Rabbit teeth of upper jaw are attached to the pre maxilla and maxilla bone, while teeth of lower jaw are attached to the dentry bone. Hippocampus, tortoise and birds do not have teeth.
➢ Difference Between Milk Teeth and Permanent Teeth
- There will two phases of dentition in ones life. i.e., primary dentition (milk teeth or deciduous teeth) and secondary dentition (permanent teeth). The permanent teeth are visible throughout a person’s lifetime. The baby teeth continue to grow till a child is about 11 years old, after that milk teeth fall and give rise to permanent teeth.
Differences are:
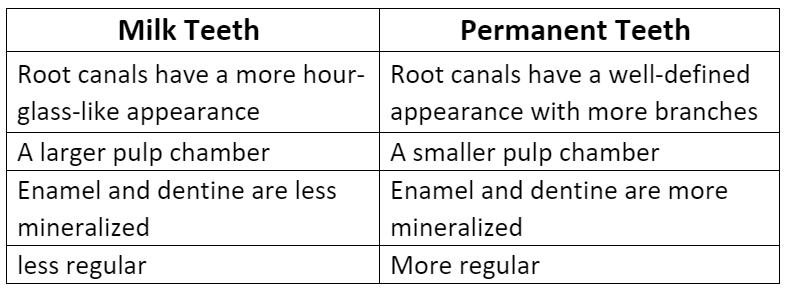
Types Of Teeth
➢ On the Basis of Appearance in Life
- Monophyodont: The teeth which appear only once in life.
Example: Pre Molar & Last molar of man. - Diphyodont: The teeth which appear twice in life.
Example: Incisors, Canines, Molars of human. - Polyphyodont: The teeth which appear more than twice in life.
Example: Fish, Amphibians.
➢ On the Basis of Position From Jaw
- Thecodont: The teeth which are present in bony socket of jaw.
Example: Man & crocodile. - Pleurodont: The teeth which are present on the lateral side of jaw bone.
Example: Reptiles. - Acrodont: The teeth which are present on the terminal part of Jaw bone.
Example: Fish, amphibian.
➢ On the Basis of Structure and Function
- Heterodont: When the teeth are of different type in mammals on the basis of structure and function.
Example: Mammal. - Homodont: Whether all teeth are of similar type in animal on the basis of structures and function.
Example: Fish, Amphibians.
➢ On the Basis of Crown
1. Secodont
- These are canine teeth of carnivorous animals.
- In this type of structure canine teeth become long and pointed which, is bended towards the backward direction.
2. Hypsodont (Smiling teeth)
- In this type of teeth the crown part is large root is either absent or small such as incisor and canine.
- These teeth are also called as smiling teeth.
3. Brachyodont (Cheek teeth)
- In this type of teeth crown part is small root is long such as premolar and molar.
- Wisdom teeth: These are the last molar teeth of humans which appear in the age of 18 to 25 year.
- The upper surface of premolar & molar is board. Some small projections are present in the upper surface of premolar and molar. These projection are called Lophs or cusps.
➢ On the Basis of Structure of Lophs
- Lophodont: In this type of teeth the lophs are large, wide and flat such as rabbit & elephant.
- Bunodont: In this type of teeth. Lophs are small and spherical in shape, such as human.
- Solenodont: In this type of teeth the lophs are large and semilunar shape.
Example: Ruminant animals (Cow, Buffalo). - Carnesial: in this type of teeth the lophs are long & pointed.
Example: Carnivorous Animal.
Note : In humans, premolar teeth appear in the alveoli of molar teeth while permanent molar teeth are developed in new alveoli.
Carnessialteeth are modified last premolar of upper jaw and first molar of lower jaw, for shearing and tearing of tendon.
Dental Formula


In humans, premolar teeth appear in the alveoli of molar teeth while permanent molar teeth are developed in new alveoli.
|
26 videos|287 docs|64 tests
|
FAQs on Teeth: Alimentary Canal - Additional Study Material for NEET
| 1. What are the different types of teeth in the human mouth? |  |
| 2. What is the dental formula and how is it used? |  |
| 3. What is the function of incisors in teeth? |  |
| 4. How do molars differ from other types of teeth? |  |
| 5. Why are canines called "eye teeth"? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|


















