UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 22nd August 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-II
Drilling in the North Sea
Subject: Geography
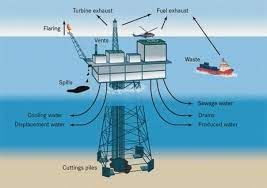
Why in News?
Recent endorsement by U.K. Prime Minister of plans for fresh fossil fuel drilling off Britain’s coast has sparked a debate among environmental experts.
- Amidst global concerns about climate change, the decision raises questions about the country’s commitment to sustainability and its impact on climate goals.
Evolution of North Sea Drilling
- Origins and Legislation: The North Sea drilling history dates back to the 1958 Geneva Convention on the Continental Shelf, which set the stage for exploration in the region.
- Continental Shelf Act: The U.K. Parliament’s enactment of the Continental Shelf Act in 1964 established the country’s jurisdiction over oil and gas resources beneath its seabed.
Milestones and Concerns in Drilling
- Early Exploration and Challenges: British Petroleum (BP) was granted the first exploration license in 1964, leading to natural gas discovery the following year.
- Forties Field Discovery: BP’s breakthrough commercial oil discovery in the Forties Field in 1970 marked a significant milestone.
- Expanding Operations and Safety Revamp: The following years witnessed increased exploration activities and installation of oil platforms. The Piper Alpha disaster in 1988 prompted crucial safety reforms.
Rationale and Concerns
- Government’s Position: In an official statement, the government justified the move as a strategy to enhance Britain’s energy independence.
- Environmental Alarm: However, environmental experts express apprehension, especially given the global push towards averting irreversible climate change.
North Sea Transition Authority and Offshore Licensing
- NTSA’s Role: The North Sea Transition Authority (NTSA) is responsible for regulating the oil, gas, and carbon storage sectors.
- Offshore Licensing Round: The NTSA is currently conducting the 33rd offshore oil and gas licensing round, aiming to award more than 100 licenses.
- Timing and Awards: The first licenses are expected to be granted in the autumn, furthering the expansion of drilling operations.
Shaping Geopolitical Energy Dependence
- Energy Security Concerns: The Prime Minister emphasized the necessity of domestic oil and gas sources, even as the country aims to reach net-zero emissions by 2050.
- Strategic Implications: The decision is portrayed as an effort to reduce reliance on oil and gas imports, which could originate from potentially unfavourable sources.
Ecological Concerns and Climate Impact
- Adverse Environmental Effects: Offshore drilling poses risks to workers, marine ecosystems, and climate health. It contributes to ocean warming, rising sea levels, and threatens marine biodiversity.
- Carbon Pollution Impact: Carbon pollution settling into oceans contributes to acidification, endangering coral reefs and shellfish.
Evaluating UK’s Climate Commitments
- Climate Change Committee Report: The Climate Change Committee (CCC) pointed out deficiencies in the U.K.’s preparations for climate change under the National Adaptation Programme.
- Adaptation Implementation: The CCC’s assessment highlighted a lack of substantial implementation of adaptation measures to address climate risks.
- Inconsistent with Paris Agreement: The Climate Action Tracker assesses the U.K.’s climate action as not fully aligned with the Paris Agreement.
- Long-Term Targets: The U.K.’s Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) and long-term targets do not reflect a fair share of global efforts to mitigate climate change.
- Incompatibility with Limits: Licensing new oil and gas extraction plans contradicts the 1.5°C temperature rise limit set by the Paris Agreement.
Conclusion
- The UK’s endorsement of offshore drilling reflects a complex balancing act between energy security, economic considerations, and environmental stewardship.
- As the world grapples with the imperative of combating climate change, the decisions made today hold the potential to shape the course of a sustainable future.
Source: The Hindu
Commonwealth Parliamentary Association (CPA)
Subject: Polity
Why in News?
Recently, Lok Sabha Speaker Om Birla inaugurated the 9th India Region Conference of the Commonwealth Parliamentary Association (CPA).
Background:-
- It was the 9th India Region Conference of the Commonwealth Parliamentary Association (CPA).
- Theme: Strengthening Democracy and Good Governance in the Digital Age.
