Types of Economies: Summary notes of Economics for UPSC GS | Indian Economy for UPSC CSE PDF Download
What are the types of economic systems?
World economies are classified into three categories based on the responsibility and structure of the production and distribution network: capitalistic, state and mixed economies.
The three economic system models that have developed over the course of human history are essentially phases in the evolutionary process. As a result, several nations have transitioned to a new mode over time.
Here we’ll learn about the parts of economies that are adapted in India and are important from UPSC point of view.
What are the Characteristics and similarities between the Economic Systems?
➤ What is the Free Market System?
 Features of Free Market System
Features of Free Market System
- A free-market economy is an economy where all markets within it are free.
- This requires protection of property rights, but no coercive regulation, no coercive subsidization, no coercive government-imposed monopolistic monetary system, and no coercive governmental monopolies.
- The United States: The U.S. economy is often cited as an example of a free market system. It has minimal government intervention in terms of regulations and pricing, and businesses operate based on supply and demand dynamics.
- Hong Kong: Hong Kong is known for its free market economy. It has low taxation, minimal government interference, and a strong emphasis on free trade.
➤ What is the Planned Economy?
A planned economy (or command economy) is an economic system in which the state or workers' councils manage the economy. It is an economic system in which the central government makes all decisions on the production and consumption of goods and services.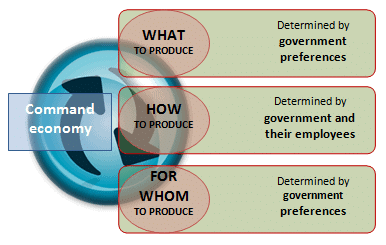
Its most extensive form is referred to as a command economy, centrally planned economy, or command and control economy. In such economies, central economic planning by the state or government controls all major sectors of the economy and formulates all decisions about the use of resources and the distribution of output.
Planners decide what should be produced and direct lower-level enterprises to produce those goods in accordance with national and social objectives.
Planned economies are in contrast to unplanned economies, such as a market economy, where production, distribution, pricing, and investment decisions are made by the private owners of the factors of production based on their individual interests rather than upon a macroeconomic plan.
Examples of Planned Economy
- North Korea: North Korea is an example of a planned or command economy. The government controls all major sectors of the economy and makes decisions on production and resource allocation.
- Cuba: Cuba has a centrally planned economy where the government plays a dominant role in economic activities, including ownership of major industries and resource allocation.
➤ What is the Mixed Economy?
A mixed economy is an economic system that includes a variety of private and government control, or a mixture of capitalism and socialism.
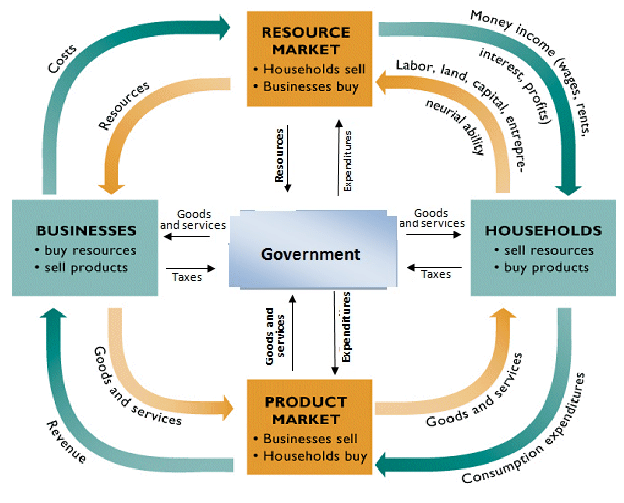 Mixed Economy Circular Flow Model
Mixed Economy Circular Flow Model
There is not one single definition for a mixed economy, but relevant aspects include: A degree of private economic freedom (including privately owned industry) intermingled with centralized economic planning and government regulation (which may include regulation of the market for environmental concerns, social welfare or efficiency, or state ownership and management of some of the means of production for nation or social objectives).
Want to learn the Types of Economies but through a Video? Watch Types of Economies: Economics and learn the Concept in Minutes.
Examples of Mixed Economy
- Canada: Canada is often considered as a mixed economy. It combines elements of free market capitalism with government intervention to ensure social welfare, environmental regulations, and public services.
- Sweden: Sweden is another example of a mixed economy. It has a strong welfare state, with government-provided healthcare, education, and social security, along with a market-oriented economy.
What are the elements of a Mixed Economy?
- To possess means of production (farms, factories, stores, etc.)
- To participate in managerial decisions (cooperative and participatory economics)
- To travel (needed to transport all the items in commerce, to make deals in person, for workers and owners to go to where needed)
- To buy (items for personal use, for resale; buy whole enterprises to make the organization that creates wealth a form of wealth itself)
- To sell (same as buy)
- To hire (to create organizations that create wealth)
- To fire (to maintain organizations that create wealth)
- To organize (private enterprise for profit, labour unions, workers' and professional associations, non-profit groups, religions, etc.)
- To communicate (free speech, newspapers, books, advertisements, make deals, create business partners, create markets)
- To protest peacefully (marches, petitions, sue the government, make laws friendly to profit making and workers alike, remove pointless inefficiencies to maximize wealth creation) p.s. the only similarity is that mixed economies are a mixture of both planned and market economy.
FAQs related to Economics in UPSC
- What are the 3 different types of economic systems?
Free market, command, and mixed economies are the three primary types of economies. In the graph below, free-market and command economies are compared; mixed economies are a hybrid of the two. Individuals and corporations make economic decisions on their own. All economic decisions in the country are made by the state's central government. - What is an Economic System?
An economic system is a government-created mechanism for distributing and organising existing resources, products, and services throughout a country or geographic region. It considers the production components of labour, capital, and resources. - What should I study for economics in UPSC?
Economics is one of the optional subjects offered by the UPSC in the civil services mains exam. Though not as popular as some other subjects like Public Administration or Geography, Economics has a good success rate among candidates.
|
139 videos|315 docs|136 tests
|
Additional FAQs on Types of Economies: Summary notes of Economics for UPSC GS - Indian Economy for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the main types of economic systems? |  |
| 2. What are the characteristics of different economic systems? |  |
| 3. What are the key elements of a mixed economy? |  |
| 4. How do economic systems impact economic growth? |  |
| 5. Why is understanding economic systems important for the UPSC exam? |  |

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|


















