UPSC Daily Current Affairs - 19th January 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
ASER 2022: Post-Covid, student count at record high, but big dip in learning
Context
After two years of a Covid-19-induced school shutdown, the recently released 17th Annual Status of Education Report (ASER) for 2022 contains both good (high enrolment) and bad news (drop in learning levels).
- ASERs (by NGO Pratham) have been surveying children aged 6 to 14 since 2005 to track trends in school enrolment, attendance and reading and arithmetic abilities.
- This year’s report (came after 2018) surveyed 7 lakh children across 19,060 villages in 616 districts in the country.
What are the Findings of the recent ASER Report?
- School enrolment touched a record high: As the pandemic subsided, school enrolment touched 4% in 2022 up from 97.2% in 2018, when the last full pre-pandemic survey was conducted.
- The proportion of girls not enrolled has also reduced: For girls aged 11-14, this share dropped from 4.1% in 2018 to 2% in 2022 (which stood at 10.3% in 2006).
- Drop in learning levels:
- Between 2014 and 2018, learning levels in terms of foundational skills in reading and arithmetic had been rising gradually.
- For example, the proportion of Class 3 students who could read a Class 2 textbook had gone up from 23.6% in 2014 to 27.2% in 2018, while those who could do at least subtraction rose from 25.3% to 28.2%.
- However, in 2022, the basic reading ability of children in Class 3 dipped by 6.8% points from 2018 and the proportion of children in Class 3 who could do at least subtraction fell to 25.9% in 2022.
- Clearly, the pandemic has resulted in learning loss. However, the loss is much greater in reading as compared to arithmetic.
- Between 2014 and 2018, learning levels in terms of foundational skills in reading and arithmetic had been rising gradually.
- A small, steady increase in the children availing private tuitions: Between 2018 and 2022, this proportion increased further - from 26.4% to 30.5% - a trend for over a decade now.
- Proportion of children in government schools has risen:
- The percentage of children (aged 11 - 14) who are enrolled in government schools has risen from 65% in 2018 to 71.7% in 2022 - a trend that was reflected in the government’s UDISE+ data.
What can be Inferred from the above Findings?
- An improvement in infrastructure variables, government schools distributing textbooks, midday meals during lockdown led to a pull factor, increasing enrolment in government schools.
- This phenomenon can also be attributed to several other factors, including job losses and the closure of budget private schools in rural areas during the pandemic.
- Private tuition probably increased because it is more flexible and provided some extra help to children when schools were closed.
- For example, if a person is unable to pay in a given month, they can pay the following month.
- The drop in reading levels is more than in maths, because maths at such a basic level, is used by people much more.
- This is despite the fact that 80% of the government schools have received guidelines and teachers have been trained under the NIPUN Bharat and Foundational Literacy and Numeracy (FLN) mission (both conceived under the National Education Policy 2020).
- The National Initiative for Proficiency in Reading with Understanding and Numeracy (NIPUN) Bharat ensures that every child in India gains foundational numeracy and literacy by the end of Grade 3.
What is the Road Ahead to Improve these Foundational Skills?
- Foundational Literacy and Numeracy is a critical thing for improving the productivity of the country.
- Therefore, an integration between the anganwadi system and the school system is urgently needed because the work starts there.
- In order to make sure that happens, the anganwadi system (especially for the education part) needs to be well-funded.
Source: Indian Express
GS-II
Grameen Udyami Scheme
Context
The Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship the felicitation program of 200 tribal women under the Grameen Udyami Scheme.
Grameen Udyami Scheme
- It was launched to augment skill training in tribal communities for their inclusive and sustainable growth.
- It is a unique multiskilling project, funded by National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) that aims to train tribal students in select states.
- It is implemented under Sansadiya Parisankul Yojana.
- Under the program, 49 ST clusters in 15 states of India have been selected by 40 tribal MPs of Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha.
- Under their leadership, the scheme in respective clusters is being implemented.
- One development associate is appointed by the MPs in each cluster.
Stated objectives
- Increase in Rural/Local Economy
- Enhance employment opportunities
- Reduce forced migration due to lack of local opportunities
- Conservation of natural resources
Scope of the project
- The project is being implemented in six states – Maharashtra, Rajasthan, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand, and Gujarat.
Benefits
- Transportation, boarding & lodging during the learning period is provided to candidates
- The training under the project will be conducted in the job roles which are relevant to the local economy.
Source: PIB
GS-III
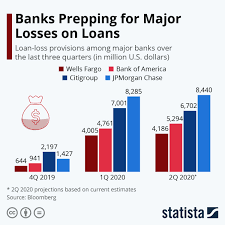
Loan Loss Provision by Banks
Context
Recently, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) published a discussion paper on “loan loss provision”.
