UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 28th November 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Silkyara Tunnel |

|
| New Zealand |

|
| Rythu Bandhu Scheme |

|
| Qatar |

|
| Centre announces phased introduction of Biogas Blending for domestic use |

|
| AstroSat |

|
| Sagittarius C (Sgr C) |

|
GS-I
Silkyara Tunnel
Subject: Geography
Why in News?
Recently, Silkyara tunnel rescue operations entered their 16th day.
Background:-
- The accident when the workers were trapped in the Silkyara Tunnel located on the Uttarkashi-Yamnotri Road.
- The collapse happened about 270m from the entrance of the Silkyara side.
- The National Disaster Response Force (NDRF), the State Disaster Relief Force (SDRF) and the police are among the main figures in the multi-agency rescue operations.
About Silkyara Tunnel:-
- Location: Uttarakhand.
- The total length of the tunnel is 5 km.
- It is meant to connect Silkyara to Dandal gaon in Uttarkashi district.
- The double-lane tunnel is pegged as one of the longest tunnels under the Char Dham all-weather road project.
- It aims to reduce the journey from Uttarkashi to Yamunotri Dham by 26 kilometres.
- From the Silkyara side, 2.3km of tunnel has been constructed, while 1.6km of tunnelling work has been completed from the Barkot end.
- Approximately, a 400m stretch of the tunnel is yet to be constructed.
- The Silkyara tunnel is part of the ongoing construction between Silkyara and Dandalgaon on the Brahmakhal-Yamunotri stretch of the National Highway under the Char Dham project.
- Char Dham Project: Launched in December 2016, it aims to enhance connectivity between the four pilgrimage sites of Char Dham—Kedarnath, Badrinath, Yamunotri, and Gangotri.
Source: Times of India
New Zealand
Subject: Geography
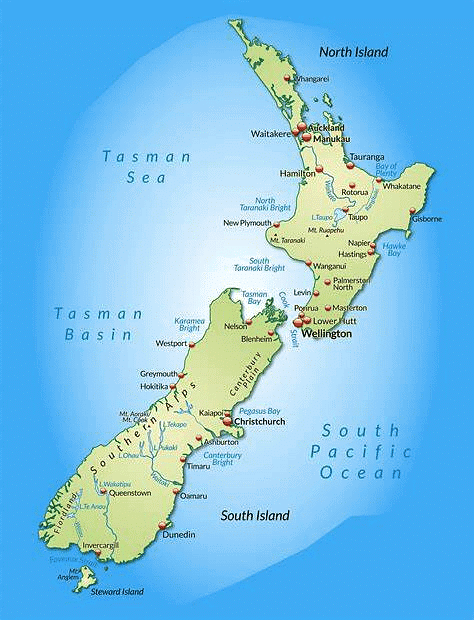
Why in News?
Recently, Christopher Luxon sworn in as New Zealand’s prime minister.
Background:-
- The swearing-in ceremony was presided over by Governor-General Cindy Kiro.
About New Zealand:-
- New Zealand, an island country in the South Pacific Ocean, the southwesternmost part of Polynesia.
- It lies more than 1,000 miles (1,600 km) southeast of Australia, its nearest neighbour.
- The country comprises two main islands—the North and the South Island—and a number of small islands, some of them hundreds of miles from the main group.
- The capital city is
- The largest urban area in Auckland.
- The North Island of New Zealand has a ‘spine’ of mountain ranges running through the middle, with gentle rolling farmland on both sides.
- The central North Island is dominated by the Volcanic Plateau, an active volcanic and thermal area.
- The massive Southern Alps form the backbone of the South Island. To the east of the Southern Alps is the rolling farmland of Otago and Southland, and the vast, flat Canterbury Plains.
India-New Zealand Relations:-
- Historical Relations: India and New Zealand have a longstanding, friendly and growing relationship. Our ties go back to the 1800s, with Indians settling in Christchurch as early as the 1850s.
- Political Relations: India and New Zealand have cordial and friendly relations rooted in the linkages of the Commonwealth, parliamentary democracy, and the English language.
- Economic relations: India NZ Business Council (INZBC) and India NZ Trade Alliance (INZTA) are the two prominent organizations working to promote India-NZ trade and investment relations.
- Cultural Relations: All Indian festivals including Diwali, Holi, Rakshabandhan, Baisakhi, Guruparv, Onam, Pongal, etc. are celebrated with much enthusiasm all over NZ.
Source: AIR
GS-II
Rythu Bandhu Scheme
Subject: Polity and Governance

