Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > The Wave Equation
The Wave Equation | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
The Wave Equation
- Wave speed is defined as:
- The distance covered by a wave within one second.
- Represented by the symbol ν and measured in meters per second (m/s).
- It signifies the rate at which energy is conveyed through a medium.
- Both transverse and longitudinal waves adhere to the wave equation.
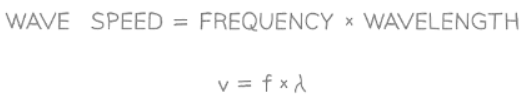
- Where:
- v = wave speed in meters per second (m/s)
- f = frequency in Hertz (Hz)
- λ = wavelength in meters (m)
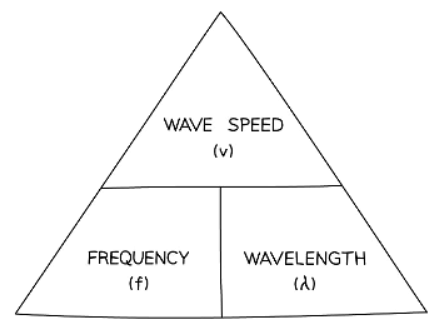
- The wave speed equation might require rearrangement, which can be facilitated using a formula triangle.
Question for The Wave EquationTry yourself: What does wave speed represent?View Solution
The document The Wave Equation | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
129 videos|148 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on The Wave Equation - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is the wave equation? |  |
Ans. The wave equation is a partial differential equation that describes how waves propagate over time and space. It is commonly used in physics and engineering to study wave phenomena like sound waves, light waves, and water waves.
| 2. What are the key components of the wave equation? |  |
Ans. The wave equation typically includes variables such as the wave function, time, position, velocity, and acceleration. These components are essential for describing the behavior of waves in different mediums.
| 3. How is the wave equation derived? |  |
Ans. The wave equation can be derived using the principles of wave mechanics, such as the conservation of energy and momentum. By applying these principles to a system with wave-like properties, one can derive the wave equation that governs its behavior.
| 4. What are some real-world applications of the wave equation? |  |
Ans. The wave equation is used in various fields, including acoustics for studying sound waves, optics for analyzing light waves, and seismology for understanding earthquake waves. It also has applications in telecommunications, medical imaging, and structural engineering.
| 5. How can the wave equation be solved numerically? |  |
Ans. The wave equation can be solved numerically using methods like finite difference, finite element, and spectral methods. These numerical techniques allow researchers to simulate wave propagation in complex systems and analyze the behavior of waves under different conditions.
Related Searches















