Theory & Procedure, Verification of Ohm's Law | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Objective:
To verify the Ohm's law.
Statement of Ohm's Law:
Ohm’s law states that at a constant temperature, current 'I' through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the potential difference or voltage 'V', across the two points. That is,




Thus, the ratio V : I is a constant. This constant is called as the resistance (R) of the conductor.
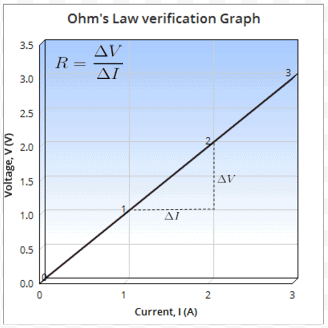
Graph:
After performing experiment for different readings of V & I and recording the observations, if we plot current on the x-axis of a graph and voltage on the y-axis of the graph, we will get a straight-line. The gradient of the straight-line graph is related to the resistance (R) of the conductor.
Related Theory:
Resistance:
- Resistance is the property of a component which restricts the flow of electric current. Energy is used up as the voltage across the component drives the current through it and this energy appears as heat in the component.
- Resistance is measured in ohms, the symbol for ohm is an omega(Ω).
Resistors connected in Series:
When resistors are connected in series their combined resistance is equal to sum of thier the individual resistances. For example if resistors R1 and R2 are connected in series their combined resistance, R, is given by:

Resistors connected in Parallel:
When resistors are connected in parallel their combined resistance is less than any of the individual resistances. Equation for the combined resistance R of 2 resistors R1and R2 connected in parallel is given by:
 OR
OR 
As performed in the real lab:
Material required :
A resistor of about 5 Ω, an ammeter ( 0 - 3 A), a voltmeter (0 - 10 V), four dry cells of 1.5 V each with a cell holder (or a battery eliminator), a plug key, connecting wires, and a piece of sand paper.
Precautions :
- All the electrical connections must be neat and tight.
- Voltmeter and Ammeter must be of proper range.
- The key should be inserted only while taking readings.
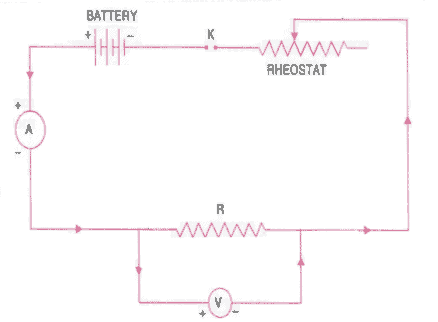
Circuit Diagram:
Procedure :
- Draw the circuit diagram as shown above.
- Arrange the apparatus as per the circuit diagram.
- Clean the ends of the connecting wires with sand paper and make them shiny.
- Make the connections as per circuit diagram. All connections must be neat and tight. Take care to connect the ammeter and voltmeter with their correct polarity. (+ve to +ve and -ve to -ve).
- Determine the zero error and least count of the ammeter and voltmeter and record them.
- Adjust the rheostat to pass a low current.
- Insert the key K and slide the rheostat contact to see whether the ammeter and voltmeter are showing deflections properly.
- Adjust the rheostat to get a small deflection in ammeter and voltmeter.
- Record the readings of the ammeter and voltmeter.
- Take atleast six sets of readings by adjusting the rheostat gradually.
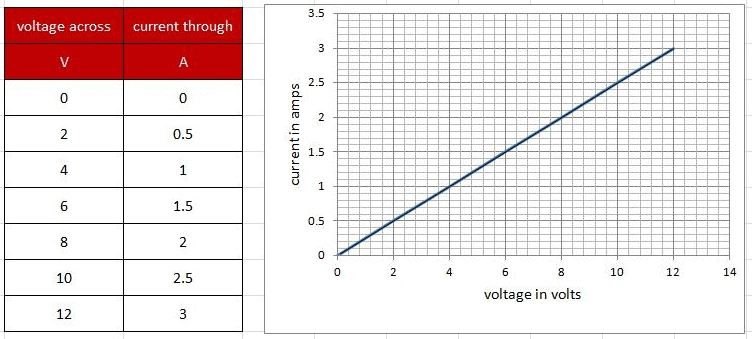
- Plot a graph with V along x-axis and I along y-axis.
- The graph will be a straight line which verifies Ohm's law.
- Determine the slope of the V-I graph. The reciprocal of the slope gives resistance of the wire.
Observations:
- Range of the given ammeter=.................... A.
- Least count of the given ammeter = ..................... A.
- Range of the given voltmeter = .....................V.
- Least count of the given voltmeter = .....................V.
- Mean value of V/I from observations, R = .......... Ω.
Observation from graph:
- Slope of I vs V graph = ...........
- R from graph = 1/ slope = .............. Ω.
Observation table:
As performed in the simulator:
- Click on Show Label checkbox to label/unlable the apparatus in the circuit.
- Click on Show Help checkbox to show/hide the 'help' for performing the lab.
- Click on the Observation Table tab below to open the Observation table.
- Drag the plug key to switch on/off the current.
- Adjust the rheostat such that ammeter shows the low value of Current (I). Note corresponding voltmeter reading.
- Increase the current by adjusting the slider of the rheostat and take about 5 or 6 sets of readings.
- Note carefully ammeter and voltmeter readings in each set and record in the Observation Table.
- Note V/I ratio for each set of reading in the Resistance column.
- Click on Plot Graph button to plot voltmeter readings (V) along the x-axis and the corresponding ammeter readings (I) along the y-axis in the graph.
|
85 videos|437 docs|75 tests
|
FAQs on Theory & Procedure, Verification of Ohm's Law - Science Class 10
| 1. What is Ohm's Law? |  |
| 2. How do you verify Ohm's Law in the classroom? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of verifying Ohm's Law? |  |
| 4. Can Ohm's Law be applied to all types of conductors? |  |
| 5. What are some practical applications of Ohm's Law? |  |



