About Commonwealth Parliamentary Association (CPA):-
- Founded: 1911.
- HQ: London, UK.
Historical Background:-
- The CPA was founded in 1911 as the Empire Parliamentary Association (EPA).
- It was registered as a charity on 22 October 1971 under the laws of the United Kingdom.
Salient Features:-
- It is an association to serve the Parliamentarians of the Commonwealth Countries.
- Objective: to promote closer understanding and cooperation for common purposes between those engaged in the Parliamentary form of Countries of the Commonwealth.
- Mission: to promote knowledge of the constitutional, legislative, economic, social, and cultural aspects of parliamentary democracy, with particular reference to the countries of the Commonwealth.
- It provides the machinery for regular consultation and exchange of ideas and information among members of Commonwealth Parliaments.
India’s commonwealth membership:-
- India was a dominion from 1947 to 1950 till our constitution became effective.
- 1949: India’s constituent assembly ratified the membership of the association declaring continuation of full membership.
- India has been playing an important role at the Commonwealth Heads of Government Meet (CHOGM).
- 1983: India also hosted the 24th commonwealth summit in New Delhi.
Source: AIR
Pak President denies signing controversial bills
Subject: International Relations

Why in News?
President Arif Alvi denied approving changes to the Official Secrets Act and the Pakistan Army Act, claiming that he was undermined by his own staff.
- The law ministry, however, asked him to take responsibility for his own actions.
- The law ministry is currently functioning on an interim basis till general elections are held later this year.
- The development comes less than two weeks after Alvi dissolved the National Assembly on the advice of then outgoing Prime Minister Shehbaz Sharif – thus paving the way for the next general elections.
Background:
- Few weeks ago, the Pakistan National Assembly and the Senate approved two bills and sent those bills for Presidential assent.
- These bills were - the Official Secrets (Amendment) Bill, 2023 and the Pakistan Army (Amendment) Bill, 2023.
- The two bills that would further enhance the Pakistan Army’s already considerable powers.
- This Act confers more powers to the army chief and calls for imprisonment for those found guilty of defaming the army.
- According to critics of the government, these laws will expand the power of the army and the state to persecute opponents and activists.
- Also, these laws were passed swiftly (within a day) in the fag end of the Pakistani National Assembly’s tenure, under questionable circumstances.
- Pak President Alvi was deemed to have given his assent to both of them. Later, he denied to have signed these bills.
- On the social media platform, the President claimed that he ordered his staff to return the bills unsigned within the stipulated time to render them ineffective.
- He alleged that his staff undermined his orders and failed to follow his instructions.
- In light of the President’s latest comments, the legal status of these bills is now up in the air.
What does the Pak Constitution say about Presidential assent?
- Under Article 75(1) of the Pakistani Constitution, after a bill has passed through both the National Assembly and the Senate, it is presented to the President for his assent.
- The President, at this juncture, has two options – either to give assent within 10 days or to return the bill along with his objections to the legislature.
- If the legislature passes it again, with or without incorporating the President’s objections, as per the Constitution, the President shall give his assent within ten days, failing which such assent shall be deemed to have been given.
- As per constitutional experts of Pakistan, the concept of deemed assent only kicks in with bills that have already been sent back to the Parliament by the President one time.
- No where does 75(1) provide that if President has not assented to the Bill within 10 days it will automatically be deemed that the President has assent and the Bill becomes an Act.
Now, what will be the legal status of the laws?
- As per legal experts from Pakistan, there are serious questions regarding the validity of both the passed bills which became laws after Presidential assent.
- The President is saying that key legal amendments have become law through fraud and subterfuge.
- Hence, there now existed strong legal grounds for the court to declare that the two laws were not validly enacted acts.
Source: Indian Express
Good Governance and e Governance
Subject: Polity and Governance
Why in News?
Recently Union Minister of State (Independent Charge) Personnel, Public Grievances, Pensions, Atomic Energy and Space said the Uttar Pradesh’s District Good Governance Index 2022, the first of its kind by any state, ready for release.
