Ultrasound | Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Ultrasound |

|
| Ultrasound Probe Selection |

|
| Doppler Ultrasound |

|
| Role of USG in Management of Liver Abscess |

|
Ultrasound
Utilizing sound waves in the range of 2-15 MHz, generated by applying an electrical pulse to a piezoelectric crystal, enables the imaging of the body. This process involves detecting the intensity of reflected waves from various organs and representing this intensity as a grayscale or color image.



Understanding how ultrasound is generated and how an image is formed requires grasping two fundamental principles.

Ultrasound Probe Selection
The choice of probe is primarily determined by the organ under examination. Lower ultrasound frequencies penetrate to greater depths, while higher ultrasound frequencies typically offer better resolution. In a general abdominal examination, where larger depths are needed to visualize organs like the liver, pancreas, and spleen, a 3-5 MHz probe (curvilinear surface) is employed. Conversely, for superficial examinations such as the thyroid, scrotum, or orbit, a 7-14 MHz probe (linear surface) is utilized.
In diagnostic radiology, ultrasound frequencies span from 2 MHz to around 15 MHz. It's crucial to note that higher ultrasound frequencies have shorter wavelengths and are more readily absorbed/attenuated. Consequently, higher frequencies are less penetrating, which is why they are employed for superficial body structures, while lower frequencies are used for deeper structures.
Medical ultrasound transducers are equipped with multiple operating frequencies. The following frequency ranges serve as a reference for the typical applications in ultrasound examinations:
- 2.5 MHz: Used for deep abdomen imaging, obstetric examinations, and gynecological imaging.
- 3.5 MHz: Employed in general abdomen imaging, obstetric examinations, and gynecological imaging.
- 5.0 MHz: Utilized for vascular imaging, breast imaging, and pelvic imaging.
- 7.5 MHz: Applied in breast imaging and thyroid examinations.
- 10.0 MHz: Commonly used for breast imaging, thyroid examinations, superficial veins, superficial masses, and musculoskeletal imaging.
- 15.0 MHz: Reserved for imaging superficial structures and musculoskeletal examinations.

Ultrasound-Advantages
- Non-Ionizing radiation
- Non-lnvasive
- Ease of use
- Reproducibility
- Speed of testing
- Low cost
Ultrasound-Applications
- Obstetric examinations
- Doppler ultrasound for vessel imaging
- Ultrasonic lithotripsy (breaking down renal and ureteral calculi)
- Disintegration of gallstones
- Removal of dental plaque
- Assisting in the excision of intracranial and hepatic tumors
- Debridement of heavily calcified cardiac valves
- Imaging for musculoskeletal disorders
- Diaphragm evaluation
- Therapeutic procedures:
- a) Atherosclerotic rupture
- b) Drainage of liver abscess
- Emergency procedures - Fast/eFast
- Breast imaging
- Echocardiogram
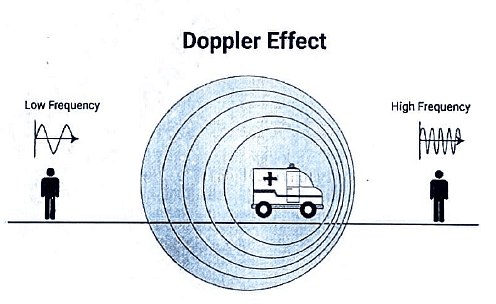
Doppler Ultrasound
- Determines blood flow through the Doppler effect, which involves the change in the perceived frequency of sound emitted by a moving source.
- Color Doppler visualizes flowing blood using the mnemonic "BART":
- RED indicates flow toward the transducer.
- BLUE indicates flow away from the transducer.
Application
- Arterial stenosis
- AV fistula
- Carotid occlusion
- DVT
- Varicose veins
- PVD
- Buergers disease

Indications of Ultrasound in Musculoskeletal disorders
- Synovial (Baker's) cysts
- Tears in the rotator cuff
- Conditions such as bursitis, tendinitis, and tendon injuries
- Enthesitis
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Deposition of urate or calcium pyrophosphate on cartilage
- Early identification of synovial inflammation or erosions
- Ultrasound-guided injection/arthrocentesis
Role of Ultrasound in evaluation of Diaphragm

Role of Ultrasonic energy in atherosclerotic rupture
Balloon angioplasty faces three unresolved limitations:
- Complete obstructions,
- Multisegment multivessel disease,
- Late restenosis.
In addressing these challenges, various new techniques are under investigation, such as
- Hot-tip thermal probes,
- Laser radiation methods,
- Atherectomy catheters,
- High-speed drills,
- Ultrasonic energy (a major advantage being its relative atraumatic nature to normal tissues, including blood vessels).
Role of USG in Management of Liver Abscess
Research: A Crucial Role of Ultrasonography in the Management of Liver Abscesses - Samita Singal, Amit Mittal, Muzzafar Zaman, Rikki Singal. The study encompassed 88 patients diagnosed with liver abscess, utilizing ultrasound-guided percutaneous aspiration or pigtail drainage for management. The findings demonstrate an ultrasonography success rate of nearly 98%, effectively avoiding unnecessary surgical interventions. It was established that needle aspiration for small abscesses and catheter drainage for large abscesses represent the safest and most effective modalities.
|
7 videos|219 docs
|
FAQs on Ultrasound - Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is ultrasound? |  |
| 2. What is Doppler ultrasound? |  |
| 3. How is ultrasound used in the medical field? |  |
| 4. Is ultrasound safe? |  |
| 5. Are there any limitations or risks associated with ultrasound? |  |

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
