Why in News?
The Election Commission recently withdrew the permission given to the Telangana government to disburse financial aid to farmers under the Rythu Bandhu Scheme.
About Rythu Bandhu Scheme:
- The Rythu Bandhu scheme, also known as the Farmer's Investment Support Scheme (FISS), is a welfare programme for farmers started by the Telangana government in 2018.
- The objective of this scheme is twofold:
- to provide a timely cash grant for the initial investment needs of farmers
- to ensure that farmers do not fall into the debt trap.
- Under the scheme, financial assistance of Rs 5,000 per acre per farmer each season is directly transferred to each farmer's account.
- This financial support was distributed biannually, allocated for both the kharif and rabi harvests.
- The assistance can be used for the purchase of inputs like seeds, fertilizers, pesticides, labour, and other investments in the field operations of Farmer’s choice for the crop season.
- Eligibility:
- The scheme is open to all resident farmers in the state who own land.
- Farmers cultivating the land in the forest, a majority of them from Scheduled Tribe communities and having a Record of Forest Rights (ROFR) document, are also eligible to receive benefits under the scheme.
- It is the country's first direct farmer investment support scheme where cash is paid directly to the beneficiary.
Source: Deccan Herald
Qatar
Subject: International Relations
Why in News?
Recently, Qatar said that an agreement was reached to extend a truce in Gaza between Israel and Hamas by two more days.
Background:-
- In a social media post, Qatar’s foreign ministry spokesperson Majed Al-Ansari said that the truce between Israel and Hamas in the Gaza Strip will be extended by two days, opening the way for further releases of hostages and prisoners.
About Qatar:-
- Qatar is located in Asia continent.
- It is primarily a desert country.
- The temperatures in the summer go above 40 degrees Celsius with high humidity.
- Qatar shares a land border with Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, and the United Arab Emirates.
- Due to the presence of massive offshore natural gas fields, the nation has one of the world’s highest per capita incomes.
- The majority of its 2.9 million people live around its capital, Doha, on its eastern coast.
Background of the ISRAEL-PALESTINE war:-
- Both Israelis and Palestinians were struggling for self-determination and sovereignty over the territory, developing respective movements for their causes.
- Both Palestinians and Israelis see the territory between the Jordan River and the Mediterranean Sea as their own, and Christians, Jews, and Muslims all hold parts of the land as sacred.
- The past seven decades have brought war and uprisings.
Historic Timeline of the war:-
- Ottoman Empire: The Ottoman Empire had controlled that part of the Middle East from the early 16th century until control of most of the region was granted to the British after World War I.
- In 1916: the Sykes-Picot Agreement secretly negotiated between Britain and France planned to carve up the Middle East into spheres of influence, and determined that the land in question was to be internationalized.
- In 1917: Britain’s foreign secretary, Lord Arthur Balfour, expressed his government’s support for “the establishment in Palestine of a national home for the Jewish people.
- 1947: After World War II, nearing the end of the British Mandate for Palestine, the United Nations General Assembly in 1947 passed Resolution 181, urging the partition of the land into two independent states — one Arab and one Jewish.
- Religiously significant Jerusalem is to be under special international administration.
- The plan is not implemented after the Arab side rejects it, arguing that it is unfavourable to their majority population.
- Violence in the regional conflict grows.
- 1948: Israel declares independence.
- Israel declared independence in May 1948.
- The next day, a coalition of Arab states, allied with Palestinian factions, attacked Israeli forces in what became the first of several Arab-Israeli wars.
- In the end, Israel gains control of an even larger portion of territory — not including the areas of the West Bank and Gaza Strip
- January 2023: Israeli forces raid the Palestinian city of Jenin, killing nine people in a shootout.
- Summer 2023: Retaliatory attacks flare
- Israel launches surprise airstrikes across the Gaza Strip in May.
- October 2023: Israel is attacked by Hamas.
- Prime Minister of Israel, Netanyahu formally declared war on Hamas on Oct. 8 following a surprise assault by Hamas militants that came a day after the 50th anniversary of the start of the 1973 Yom Kippur War.
Source: AIR
GS-III
Centre announces phased introduction of Biogas Blending for domestic use
Subject: Economy

