Time | Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
What do I need to know about time for IGCSE?
- Both 12-hour and 24-hour times could be used
- In the 12-hour clock system:
- AM is between midnight (12am) and midday (12pm)
- PM is between midday (12pm) and midnight (12am)
- Times may have to be read from both analogue and digital clocks
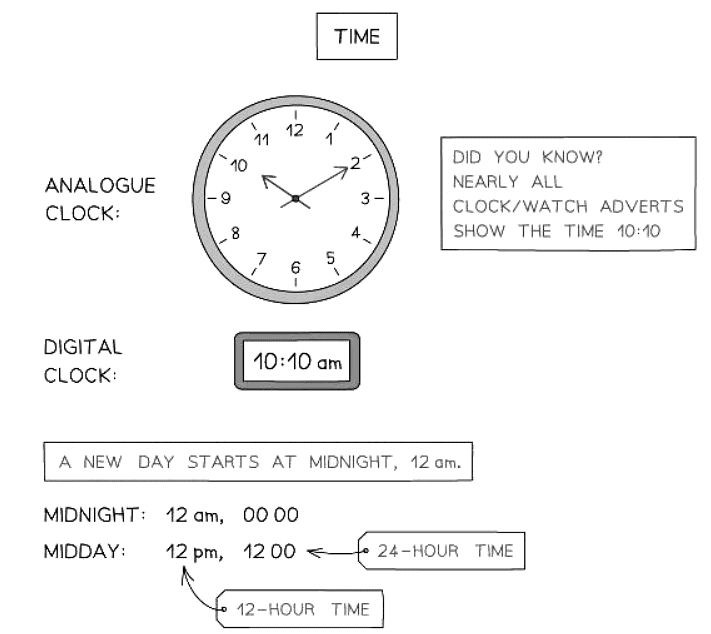
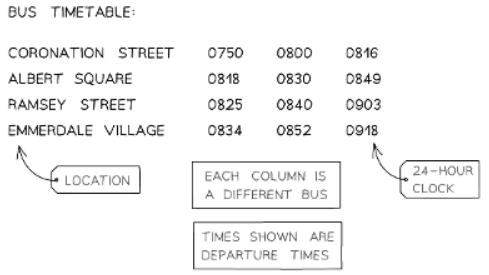
- Times may have to be read from timetables
- Time operates differently from the base-10 number system, making calculations somewhat tricky.
- 60 seconds in a minute
- 60 minutes in an hour
- 24 hours in a day
- 7 days in a week
- 365 days in a year
- ... and many more !

- Knowing the number of days in each calendar month is important, and the following poem might help you remember...
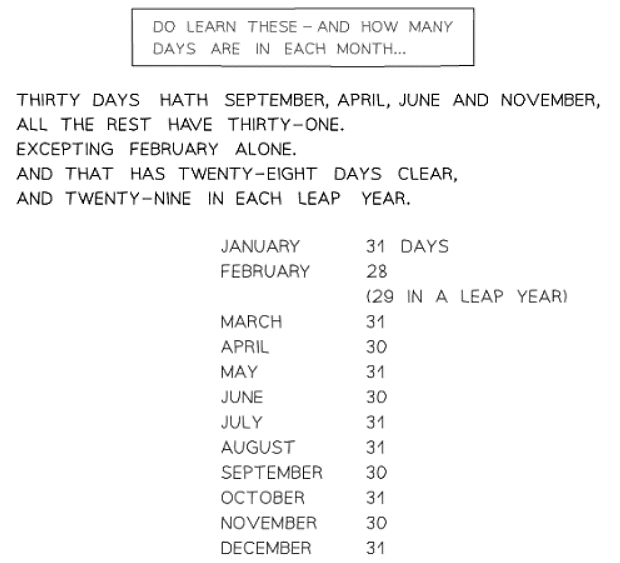
How do I read a clock?
