Theory & Procedure, Parallelogram Law of Vectors | Additional Study Material for NEET PDF Download
Objective
Our objective is to find the weight of a given body using the Parallelogram Law of Vectors.
Theory
What does the Parallelogram Law of Vectors state?
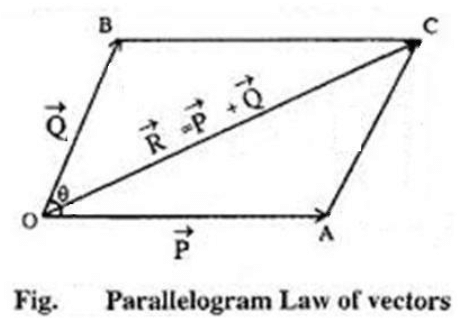
If two vectors acting simultaneously on a particle are represented in magnitude and direction by the two adjacent sides of a parallelogram drawn from a point, then their resultant is completely represented in magnitude and direction by the diagonal of that parallelogram drawn from that point.
Parallelogram Law of Vectors explained
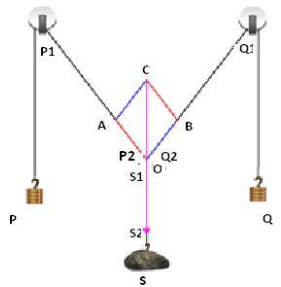
Let two vectors P and Q act simultaneously on a particle O at an angle . They are represented in magnitude and direction by the adjacent sides OA and OB of a parallelogram OACB drawn from a point O.Then the diagonal OC passing through O, will represent the resultant R in magnitude and direction.
On a Gravesand's apparatus, if the body of unknown weight (say S) is suspended from the middle hanger and balancing weights P and Q are suspended from othe two hangers then,
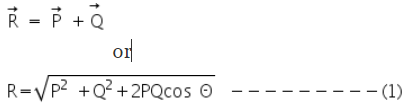
The unknown weight can be calculated from the equation (1).
On a Gravesand's apparatus, if the body of unknown weight (say S) is suspended from the middle hanger and balancing weights

P and Q are suspended from the other two hangers then,
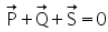
Now construct a parallelogram OACB by assuming a scale (say 1cm=50 gwt) corresponding to the weights P and Q. The diagonal of the parallelogram OC will give the resultant vector. The weight of the unknown body,
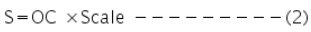
If W is the actual weight of the body, then the percentage error in the experiment can be calculated using the equation,
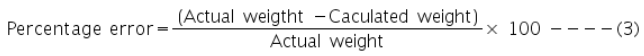

Learning Outcomes
- Students learn what is parallelogram law of vectors.
- They become familiar with the Gravesands apparatus.
- Students are able to find the unknown weight of an object using the parallelogram law of vectors.
Materials Required
- Parallelogram Law of Forces apparatus (Gravesand's apparatus)
- Plumb line
- Two hangers with slotted weights
- A body (a wooden block) whose weight is to be determined
- Thin strong thread
- White drawing paper sheet
- Drawing pins
- Mirror strip
- Sharp pencil
- Half meter scale
- Set squares
- Protractor
Real Lab Procedure
- Set up the Gravesand's apparatus and ensure its board is vertical. This can be tested using the plumb line. Test if the pulleys (let us name them - P1 and Q1) are frictionless. If you feel any friction, oil them.
- Fix the white drawing paper sheet to the board using the drawing pins.
- Take three pieces of strong threads and tie one end of all three together to make a knot. (Let us name this knotted end - O). This knot becomes the junction of the three threads.
- From the other ends of the two threads, tie a weight hanger with the same slotted weights in each; we will name these weights as P and Q.
- From the end of third thread tie the given body, which is the wooden block, which we will name as S.
- Pass the threads with weights P and Q over the pulleys and let the third thread with the block S, stay vertical in the middle of the board.
- The weights P, Q and the wooden block S acts as the three forces along the three threads. At the junction O, the forces are in equilibrium.
- Now adjust the weights P and Q (forces) such that the junction O stays in equilibrium slightly below the middle of the paper.
- See that all the weights hang freely and that none of them touch the board or the table.
- Mark the position of junction O on the paper using a sharp pencil.
- Slightly disturb the weights P and Q and then leave them.
- Once settled, note the position of junction O. Make sure that this point is very close to the earlier position.
- Take the mirror strip and keeping it lengthwise under each thread, mark the position of the ends of the image of the thread in the mirror, covering the image by the thread. These new positions are P1, P2 for the thread with the weight P, and Q1 and Q2 for the thread with the weight Q and S1, S2 for the thread with the weight S.
- Remove the paper from the board and with the help of the half metre scale draw lines through the points P1 and P2 to represent P, through points Q1 and Q2 to represent Q and through points S1 and S2 to represent S. These lines must meet at point O.
- Assuming a scale of 1cm = 50 g, mark OA = 3 cm and OB =3 cm to represent P=150g and Q= 150g.
- Complete parallelogram OACB using the set squares and join OC. This represents the resultant vector R which corresponds to the weight S.
- Measure OC and multiply it by the scale (50 g) to get the value of the unknown weight (S).
- For different sets of observation, change P and Q suitably.
- We can find the weight of the wooden block (R) using the equation (1).
- Take the mean of the two values to get the actual weight of the body.
- To find the percentage error in the experiment, measure the actual weight of the body using a spring balance.
- Calculate the percentage error using equation (3).
Simulator Procedure (as performed through the Online Labs)
- Click on any of the object to select it.
- You can change the hanging weights both on the right and left side, using the slider.
- Click on the show parallelogram button that gives you the parallelogram based on the weights on the left and right.
- Click on the show protractor button and measure the angle AOB using the protractor.
- Use the show scale button to use the scale to take the diagonal length of the parallelogram.
- Calculate the value of the unknown mass using equation (1) and the value of OD x 20gm using equation (2)and find its mean value.
- Enter the unknown weight (mean value) of the object in the text box provided to check your answer.
Observations
To find the actual weight of the unknown mass, W
Least count of spring balance = _________g
Zero error of spring balance = ________g
Weight of unknown body by spring balance = ________g
To find the weight of the unknown mass using parallelogram law of vectors
Scale. Let 50 g=1 cm
No:of obs | Forces | Valuesof | Slides | Resultant force R (g wt) | Unknown weight S (g wt) | Weight by spring balance (g wt) | Error | ||||
P (g wt) | Q (g wt) | 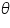 | cos  | OA (cm) | OB (cm) | OC (cm) | |||||
1 | |||||||||||
2 | |||||||||||
3 | |||||||||||
4 | |||||||||||
5 | |||||||||||
Calculation
Mean value of unknown weight S = ---------- gwt.
Mean value of unknown weight, R =---------gwt
Unknown weight = (S+R)/2 = ------------gwt= ---------------kgwt
Percentage error = ---------
Result
The unknown weight of given body = ------------------ kgwt .
The result shows the error is within limits of the experiment error.
|
26 videos|312 docs|64 tests
|
FAQs on Theory & Procedure, Parallelogram Law of Vectors - Additional Study Material for NEET
| 1. What is the Parallelogram Law of Vectors? |  |
| 2. How is the Parallelogram Law of Vectors derived? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the Parallelogram Law of Vectors? |  |
| 4. Can the Parallelogram Law of Vectors be applied to more than two vectors? |  |
| 5. Can the Parallelogram Law of Vectors be used to subtract vectors? |  |






