Why in News?
The Centre plans to enhance its domestic energy sustainability by introducing mandatory blending of compressed biogas (CBG) with Natural Gas.
Mandatory Biogas Blending
This initiative aims to reduce the country’s reliance on natural gas imports and lower emissions.
- Initial Phase (April 2025): The mandatory blending of CBG with natural gas will begin at 1%. This blend will be suitable for use in automobiles and households.
- Progressive Increase (By 2028): The government plans to gradually increase the mandatory blending percentage to around 5% by 2028. This step will further reduce the dependence on pure natural gas.
Why such move?
- India is among the world’s largest importers of oil and gas, with nearly half of its gas consumption relying on imports.
- The blending initiative is designed to curb import costs and enhance energy security.
- These measures align with India’s broader objective of achieving net-zero emissions by 2070.
Comparative Analysis of Biogas, Natural Gas, and LPG
| Biogas | Natural Gas | LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas) | |
| Composition | Organic matter decomposition (mainly methane and CO2). | Fossil fuel (primarily methane). | Byproduct of natural gas processing (propane, butane). |
| Production | Anaerobic digestion of organic waste. | Extracted from underground, requires refining. | Obtained during natural gas processing and refining. |
| Energy Content | Lower due to high CO2 content. | High, efficient for heating and power. | High per volume, efficient in liquefied state. |
| Environmental Impact | Renewable, carbon-neutral. | Cleaner than coal/oil, but emits greenhouse gases. | Fewer pollutants than gasoline/diesel, emits greenhouse gases. |
| Uses | Heating, electricity, vehicle fuel, cooking in rural areas. | Heating, electricity, industrial processes, vehicle fuel. | Heating, cooking, vehicles, industrial applications. |
| Storage/Transport | Stored as gas or liquid; requires tanks. | Pipelines for gas; LNG for long-distance. | Pressurized tanks as liquid. |
Source: Indian Express
AstroSat
Subject: Science and Technology

Why in News?
India's first multi-wavelength space telescope, AstroSat, has successfully detected its 600th Gamma-ray Burst (GRB), an event named GRB 231122B.
About AstroSat:
- It is India’s first dedicated multi-wavelength space observatory aimed at studying celestial sources in X-ray, optical, and UV spectral bands simultaneously.
- AstroSat, with a lift-off mass of 1515 kg, was launched by the Indian launch vehicle PSLV from Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota, on September 28, 2015, into a 650 km orbit inclined at an angle of 6 degrees to the equator.
- The spacecraft control centre at Mission Operations Complex (MOX) of ISRO Telemetry, Tracking and Command Network (ISTRAC), Bengaluru, manages the satellite during its entire mission life.
- The minimum useful life of the AstroSat mission is around 5 years.
- It carries a total of five scientific payloads, enabling imaging and studying the temporal and spectral properties of galactic and extra-galactic cosmic sources in a wide range of wavelengths on a common platform.
- Scientific Objectives:
- To understand high energy processes in binary star systems containing neutron stars and black holes.
- Estimate magnetic fields of neutron stars.
- Study star birth regions and high energy processes in star systems lying beyond our galaxy.
- Detect new, briefly bright X-ray sources in the sky.
- Perform a limited deep-field survey of the Universe in the Ultraviolet region.
Source: India Today
Sagittarius C (Sgr C)
Subject: Science and Technology

Why in News?
Recently, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) captured a stunning image of the dense centre of the Milky Way galaxy with clarity never seen before.
About Sagittarius C (Sgr C):
- It is the star-forming region known to be situated approximately 300 light-years from the Milky Way's central supermassive black hole, Sagittarius A*.
- It is revealing a bustling cluster of protostars within an infrared-dark cloud.
- These nascent stars are in the process of accumulating mass, their outflows glowing intensely in the infrared spectrum, akin to embers in a cosmic bonfire.
- The cloud that protostars are emerging from is so dense that the light from stars behind it cannot reach Webb.
- Scattered throughout are smaller infrared-dark clouds, akin to celestial voids against the starry backdrop, signalling the birthplaces of future stars.
- Webb's Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) has detected extensive emissions from ionised hydrogen on the periphery of the dark cloud, highlighted in a striking cyan hue.
Key facts about the James Webb Space Telescope
- It was built in collaboration between NASA, the European Space Agency(ESA) and the Canadian Space Agency.
- It was launched in December 2021.
- It is presently at a point in space known as the Sun-Earth L2 Lagrange point.
- Lagrange Point 2 is one of the five points in the orbital plane of the Earth-Sun system.
- It's the largest, most powerful infrared space telescope ever built.
- Objectives: It will examine every phase of cosmic history, from the Big Bang to the formation of galaxies, stars, and planets to the evolution of our Solar System.
Source: India Today
|
39 videos|4265 docs|898 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 28th November 2023 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the Silkyara Tunnel in New Zealand? |  |
| 2. What is the Rythu Bandhu Scheme in Qatar? |  |
| 3. What is the phased introduction of Biogas Blending for domestic use announced by the Centre? |  |
| 4. What is AstroSat? |  |
| 5. What is Sagittarius C (Sgr C)? |  |
|
39 videos|4265 docs|898 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|

















