The Big Bang Theory | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
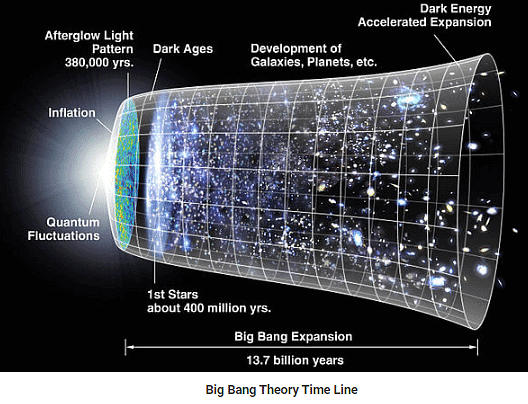
The Big Bang Theory is a scientific model that explains the origin of the universe. It proposes that approximately 13.7 billion years ago, all matter and energy in the cosmos were concentrated into an incredibly small, dense point, much smaller than an atom. At this moment, there was no existence of matter, energy, space, or time. Suddenly, a massive explosion occurred, leading to the rapid expansion of the universe, during which matter, energy, space, and time were created. This expansion allowed matter to come together and form gas clouds, stars, and planets.
The Pre-Big Bang Phase
The conditions of the universe just before the Big Bang are not fully understood by scientists. The prevailing theory known as the "inflationary universe" model suggests that all of space was filled with an intensely concentrated and unstable form of energy. At the instant of the Big Bang, this energy transformed into particles of matter. However, the exact mechanism of how space and time came into existence in the first place remains a mystery.
The First Few Minutes to Next Thousand Years
Following the initial expansion, the universe gradually cooled down, allowing the formation of subatomic particles, such as photons, electrons, protons, and neutrons. In the first three minutes after the Big Bang, simple atomic nuclei were created. However, it took thousands of years for the first electrically neutral atoms to form. The vast majority of atoms produced during the Big Bang were hydrogen, accompanied by helium and traces of lithium.
The Importance of Hydrogen
One crucial aspect of the Big Bang is that if the universe had remained hot and dense for much longer, the hydrogen would have transformed into other chemical elements through nuclear fusion processes. This outcome would have had a significant impact on the existence of life as we know it. Hydrogen is a primary building block for water, and without it, there would be no water, which is vital for life's sustenance.
The Future of the Universe
Some scientists believe that the expansion of the universe is finite and will eventually slow down, leading to a contraction phase known as the "Big Crunch." During this phase, the universe will collapse back in on itself. The Big Crunch would have significant implications for the fate of the cosmos, but its occurrence is still a subject of scientific debate and research.
Evolution of the Universe: From Opaque to Transparent & The Mystery of Dark Energy and Inflation
The early Universe underwent significant transformations, resulting in the transition from an opaque state to a transparent one. This transition allowed us to observe the Cosmic Background Radiation, the afterglow of the Big Bang. Additionally, the Universe's expansion was expected to slow down due to the gravitational pull of matter, but observations revealed an unexpected acceleration attributed to a mysterious force known as dark energy. To address cosmological problems like the homogeneity of the Universe, scientists proposed the concept of inflation, a rapid expansion phase shortly after the Big Bang.
Earlier Opaque Universe vs Later Transparent Universe
Formation of Photons and Scattering:
- Photons (light) as elementary particles were generated shortly after the Big Bang.
- Early electrons scattered these photons, making the Universe opaque.
- The scattering was similar to sunlight scattering from water droplets in clouds.
Recombination and Transparency:
- As the Universe cooled, electrons combined with nuclei, forming neutral atoms (recombination).
- Recombination led to the absorption of free electrons, causing the Universe to become transparent.
- The afterglow of the Big Bang, Cosmic Background Radiation, is composed of these photons.
- Today, we can observe this radiation, giving us insights into the early Universe.
Dark Energy and the Acceleration of Universe's Expansion
Expectation of Slowing Expansion:
- It was assumed that the matter in the Universe would slow down the rate of its expansion.
- Mass creates gravity, which exerts a pull that was expected to decelerate the expansion.
Supernovae Observations:
- Surprisingly, supernovae observations indicated that the Universe's expansion is accelerating.
- Some unknown force, unlike regular matter or energy, is pushing galaxies apart.
- This force is referred to as dark energy, though its nature remains largely unknown.
Nature of Dark Energy:
- Dark energy could be a dynamic fluid not previously known to physics.
- Alternatively, it might be a property of the vacuum of empty space.
- Another possibility is that it involves some modification to general relativity.
Inflationary Model and the Question of Equilibrium
The Homogeneity Problem:
- The early Universe appeared to be too homogeneous, raising questions about how distant regions came to the same temperature.
- This lack of equilibrium posed a cosmological challenge.
The Proposal of Inflation:
- The inflationary model suggests a short period of rapid expansion shortly after the Big Bang.
- During inflation, the Universe experienced an incredible burst of expansion.
- The cause of inflation is attributed to an unknown form of unstable energy present at the time.
Uneven Distribution of Primordial Energy:
- The inflationary model predicts that the primordial energy was unevenly distributed in space due to quantum noise during the Universe's extremely small phase.