- This paper proposed a framework for adopting an expected loss (EL)-based approach for provisioning by banks in case of loan defaults.
- Presently, banks are required to make loan loss provisions based on an incurred loss approach.
What is loan-loss provision?
- The RBI defines a loan loss provision as an expense that banks set aside for defaulted loans.
- In other words, a loan loss provision is a cash reserve that banks set aside to cover losses incurred from defaulted loans.
- Basically, it is an income statement expense banks can tap into when borrowers are unlikely to repay their loans.
- In the event of a loss, instead of taking a loss in its cash flows, the bank can use its loan loss reserves to cover the loss.
- For example: Let’s say a bank has issued $100,000 total in loans and has a loan loss provision of $10,000.
- On one of their defaulted loans, the borrower repaid only $500 of the outstanding $1,000.
- To cover the $500 loss from the defaulted loan, the bank would deduct $500 from the loan loss provision.
- The level of loan loss provision is determined based on the level expected to protect the safety and soundness of the bank.
What is the present approach followed by banks to make loan loss provisions?
- Banks in India are currently required to make loan loss provisions based on incurred loss model.
- This model assumes that all loans will be repaid until evidence to the contrary (known as a loss or trigger event) is identified.
- Only at that point is the impaired loan (or portfolio of loans) written down to a lower value.
What is the problem with the incurred loss-based approach?
- The incurred loss approach requires banks to provide for losses that have already occurred or been incurred.
- The delay in recognising expected losses under this approach was found to exacerbate the downswing during the financial crisis of 2007-09.
- Faced with a systemic increase in defaults, the delay in recognising loan losses resulted in banks having to make higher levels of provisions.
- This ate into the capital maintained by the bank which in turn affected banks’ resilience and posed systemic risks.
- Further, the delays in recognising loan losses overstated the income generated by the banks.
- This, coupled with dividend payouts, impacted their capital base because of reduced internal accruals — which too, affected the resilience of banks.
What has been proposed by the RBI?
- RBI has proposed a framework for adopting an expected loss (EL)-based approach for provisioning by banks in case of loan defaults.
- Under this practice, a bank is required to estimate expected credit losses based on forward-looking estimations.
- Under this, banks will need to classify financial assets into one of three categories — Stage 1, Stage 2, or Stage 3 — depending upon the assessed credit losses on them, at the time of initial recognition as well as on each subsequent reporting date, and make necessary provisions.
What are the different stages proposed under the expected loss (EL)-based approach?
- Stage 1 assets
- Financial assets that have not had a significant increase in credit risk since initial recognition or that have low credit risk at the reporting date.
- For these assets, 12-month expected credit losses are recognised and interest revenue is calculated on the gross carrying amount of the asset.
- Stage 2 assets
- Financial instruments that have had a significant increase in credit risk since initial recognition, but there is no objective evidence of impairment.
- For these assets, lifetime expected credit losses are recognised, but interest revenue is still calculated on the gross carrying amount of the asset.
- Stage 3 assets
- Financial assets that have objective evidence of impairment at the reporting date.
- For these assets, lifetime expected credit loss is recognised, and interest revenue is calculated on the net carrying amount.
What are the benefits of this new approach?
- The expected credit losses approach will further enhance the resilience of the banking system in line with globally accepted norms.
- It is likely to result in excess provisions as compared to shortfall in provisions as seen in the incurred loss approach.
Source: Indian Express
World Economic Forum Annual Meeting 2023
Context
Recently, Union minister Ashwini Vaishnaw addressed a session on India’s road to a $10-trillion economy at the World Economic Forum (WEF) in Davos.
- The annual meeting of WEF is taking place in Davos from Jan. 16 until Jan. 20, 2023.
- The theme of this year’s summit is “Cooperation in a Fragmented World”.
World Economic Forum
- The World Economic Forum is the international non-governmental organization for Public-Private Cooperation.
- It was founded in January 1971 by German engineer and economist Klaus Schwab.
- The Forum engages the foremost political, business, cultural and other leaders of society to shape global, regional and industry agendas.
- It has no independent decision-making power.
- HQ: Cologny-Geneva, Switzerland.
Davos meet
- Annually, the WEF organizes a meeting at the end of January in Davos, a mountain resort in Graubünden, in the eastern Alps region of Switzerland.
- The Annual Meeting, also known as the Davos Agenda, has the objective of orienting global leaders on the imperatives of the year ahead.
Different reports published by WEF
- WEF also produces a series of annual reports such as –
- Global Competitiveness Report,
- Global Information Technology Report,
- Global Gender Gap Report,
- Global Risks Report,
- Global Travel and Tourism Report,
- Financial Development Report and
- Global Enabling Trade Report.