About Good Governance and e governance:
- According to the World Bank “good governance is central to creating and sustaining an environment which fosters strong and equitable development and it is an essential complement to sound economic policies”.
- Good governance is the process of measuring how public institutions conduct public affairs and manage public resources and guarantee the realization of human rights in a manner essentially free of abuse and corruption and with due regard for the rule of law.
- On the other hand, E-government is the use of technological communications devices, such as computers and the Internet, to provide public services to citizens and other persons in a country or region.
- E-government offers new opportunities for more direct and convenient citizen access to government and for government provision of services directly to citizens.
Significance:
- Responsiveness: Good governance requires that institutions and processes try to serve all stakeholders within a reasonable timeframe.
- Rule of law: Good governance requires fair legal frameworks that are enforced impartially.
- It also requires full protection of human rights, particularly those of minorities.
- Impartial enforcement of laws requires an independent judiciary and an impartial and incorruptible police force.
- Transparency: These helps make all functions of the business transparent.
- All official information can be uploaded onto the internet.
- The citizens specifically access whichever information they want, whenever they want it, at their convenience.
- Data Driven Governance: Technology facilitates communication.
- The Internet and smartphones have enabled instant transmission of high volumes of data that acts as a fodder for effective governance.
- Costs Saving: A lot of Government expenditure goes towards the cost of buying stationery for official purposes.
- Letters and written records consume a lot of stationery.
- However, replacing them with smartphones and the internet can save crores of money in expenses every year.
- Accountability: Transparency directly links to accountability.
- Once the functions and information of the governance is available to the citizens, the government is more accountable to its actions.
- Land Record Monitoring: A vast developing country like India, with its diverse land tenure system requires effective land monitoring.
- In order to ensure that transactions related to properties are not fraudulent, along with physical transactions, online record maintenance is a key feature of e-governance in India.
- Speedy delivery: To ensure speedy administration of services and information.
- To reduce difficulties: for business, provide immediate information and enable digital communication by e-business.
Challenges:
- Lack of computer literacy: India is still a developing country and a vast majority of the citizens lacks computer literacy, which hinders the effectiveness of e-governance.
- Lack of accessibility: to the internet or even computers in some parts of the country is a disadvantage to e-governance.
- E-Governance results in a loss of human interaction: As the system becomes more mechanized, lesser interaction takes place among people.
- Risk: It gives rise to the risk of personal data theft and leakage.
- E-Governance leads to a lax administration: The service provider can easily provide excuses for not providing the service on technical grounds such as “server is down” or “internet is not working”, etc.
- Corruption at various levels and centralization of power and authority: 2021 Corruption Perceptions Index ranked India in 85th place out of 180.
- Criminalization of politics and weak legislators with criminal records, poor knowledge about development issues and low level of education.
- Poor people’s participation in development processes.
- Poor coordination among the political, administrative and community-level organizations and institutions.
Govt. Initiatives for Good Governance and e governance in India:
- Right to Information Act: The enactment of the Right to Information Act 2005 marks a significant shift for Indian democracy, because the greater the access of citizens to information, the greater will be the responsiveness of the government to community needs.
- Citizen’s Charter: A Citizens’ Charter represents the commitment of the Organisation towards standard, quality and time frame of service delivery, grievance redress mechanism, transparency and accountability.
- Sevottam model: Sevottam is an assessment-improvement model that has been developed with the objective of improving the quality of public service delivery in the country.
- in is a national citizen engagement platform where people can share ideas and be involved with matters of policy and governance.
- UMANG is a Unified Mobile Application which provides access to central and state government services including Aadhar, Digital Locker, PAN, Employee Provident Fund services, etc.
- PayGov facilitates online payments to all public and private banks.
- Mobile Seva aims at providing government services through mobile phones and tablets.
- Computerisation of Land Records ensures that landowners get digital and updated copies of documents relating to their property.
- PRAGATI (Pro-Active Governance and Timely Implementation) is aimed at starting a culture of Pro-Active Governance and Timely Implementation.
- It is also a robust system for bringing e-transparency and e-accountability with real-time presence and exchange among the key stakeholders.
