The Individual Processes: Work Stress and Stress Management | NABARD Grade A & Grade B Preparation - Bank Exams PDF Download
Introduction
Stress is a universal aspect of human life, not confined to any particular culture but experienced in diverse forms and degrees. Each encounter with stress serves as a reminder that life's stability is never guaranteed, and unforeseen events can disrupt it. The concept of stress in organizations is pervasive, carrying significant practical and economic implications. It is often associated with elevated absenteeism rates.
Dr. Hans Selye
Dr. Hans Selye, in 1942, defined stress as the body's non-specific response to any demand placed on a person. Stress manifests as symptoms like headaches and backaches. Workplace stress occurs when an employee perceives challenges or threats in their work environment, leading to changes in their physical or mental state. There are four stress concepts: stimulus (focuses on situational conditions), response (centers on physiological reactions), transactional (considers individual reactions to stressors), and discrepancy (acknowledges that different situations can result in similar physiological responses affected by coping efforts).
- Dr. Hans Selye, in 1942, defined stress as the body's non-specific response to any demand placed on a person.
- Workplace stress occurs when an employee perceives challenges or threats in their work environment, leading to changes in their physical or mental state.
- There are four stress concepts: stimulus (focuses on situational conditions), response (centers on physiological reactions), transactional (considers individual reactions to stressors), and discrepancy (acknowledges that different situations can result in similar physiological responses affected by coping efforts).
- Stress symptoms may include headaches and backaches.
- The stimulus concept focuses on situational conditions or events that are perceived as stressful, like high time pressure or interpersonal conflicts at work.
- The response concept emphasizes physiological reactions as a crucial component of stress, but it doesn't consider the impact of coping efforts on an individual's reactions.
Understanding Stress in the Workplace: Key Concepts and Models
- Stress concepts can be categorized into those focusing on the situation and the individual.
- The transactional concept, introduced by Lazarus in 1966, suggests stress arises from interactions between individuals and their environment, involving perceptions, expectations, interpretations, and coping responses.
- The discrepancy concept views stress as a misalignment between an individual's desires and the environment (Edwards, 1992), but operationalizing this concept poses challenges.
- One influential stress model is Lazarus' transactional model, defining stress as a relationship between an individual and the environment appraised as taxing or exceeding resources and threatening well-being.
- According to the Cybernetic Model by Edwards (1992), stress is a mismatch between an employee's perceived and desired states, significant if considered important by the employee.
Factors that Trigger Workplace Stress
- Low Salaries: Inadequate pay causing financial strain.
- Excessive Workloads: Overwhelming amount of tasks and responsibilities.
- Limited Growth Opportunities: Few chances for career advancement.
- Unengaging Work: Monotonous or unchallenging tasks leading to boredom.
- Lack of Social Support: Insufficient camaraderie or assistance from colleagues.
- Lack of Control: Feeling powerless over job-related decisions.
- Conflicting Demands: Juggling conflicting tasks or unclear expectations.
Levels of Stress
- Acute Stress: Occurs due to sudden demands or pressures, leading to emotional and physical symptoms like anxiety, fatigue, and headaches.
- Episodic Stress: Repeated episodes of acute stress, often seen in individuals with chaotic or disorganized lifestyles.
- Chronic Stress: Persistent stress, linked to long-term issues like financial troubles or dysfunctional work environments.
Levels of Stress
- Episodic Stress:
- Definition: Regular and repeated experience of acute stress.
- Characteristics: Belligerence, low tolerance, impatience, and urgency.
- Similarities with Acute Stress: Emotional symptoms like anxiety, along with physical symptoms.
- Risks: Increased vulnerability to heart disease, chest pain, asthma, hypertension, and persistent headaches.
- Chronic Stress:
- Definition: Persistent stress due to long-standing stressors.
- Causes: Family issues, poverty, long-term illness, and job strain.
- Physiological Response: Follows a three-stage pattern described by Hans Selye.
- Interaction: Stress is an interaction between the individual and environmental demands.
- Perception and Response: Employee's response is linked to how they perceive and assess the stressor, available resources, and personal characteristics.
Factors Contributing to Workplace Stress
- Technological Changes:
- Impact: Evaluation of adaptation to a changing technological environment.
- Individual Capacity: Varies; some can improve skills, while others face challenges.
- Perceived Risk: Can cause stress when viewed as a threat to health.
- Health Effects of Chronic Work Stress:
- Physical Consequences: Unstable blood pressure, increased cholesterol, muscle tension, diabetes, hypertension, ulcers, headaches, substance abuse, and clinical depression.
- Cognitive Challenges: Difficulty concentrating and retaining information.
- Emotional Impact: Anxiety, anger, irritability, affecting interpersonal relationships.
- Workplace Consequences:
- Productivity: Decreases due to stress.
- Absenteeism: Increases in response to chronic stress.
- Workplace Dysfunction: Creates persistent patterns of dysfunction in the organization.
Causes and Consequences of Stress
Interpersonal Stressors in the Workplace
- Physical Violence:
- Effects: Severe suffering, mental health problems, anxiety, substance abuse, and depression.
- Gender Differences: Both men and women affected, but women may show more physical symptoms and unhealthy coping behaviors.
- Common Stressors Categories (Murphy, 1995):
- Job-related Factors:
- Source: Disagreement between employee and job demands.