World Economic Forum Annual Meeting 2023
- The 53rd edition of the annual World Economic Forum summit is being held at the Swiss town of Davos.
India’s participation
- This year marks 36 years of the Forum’s collaboration with India.
- At the summit, India is represented by a high-level delegation which includes Union Ministers, Chief Ministers, Business leaders etc.
- In line with this year’s WEF theme, “Cooperation in a Fragmented World”, India has reiterated its position as a resilient economy with a strong leadership providing stable policy to the global investors at the summit.
- India’s focus areas at WEF this year are investment opportunities, infrastructural landscape and its inclusive & sustainable growth story.
Key highlights of the speech delivered by Union Minister Ashwini Vaishnav
- India’s pragmatic approach ensured high growth, moderate inflation
- India took a pragmatic approach in dealing with humanitarian and economic crises triggered by the pandemic and has ensured moderate inflation and high growth in the country.
- Indian government focused on vulnerable population for financial aid, free food and free vaccines and all that was done on digital platforms.
- India’s recent economic performance
- India witnessed the highest ever inflow of Foreign Direct Investment worth $84 Bn during 2021-2022.
- This FDI came into 57 sectors, from 101 countries and across 30 states and UTs.
- Real GDP Growth across FY21-22 was an unprecedented 8.7% and absolute GDP value in FY21-22 reached $3.1 Tn.
- Recent estimates point towards a $5 Tn economy by 2025.
- India witnessed the highest ever inflow of Foreign Direct Investment worth $84 Bn during 2021-2022.
- India on a consistent growth path
- Despite the global turmoil, over the last few years, India is following a consistent growth path of 6-8%.
- The focus to invest in infrastructure has helped improve productivity and job generation.
- Due focus on moderating inflation and appropriate fiscal and monetary policy measures will help ensure India’s GDP momentum in the next 10 years.
India@100: Realising the potential of a $26 trillion economy
- The report, ‘India@100: Realising the potential of a $26 trillion economy’, was launched by the Union Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw, on the sidelines of the summit.
- The report has been prepared by the consulting firm EY
- As per this report, India’s economy will reach $26 trillion by 2047, the 100th year of the country’s independence.
- Other highlights of this report
- The report underscores the growth trajectory of the Indian economy, that is projected to be the highest for any large economy over the coming decades.
- It recommends ensuring macro-economic stability and resilience, and continued thrust on reforms.
- This will be especially relevant against the backdrop of on-going geo-political conflict, inflationary pressures and slowing global growth.
Source: Indian Express
What is National Coal Index (NCI)?

Context
The Ministry of Coal has launched the sixth round of commercial coal mines’ auction for 141 coal mines.
What is the news?
- As per the provisions of the tender document, the Performance Bank Guarantee (PBG) to be submitted for each successfully auctioned coal mine is to be revised annually based on the National Coal Index (NCI).
What is National Coal Index (NCI)?
- Ministry of Coal has started commercial auction of coal mines on revenue share basis.
- In order to arrive at the revenue share based on market prices of coal, one National Coal Index (NCI) is conceptualized.
- The NCI is a price index which reflects the change of price level of coal on a particular month relative to the fixed base year.
- The base year for the NCI is FY 2017-18.
- NCI is a price index combining the prices of coal from all the sales channels- Notified Prices, Auction Prices and Import Prices.
- It is released every month.
Components of NCI
- The concept and design of the Index as well as the Representative Prices have been developed by the Indian Statistical Institute, Kolkata.
- NCI is composed of a set of five sub-indices: three for Non-Coking Coal and two for Coking Coal.
- The three sub-indices for Non-Coking Coal are combined to arrive at the Index for Non-Coking Coal and the two sub-indices for Coking Coal are combined to arrive at the Index for Coking Coal.
- Thus, indices are separate for Non-coking and Coking Coal.
- As per the grade of coal pertaining to a mine, the appropriate sub-index is used to arrive at the revenue share.
Implementation of NCI
- The amount of revenue share per tonne of coal produced from auctioned blocks would be arrived at using the NCI by means of a defined formula.
- The Index is meant to encompass all transactions of raw coal in the Indian market.
- This includes coking and non-coking of various grades transacted in the regulated (power and fertilizer) and non-regulated sectors.
- Washed coal and coal products are not included.
Source: Indian Express
Why India needs a fresh Fertilizer Policy?

Context
The government is expected to come out with a new fertilizer policy.
What is the news?
- A task force to examine the production and promotion of bio-fertilizer and organic fertilizers has already been set up under the NITI Aayog.
How much fertilizer does India consume?
- Total consumption of fertilizers between April and mid-December 2022 was 40.146 million metric tonnes (mmt), with production of 32.076 mmt and imports of 12.839 mmt.