Source: PIB
GS-III
Yasuni National Park
Subject: Environment and Ecology
Why in News?
Ecuadorians made a historic decision by rejecting oil drilling by a referendum in Yasuni National Park, a biodiverse Amazonian region.
About Yasuni National Park
- Yasuni National Park, declared a UNESCO biosphere reserve in 1989, spans 1 million hectares and harbors exceptional biodiversity.
- It is part of the Amazon rainforest, which itself is a global hotspot for species diversity.
- It is situated in the northeastern part of Ecuador, within the Napo and Pastaza provinces.
- It covers an area of approximately 9,820 square km (3,791 square miles).
- The park is considered one of the most biologically diverse areas on Earth.
Unique features
- Biodiversity: It is estimated that Yasuni contains around 670 species of birds, over 150 species of amphibians, and numerous large mammals like jaguars, pumas, and tapirs.
- Indigenous Communities: Yasuni is home to several indigenous communities, including the Waorani and Kichwa peoples, who have lived in the area for generations and have a deep connection to the land.
Source: The Indian Express
Why are onion prices rising?
Subject: Economy

Why in News?
After a long slump, onion prices are again on the rise, causing concern for the central government.
- As a result, the Ministry of Finance imposed a 40 per cent export duty on onions. This led traders to close onion auctions indefinitely in Nashik district, Maharashtra.
Production of Onion in India
- Background
- India is the second-largest onion-growing country in the world. The Indian onions are famous for their pungency and are available round the year.
- Indian onions have three crop cycles. The choice of season depends on the region's climate and the onion variety being cultivated. Onions are more commonly associated with the Rabi season.
- Varieties
- India cultivates various onion varieties, with the most common ones being red onions and white onions.
- There are certain varieties of yellow onion which are suitable for export in European countries.
- Cultivation Practices
- Onions are primarily grown through seeds, although bulb-to-bulb planting is also practiced.
- The crop requires well-drained soil and is often cultivated in sandy or loamy soils.
- Adequate irrigation is essential, and farmers may use drip irrigation systems to conserve water.
- Onion producing states
- The Major Onion producing states are Maharashtra, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Bihar, Andhra Pradesh, Rajasthan, Haryana and Telangana.
- Maharashtra ranks first in Onion production.
- Export
- The country has exported ~2,525,258 MT of fresh onion to the world, worth Rs. 4,522.79 crores/ 561.38 USD Millions during the year 2022-23.
- Major Export Destinations (2022-23): Bangladesh, Malaysia, UAE, Sri Lanka, Nepal and Indonesia.
News Summary
- Prices of onions have seen a steep rise since the start of August.
- At Lasalgaon’s wholesale market in Niphad taluka of Nashik, the average price of the bulb has risen from Rs 1,370/quintal on August 1 to Rs 2,050/quintal on August 19.
- In contrast, back in March-May, onion growers faced financial distress, when their produce was sold between Rs 500/quintal and Rs 700/quintal.
Why are onion prices on the rise?
- The present price rise has two aspects to it: first is the shortage in stored produce; the second has to do with lower-than-expected acreage of the bulb itself.
- Unlike other vegetables such as okra or beans, onions are not grown around the year.
- The fallout began last year when the country saw a dip in onion acreage.
- The Crop and Weather Watch Group noted that as against the 3.76 lakh hectares target for onion, the country had seen sowing over 3.29 lakh hectares.
- The situation worsened due to the damage to the Rabi crop in March–April, when most onion-growing states, including Maharashtra, saw unseasonal rain and hailstorm.
- Also, farmers, who generally offload their Rabi onions only post-June, were forced to do so from May itself because of quality concerns of the stored produce.
- Therefore, the month of May saw increased arrivals which along with inferior quality saw a price crash.
- The Maharashtra government had in March announced a special scheme to support onion growers with a subsidy of Rs 300/quintal. Most farmers said the scheme is yet to reach them.
- As a result, the supply-demand mismatch has resulted in the present price rise.
What has export to do with the present price rise?
- The domestic price rise comes at a time when demand for Indian onion in the international market has been quite high.
- The majority of the demand is from Bangladesh and West Asia.
