The Vedic Literature | General Awareness - Bank Exams PDF Download
The Vedas
The Vedas are the oldest sacred scriptures of Hinduism. In ancient times, the term "Veda" refers to "sacred spiritual knowledge" and comes from the Sanskrit word "Vid," which means "to know." The Vedas are collections of hymns and prayers dedicated to different gods and were seen as infallible texts that were originally passed down orally. Because they are considered divine revelations from God, they are classified as Apaurushaya, meaning they are not of human origin. The Vedas were so revered that they were memorized and known as 'Shruti,' which means "that which is heard," representing eternal truths revealed to humanity. In contrast, 'Smriti' means "that which is remembered" and refers to texts that are supplementary and can change over time. Vedas
Vedas
Types of Vedas
The Vedas are divided into four main collections, known as Samhitas, each serving a unique purpose:
Rig Veda
- Oldest religious text in the world
- A collection of hymns. Were recited at the time of sacrificial rites and other rituals with utmost devotion.
- Contains 1028 hymns (1017+11 valakhilyas) and is divided into 10 mandalas.
- The X mandala contains the famous Purushsukta which explains that the 4 varnas (Brahmans, kshatriya, vaishya andshudra) were born from the mouth, arms, thighs and feet of the creator, Brahma.
- The third mandala contains the Gayatri mantra (addressed to sun).
- Book Name: Book of Mantras
Sama Veda
- Derived from the root ‘Saman’, i.e, ‘melody’. It is a collection of melodies.
- It has 1603 verses but except 99 all the rest have been borrowed from Rig Veda.
- Contains ‘Dhrupada Raga’.]
- Book Name: Book of Mantras
Yajur Veda
- Deals with the procedure for the performance of sacrifices.
- Book Name: Book of Rituals
Atharva Veda
- Divided into 20 kadas (books) and has 711 hymns- mostly dealing with magic (along with personal problems of people).
- Book Name: Book of Spells
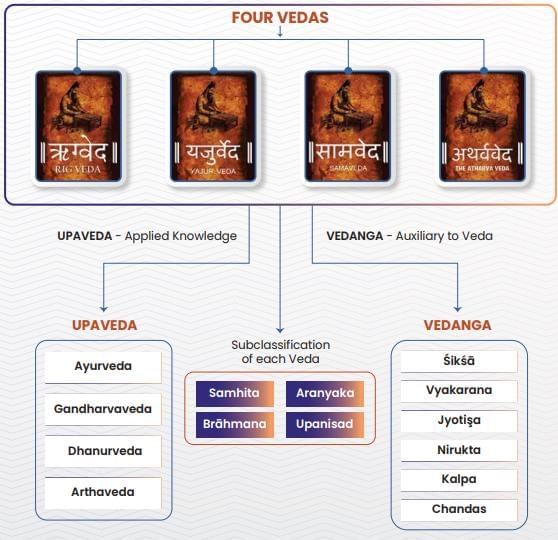
Parts of the Vedas
Each Veda is divided into four parts:
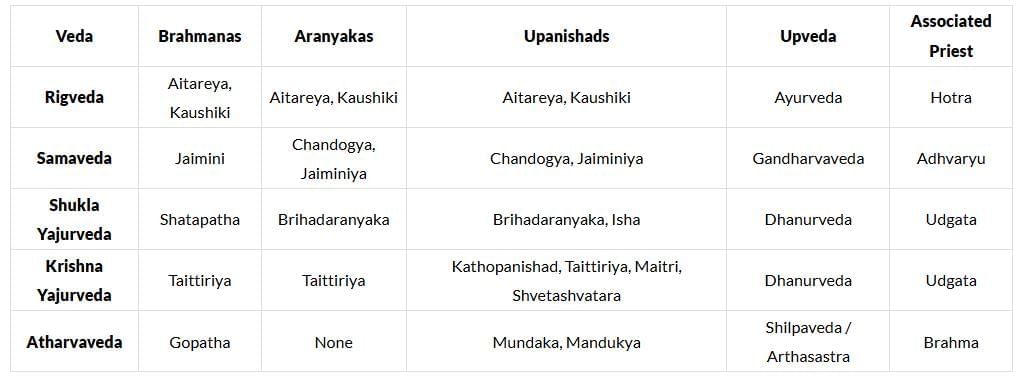
Brahmans
- They explain the hymns of the vedas in an orthodox manner.
- Each veda has several Brahmanas attached to it.
- Rigveda: kaushetki and Aitreya
- Yajurveda: Taitriya and Shatpatha
- Samaveda: Panchvish and Jemineya
- Atharvaveda: Gopath
Aranyakas
- Called ‘forest books’ , written mainly by the hermits living in the jungles for their pupils.
- Deals with mysticism and philosophy. Opposed to sacrifice and emphasize ‘meditation’.
Upanishads
- The word means ‘to sit down near someone’ and denotes a student sitting near his guru to learn.
- They are the main source of Indian philosophy.
- There are 108 Upanishads.
- They also condemn the ceremonies and the sacrifices.
Samhitas
Collections of holy songs dedicated to gods and goddesses.
Notable Texts and Concepts
Smritis
- Explains rules and regulations in the Vedic life.
- Main are manusmriti, naradsmriti, yagyavalkyasmriti
 Smritis
Smritis
Vedangas
- Six vedangas are Shiksya, Kalpa, Vyakarana, Nirukta, Chhanda and Jyotisha.
- Shiksha deals with pronunciation.
- Kalpa with rituals.
- Vyakarana with grammar.
- Nirukta with etymology.
- Chhanda with meter.
- Jyotisha with astronomy.
Darshans
There are 6 schools of indian philosophy known as Shad – Darshanas. These are given by 6 philosophers of Ancient India
- Nyaya ( Analysis) Darshana
- Vaishesika Darshana: Kanada Rishi
- Sankhaya Darshana : Kapila.
- Yoga Darshana : Patanjali.
- Purva Mimansa : Jaimini.
- Uttara Mimansa : Badaryana or Vyasa ( wrote mahabharata, classified Vedas, composed the puranas, gave vedantic philosophy).
Upavedas
There are four upavedas :
- Dhanurveda (deals with art and warfare) (Upaveda of Yajur Veda).
- Gandharva veda (deals with art and music) (Upaveda of Sama veda).
- Shilpa veda (deals with architecture) ( Upaveda of Atharva veda).
- Ayurveda (deals with medicine) ( Upaveda of Rig veda).
Epics
 Ramayana and Mahabharata
Ramayana and Mahabharata
- Though the two epics- the Mahabharata and the Ramayana- were compiled later, they reflect the state of affairs of the later vedic period.
- The Ramayana, attributed to Valmiki, is considered older than the Mahabharata and describes the period from the tenth century BC to the fourth cetury AD. Mahabharata, attributed to Vedvyas is also called Jaya Samhita and Satasahasri Samhita and has one lakh verses.
- The Ramayana, attributed to Valmiki, has 24,000 verses. Its composition started in the fifth century BC and passes through five stages; the fifth stage ended in the twelfth century AD.
|
365 videos|700 docs|149 tests
|
FAQs on The Vedic Literature - General Awareness - Bank Exams
| 1. What is Vedic literature? |  |
| 2. How many Vedas are there in Vedic literature? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the Vedic literature? |  |
| 4. Are the teachings of the Vedic literature still relevant today? |  |
| 5. How can one study and understand the Vedic literature? |  |

