- The gap between demand and production is met through timely imports.
How is fertilizers availability monitored?
- Some steps undertaken by the government to improve the availability of fertilizers include:
- Assessment of state-wise requirements every month;
- 100% neem coating of urea, which increases nutrient efficiency;
- Monitoring of crop yield and soil health; and
- Online monitoring of the movement of fertilizers through the integrated Fertilizer Monitoring System.
Impact of the current policy
- Heavy subsidies: This has prompted many farmers to use chemical fertilizers like urea, which leads to higher productivity, but affects soil fertility in the long run.
- Excessive and inefficient use of fertilizers: This leads to nutrient losses to the environment and could also result in drinking water contamination and impact human lives as a result of unsafe storage practices, as per a UN report.
- Emission causing: With the subsidy being released directly to companies, technology-inefficient companies are being protected causing carbon emission.
- While attempts have been made to reform the fertilizer policy, they had to be rolled back after pressure from various quarters.
Trend in government expenditure
- Food subsidy: The government has spiked spending on food, fertilizer and fuel subsidy by nearly 70%.
- Increased expenditure: For 2023-24, the fertilizer ministry might seek budgetary support of ₹2.5 trillion subsidy – outgo for FY23 has already crossed ₹2 trillion.
- Increased import bill: Russia being a major exporter of liquefied natural gas -critical input for manufacturing of urea – has also led to higher prices.
Steps taken in 2022
- Implementation of DBT: The department of fertilizers disbursed subsidies for urea and nutrient-based subsidy, and implemented direct benefit transfer.
- One Nation One Fertilizers Scheme: It also implemented the ONOF scheme which aims to ensure timely supply of fertilizers.
- Model fertilizer retail outlets: The existing village, block/sub district/taluk and district level fertilizer retail outlets are being converted into model fertilizer retail outlets.
Way forward
- Promoting local fertilizers: Lower duty on imported phosphoric acid to raise the competitiveness of local fertilizer manufactures, and an incentive for promoting organic fertilizers, could be proposed.
- Bio-fertilizer and organic fertilizers: A task force on bio-fertilizer and organic fertilizers has already been set up under NITI Aayog.
- Curbing hefty subsidies: Considering the long-term interests of agriculture and the effects of using inorganic fertilizers, saving a huge amount on account of subsidy support is a step in the right direction.
Source: Indian Express
Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code
Context
The Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) has proposed sweeping changes to the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code.
- The Ministry aims to bring more technology, transparency, and speediness to the corporate insolvency resolution process.
Background:
- In a growing economy like India, a healthy credit flow and generation of new capital are essential, and when a company or business turns insolvent or “sick”, it begins to default on its loans.
- In order for credit to not get stuck in the system or turn into bad loans, it is important that banks or creditors are able to recover as much as possible from the defaulter and as quickly as they can.
- The business can either get a chance, if still viable, to start afresh with new owners, or its assets can be liquidated or sold off in a timely manner.
- This way fresh credit can be pumped into the system and the value degeneration of assets can be minimised.
What is the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC)?
- In 2016, at a time when India’s Non-Performing Assets and debt defaults were piling up, the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC) code was introduced.
- It was introduced to overhaul the corporate distress resolution regime in India and consolidate previously available laws to create a comprehensive time-bound mechanism.
- Insolvency resolution in India took 4.3 years on an average.
- In comparison, countries such as UK and USA took 1 year and 1.5 years, respectively.
- The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code 2016 was implemented through an act of Parliament.
- The Code aims to promote entrepreneurship, availability of credit and balance the interests of all the stakeholders.
What is the mandate of the IBC?
- When insolvency is triggered under the IBC, there can be two outcomes: resolution or liquidation.
- All attempts are made to resolve the insolvency by either coming up with a restructuring or new ownership plan and if resolution attempts fail, the company’s assets are liquidated.
What is the timeframe for completion of the exercise under the code?
- Companies have to complete the entire insolvency exercise within 180 days under the IBC.
- The deadline may be extended if the creditors do not raise objections on the extension.
- For smaller companies including startups with an annual turnover of Rs 1 crore, the whole exercise of insolvency must be completed within 90 days.
Who regulates the IBC proceedings?
- Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI) has been appointed as a regulator and it can oversee these proceedings.
- IBBI has 10 members; from Finance Ministry, Law Ministry and the Reserve Bank of India.
Source: Indian Express
|
38 videos|5288 docs|1117 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs - 19th January 2023 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the GS-I exam? |  |
| 2. What is the GS-II exam? |  |
| 3. How can I prepare for the UPSC examination? |  |
| 4. What are the important topics to focus on for GS-III? |  |
| 5. How can I improve my answer writing skills for the UPSC examination? |  |