- With a 40 per cent export duty, the price parity of the trade will be destroyed.
- Many traders had already signed contracts for exports at a lower price and this duty would have to be incurred by them.
- Around 4,500 tonnes of onion is in transit for which the exporters would have to suffer the losses.
- Increased export duty, the government feels would stem the bulb from leaving the country and would allow more availability in the local market.
- This will ensure smoother supply and lower prices.
Will this step ensure lower prices?
- To some extent, a price correction is possible. However, the larger concern that traders and farmers point out is the moisture stress the Kharif crop is under.
- India has reported 1.05 lakh hectares of Kharif onion. The crop is under moisture stress with rains being absent from the first week of August.
- In case the monsoon does not revive soon, the Kharif crop might not be able to meet the demand of the market in the days to come. This, in turn, will lead to price rise.
Source: The Indian Express
Palm cockatoo
Subject: Environment and Ecology

Why in News?
Recently, six Palm cockatoos (Probosciger aterrimus) birds– were rescued from Assam’s Cachar district by the police.
About Palm cockatoo:
- It is also known as the goliath cockatoo or great black cockatoo, is a large smoky-grey or black parrot of the cockatoo family.
- It has a very large black beak and prominent red cheek patches.
- Distribution:
- It is native to New Guinea, Aru Islands, and Cape York Peninsula.
- They occur in rainforests, such as gallery forests, forest edges, eucalypt and paperbark woodlands, monsoon woodlands, dense savannas and partly cleared areas.
- They choose big trees for roosting and nesting.
- Threats
- It is under threat by habitat loss through logging and seasonal fires, which each year destroy their nest trees in significant numbers.
- Conservation status
- IUCN: Least Concern
Source: Hindustan Times
Green Hydrogen Standard
Subject: Environment and Ecology

Why in News?
The Government has notified the Green Hydrogen Standard for India for the progress of the National Green Hydrogen Mission.
About Green Hydrogen Standard:-
- Issued in 2023.
- Issued by: Ministry of New and Renewable Energy
- Objectives: progress of the National Green Hydrogen Mission (NGHM).
- NGHM: It is a part of the National Hydrogen Mission (NHM) which was announced by the finance minister in the Union Budget 2021-22.
- Its objective was to make India a global hub for the production and export of green hydrogen and fulfill India’s Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs).
- The Ministry of New & Renewable Energy has defined Green Hydrogen through these standards.
- The standard, outlines the emission thresholds that must be met in order for hydrogen produced to be classified as Green.
- Definition: Green Hydrogen is defined as having a well-to-gate emission including water treatment, electrolysis, gas purification, drying, and compression of hydrogen of not more than 2 kg CO2 equivalent/kg H2.
- The definition encompasses both electrolysis-based and biomass-based hydrogen production methodology.
- Electrolysis: a chemical process that involves using an electric current to drive a non-spontaneous chemical reaction.
- Methodology: A detailed methodology for measurement, reporting, monitoring, on-site verification, and certification of green hydrogen and its derivatives shall be specified by the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy.
- Bureau of Energy Efficiency, Ministry of Power: it shall be the Nodal Authority for accreditation of agencies for the monitoring, verification, and certification of Green Hydrogen production projects.
Significance:-
- The Green Hydrogen Standard bring a lot of clarity to the Green Hydrogen community in India and was widely awaited.
- With this, India became one of the first few countries in the world to announce a definition of Green Hydrogen.
Green hydrogen:-
- Hydrogen is a chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1.
- It exists only in combination with other elements.
- Thus, it has to be extracted from natural compounds, like water.
- Based on the extraction process, Hydrogen is categorized into:-
- Grey hydrogen: produced from fossil fuels.
- Blue hydrogen: produced from fossil fuels with carbon capture and storage.
- Green Hydrogen: produced entirely from renewable power sources.
Advantages of Green Hydrogen:-
- Environment Friendly.
- Reduced Dependence on Rare Minerals.
- Reduces Import Bill.
- Efficient utilization of Renewable Energy.
Source: AIR
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|
