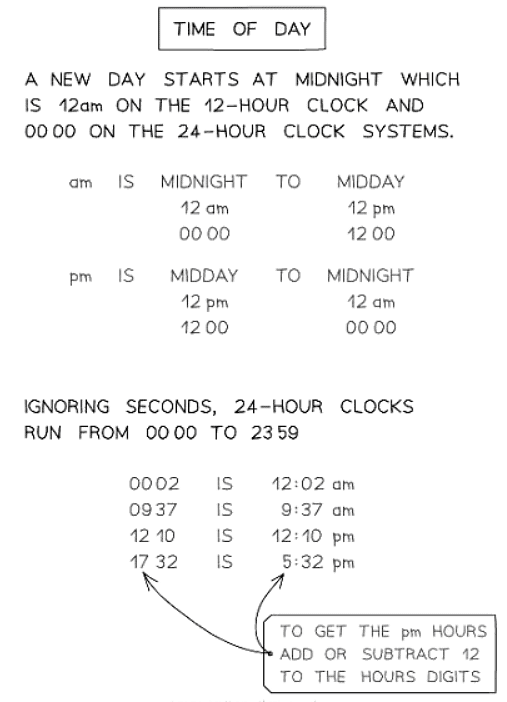
- A 12-hour clock goes round once for am and once for pm:
- AM: Midnight (12am) to Midday (12pm)
- PM: Midday (12pm) to Midnight (12am)
- A 24-hour clock uses four digits - two for the hour, two for the minutes:
- Example: 1134 is 11:34 am
- The day starts at midnight (0000)
- 1pm is 1300, 2pm is 1400, ..., 10pm is 2200, 11pm is 2300
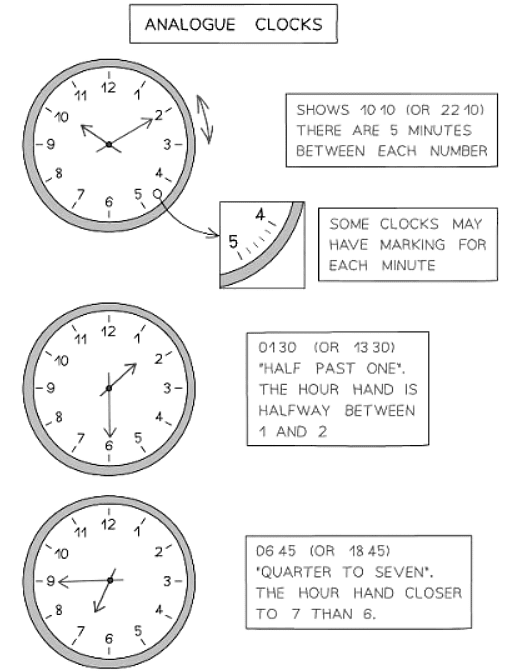
- Analogue clocks operate in a 12-hour format.
- On an analogue clock's minute hand, each number represents five minutes. Some clocks may have markings for individual minutes.
- The hour hand on an analogue clock is continuously moving.
- When it is "half past" the hour, the hour hand should be positioned midway between two numbers, with the minute hand pointing at the 6.
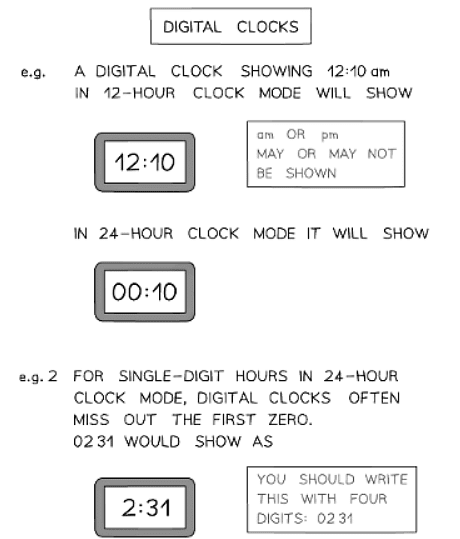
- Digital clocks can display time in either 24-hour format or 12-hour format.
- A ":" is commonly used between the hours and minutes (e.g., 12:45).
- When using 24-hour time, "am" or "pm" does not need to be specified.
- For single-digit hours, the leading zero is often omitted (e.g., 9:23).
- Timetables, such as those for buses or trains, typically utilize the 24-hour time format.
- Times in timetables are listed as four digits without the ":" separator.
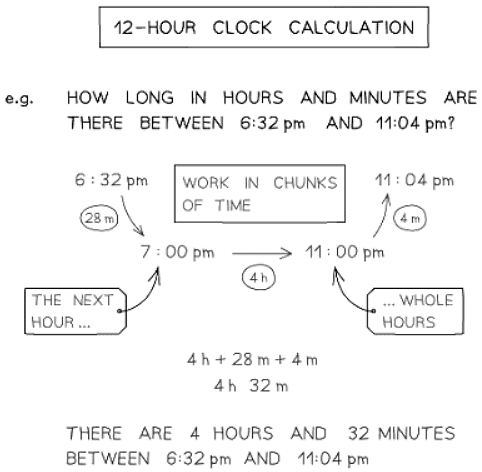
How do I calculate with time in terms of the 12-hour clock?
- Divide the time calculation into chunks: start by calculating the minutes until the next hour, then move on to whole hours, and finally calculate the remaining minutes until the final time.
- Understand when the 12-hour clock transitions between AM and PM. Remember, 12 PM is midday, and 12 AM is midnight.