- This distribution pattern would have been transferred to the matter in the Universe, observable in the photons during recombination.
Proofs of the Big Bang: Understanding the Origin of the Universe
- Expanding Galaxies: Hubble's Revelation
Heading: Expanding Galaxies and the Hubble Observation
In 1929, the astronomer Edwin Hubble made a groundbreaking observation. He noticed that galaxies beyond our Milky Way were all moving away from us. Even more intriguing was the fact that their speed of movement was directly proportional to their distance from our galaxy. This realization led Hubble to a momentous conclusion: there must have been a time when the entire Universe was condensed into a single point in space. This epoch, now estimated to be about 14 billion years ago, marked the beginning of the Universe and came to be known as the "Big Bang." - Cosmic Background Radiation: Afterglow of the Big Bang
Heading: Cosmic Background Radiation - Traces of the Big Bang
The aftermath of the Big Bang left behind a distinct remnant known as cosmic background radiation. These are early photons, the faint echoes of the colossal explosion that started the Universe. Over time, these photons have continued to travel through space and can still be observed today, providing valuable insights into the early stages of the Universe.
Missions to Study the Big Bang
- Cosmic Background Explorer (COBE)
Heading: COBE Mission - Capturing the Universe's Baby Pictures
To unravel the mysteries of the cosmic background radiation, NASA launched the Cosmic Background Explorer (COBE) mission. This pioneering endeavor aimed to capture "baby pictures" of the Universe when it was merely 400,000 years old. By studying these ancient microwave radiation patterns, scientists gained crucial information about the Universe's early structure and composition. - Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP)
Heading: WMAP Mission - Enhanced Resolution of Cosmic Background Radiation
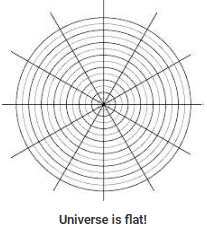
Building upon COBE's achievements, NASA's Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) embarked on a mission to examine the cosmic background radiation in even greater detail. With substantially improved resolution compared to its predecessor, WMAP scanned the entire celestial sphere, meticulously measuring temperature differences in the microwave radiation, which is almost uniformly dispersed throughout the Universe. The data gathered by WMAP revealed a detailed map of the sky, highlighting regions with varying temperatures. By combining this evidence with theoretical models, scientists deduced that the Universe possesses a "flat" geometry, adhering to the principles of Euclidean geometry on cosmological scales. - Planck Mission
Heading: Planck - Precision Mapping of Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
In 2009, the European Space Agency, in collaboration with NASA, launched the Planck mission. This mission aimed to create the most accurate maps of cosmic microwave background radiation to date. Armed with cutting-edge instruments capable of detecting minute temperature fluctuations on the order of a few millionths of a degree, Planck scanned the entire sky across nine wavelength bands. This meticulous survey enabled scientists to discern even finer details of the early Universe's temperature fluctuations, pushing the boundaries of astrophysical precision. - Continuing the Legacy: Telescopes Studying Universe's Expansion
Telescopes in the Modern Era
Hubble Space Telescope and Spitzer Space Telescope - Carrying on Hubble's Legacy
Present-day NASA spacecraft, such as the Hubble Space Telescope and the Spitzer Space Telescope, continue the work initiated by Edwin Hubble. These advanced telescopes play a pivotal role in measuring and monitoring the ongoing expansion of the Universe. Their observations provide essential data for refining cosmological models and deepening our understanding of the Universe's evolution.
The Big Bang Theory Explained in Layman's Terms
The Big Bang Theory is a scientific explanation for the origin of the universe. It suggests that the universe began as a state of high energy and has been expanding and cooling over billions of years. In simple terms, this theory describes how everything we see today, such as planets, stars, and galaxies, originated from a tiny, dense point.
- The Primordial Universe:
At the very beginning, the entire universe was filled with energy but no matter. This energy transformed into small particles called photons. Alongside photons, free electrons were also present during this early stage. - Scattering of Photons:
The photons present in the early universe were scattered by the free electrons, causing the universe to appear dark and opaque. This scattering was a significant obstacle to the transmission of light. - Formation of Atoms:
As the universe continued to expand and cool down, electrons combined with protons and neutrons, leading to the formation of atoms. In particular, hydrogen, the simplest and most abundant element, was formed during this process. - The Transparent Universe:
With the formation of atoms, the universe became transparent. This change occurred because the newly formed atoms did not have free electrons to scatter photons anymore. As a result, light could now travel freely through space. - Expansion and Cooling:
Even as the universe became transparent, it did not stop evolving. Some unknown form of energy, referred to as dark energy, continued to push the particles apart, causing the universe to expand at an accelerated rate. Simultaneously, the universe continued to cool down. - The Emergence of Structure:
As the universe cooled further, atoms began to combine and form molecules, which then combined to create more complex compounds. Over an extensive period, this process resulted in the formation of celestial structures such as planets, stars, and galaxies. - The Shape of the Universe:
Upon studying the universe, scientists have determined that its overall shape appears to be flat. This suggests that the expansion of the universe took place in a two-dimensional manner, analogous to an explosion occurring on a flat surface.
|
90 videos|491 docs|209 tests
|





