- Transition: Challenging stress becomes distress when control is lost.
- Role in the Organization:
- Stressors: Role conflict, role ambiguity, and work intensification.
- Career Development:
- Impact: Stress when employees struggle with roles in their lives.
- Interpersonal Work Relationships:
- Challenge: Difficulty in understanding, reconciling, or performing various roles.
- Organizational Structure or Climate:
- Key Stressor: Lack of control over tasks, pace of work, and work schedule.
- Job-related Factors:
Overall Impact of Workplace Stress
- Mental Health Issues: Anxiety, substance abuse, depression.
- Gender Differences: Women more prone to physical symptoms and unhealthy coping.
- Job Stress Factors: Control, role conflict, ambiguity, and organizational structure contribute to stress.
Stress Management in the Workplace
- Awareness and Adaptation:
- Approach: Employees adapt to stress to the point of being unaware.
- Focus: Remove unnecessary stressors causing tension and burnout.
- Effective Stress Management:
- Strategy: Identify and eliminate root causes of stress.
- Consideration: Prioritize removing stressors over general stress fitness.
- Investigation and Change:
- Organization's Role: Investigate main stress causes in the workplace.
- Recommendation: Change corporate culture and reward systems to support work-life balance.
- Empowering Employees:
- Solution: Empower employees for more control over work and environment.
- Impact: Effective in eliminating workplace stressors.
- Role-Related Stressors:
- Mitigation: Match employees' capabilities with suitable positions.
- Focus Areas: Reduce noise, address safety risks to minimize stress.
- Workplace Bullying Prevention:
- Approach: Establish clear behavior guidelines and provide feedback.
- Outcome: Minimize workplace bullying and associated stress.
Overall Stress Management Approach
- Root Cause Elimination: Focus on removing main stressors.
- Empowerment: Give employees control for stress reduction.
- Role Matching: Align capabilities with job positions.
- Safety Improvement: Address noise and safety risks.
- Bullying Prevention: Establish guidelines and feedback mechanisms.
Figure: Stress management strategies
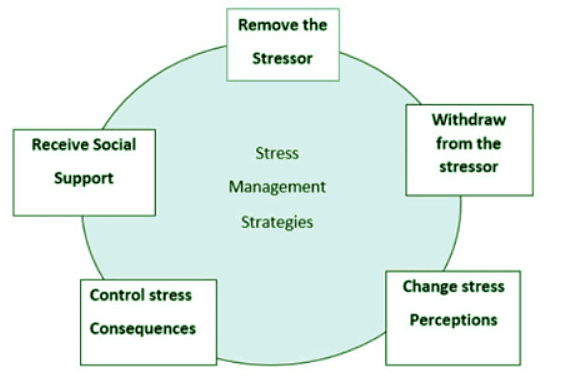
Manager's Role in Stress Reduction
- Changing Working Conditions:
- Objective: Create a more favorable environment for effective coping.
- Barrier Removal: Address issues like work overload, isolation, and lack of autonomy.
- Facilitating Employee Improvement:
- Manager's Role: Provide services like employee assistance programs.
- Purpose: Help employees work through issues hindering proper appraisal of situations.
- Skills Development: Introduce stress management resources, behavioral skills, and cognitive-behavioral interventions.
- Recognizing Stressful Relationships:
- Manager's Insight: Identify stressful relationships within the individual or group and work setting.
- Strategy: Develop a plan to reduce tension in those relationships.
Overall Stress Reduction Strategies
- Environment Optimization: Modify working conditions for better coping.
- Employee Support Services: Provide assistance programs and stress management resources.
- Skills Enhancement: Introduce behavioral and cognitive interventions for stress relief.
- Relationship Recognition: Identify and address stressful relationships for tension reduction.
Summary: Stress in the Workplace
- Definition: Stress is a natural response to threatening situations perceived by an individual at work or in life.
- Causes (Stressors): Environmental conditions, physical work settings, various life roles, interpersonal relationships, and organizational factors.
- Common Stressors: Conflicts between work and non-work obligations often contribute to stress.
- Health Consequences: Workplace stress can lead to significant psychological and physiological issues.
- Physical Disorders: Linked to ailments like heart disease, hypoadrenia, immunosuppression, and chronic pain.
- Psychological Impact: Includes depression, persistent anxiety, pessimism, and resentment.
Summary: Impact and Coping with Workplace Stress
- Organizational Impact:
- Symptoms lead to workplace antagonism, low morale, interpersonal conflict, increased expenses, decreased productivity, and higher absenteeism.
- Stress Management Strategies:
- Removing Stressors: Direct elimination of unnecessary stress factors.
- Changing Perception: Facilitating employees to alter their view of the environment, reducing its perceived stressfulness.
- Wellness Programs: Encouraging better physical health to build resilience against stress.
- Social Support: Providing emotional, informational, and material resources for coping with stress.
|
847 videos|1297 docs|420 tests
|
FAQs on The Individual Processes: Work Stress and Stress Management - NABARD Grade A & Grade B Preparation - Bank Exams
| 1. What is the definition of stress in the workplace? |  |
| 2. What are the key concepts and models used to understand stress in the workplace? |  |
| 3. What are the causes and consequences of stress in the workplace? |  |
| 4. How can stress be managed in the workplace? |  |
| 5. What role do managers play in stress reduction in the workplace? |  |
