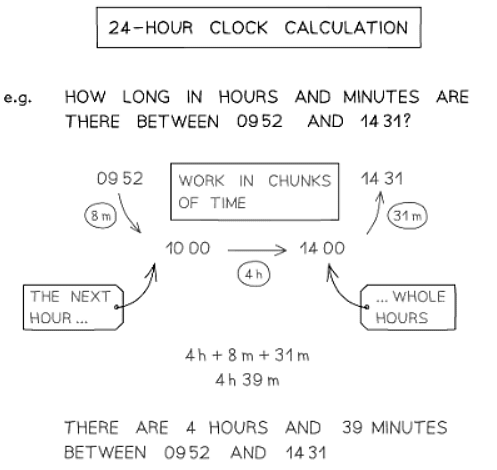
How do I calculate with time in terms of the 24-hour clock?
- Break down time calculations into chunks similar to 12-hour clock methods.
- For example, calculate the minutes remaining until the next hour, then the whole hours, and finally the minutes until the end time.
- If the hour exceeds 12, subtract 12 to determine the 12-hour PM time.
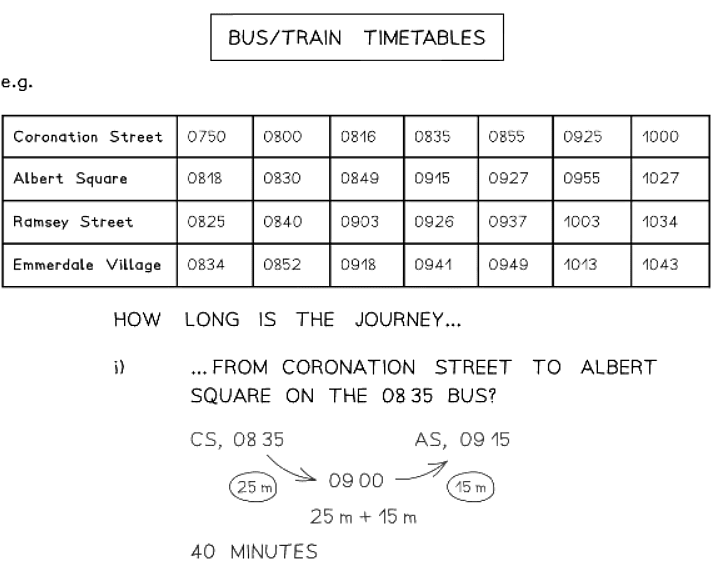
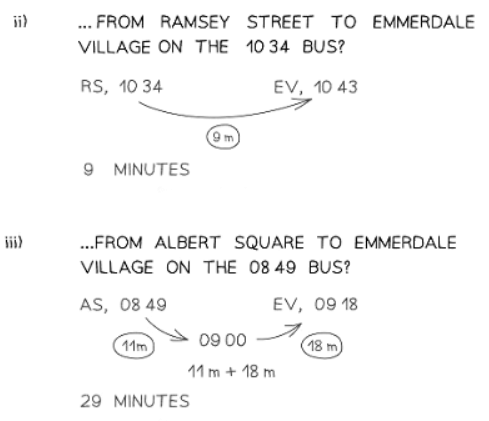
How do I use bus and train timetables?
- These tend to use the 24-hour clock system
- Each column represents a different bus/train - these are often called "services" (e.g., "The 0810 service from London King's Cross")
- The time in each cell usually indicates departure times (when the bus/train leaves that stop/station). The last location on the list usually shows the arrival time
The document Time | Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
82 videos|394 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Time - Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. How can I convert between different units of time, such as hours to minutes or days to hours? |  |
Ans. To convert between different units of time, you can use conversion factors. For example, to convert hours to minutes, you would multiply the number of hours by 60 (since there are 60 minutes in an hour). To convert days to hours, you would multiply the number of days by 24 (since there are 24 hours in a day).
| 2. What is the formula for calculating the total time elapsed when given the start and end times? |  |
Ans. To calculate the total time elapsed between two given times, you would subtract the start time from the end time. For example, if the start time is 3:00 PM and the end time is 5:30 PM, you would subtract 3:00 from 5:30 to get 2 hours and 30 minutes.
| 3. How can I convert between different units of money, such as dollars to pounds or euros to yen? |  |
Ans. To convert between different units of money, you would need to know the current exchange rate between the two currencies. You would then multiply the amount in the first currency by the exchange rate to get the equivalent amount in the second currency.
| 4. What is the process for calculating the total cost when given the price of an item and the quantity purchased? |  |
Ans. To calculate the total cost when given the price of an item and the quantity purchased, you would multiply the price of the item by the quantity purchased. For example, if an item costs $10 and you buy 5 of them, the total cost would be $50 (10 x 5).
| 5. How can I convert between different units of time and money in real-life scenarios, such as calculating hourly wages or budgeting for a trip? |  |
Ans. To convert between different units of time and money in real-life scenarios, you would need to apply the appropriate conversion factors and formulas. For example, to calculate hourly wages, you would multiply the number of hours worked by the hourly rate. To budget for a trip, you would convert expenses from one currency to another using exchange rates.
Related Searches
















