Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Economics for GCSE/IGCSE > Understanding Employment
Understanding Employment | Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Employment Terminology
Crucial concepts to comprehend include employment, labour force, unemployment, and full employment.
- Employment: Signifies the utilization of labor as a production factor within the economy.
- Unemployment: An individual is deemed unemployed if they are not engaged in work but are actively seeking employment.
- Labour force: Divides a country's population into two categories—labour force and non-labour force.
- The labour force encompasses all actively working individuals plus those seeking work (unemployed).
- The non-labour force comprises individuals not seeking employment, such as stay-at-home parents, retirees, and students, who are economically inactive.
- Full employment: Denotes the ideal state wherein all willing and able individuals in the economy are employed.
Question for Understanding EmploymentTry yourself: What is the definition of employment?View Solution
Changing Employment Patterns
- Many economies are witnessing shifts in employment trends among their workforce due to various reasons.
Causes of Changes in Employment Patterns
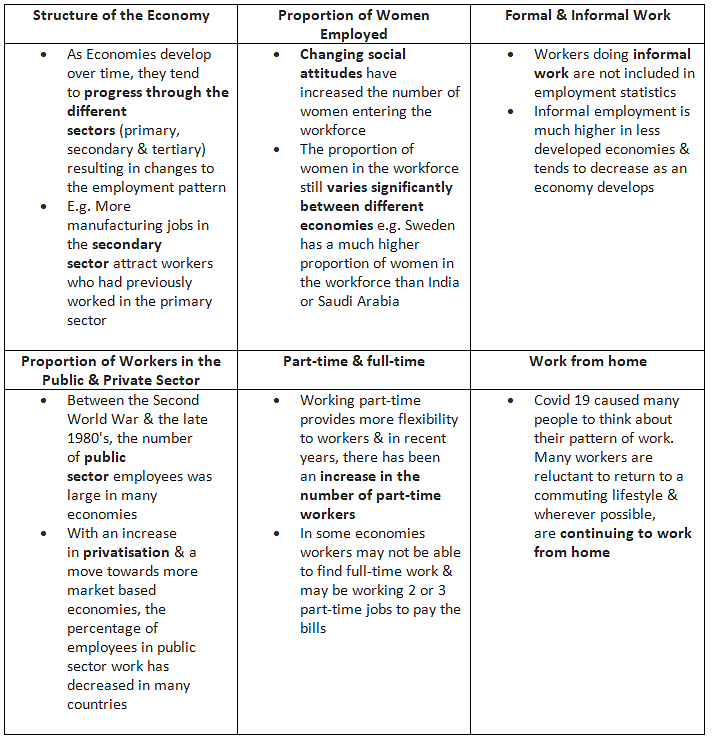
The document Understanding Employment | Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Economics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
56 videos|97 docs|38 tests
|
FAQs on Understanding Employment - Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is the difference between the labour force and the non-labour force? |  |
Ans. The labour force refers to the portion of the population that is either employed or actively seeking employment, while the non-labour force includes individuals who are not employed and not seeking employment, such as students, retirees, and homemakers.
| 2. What does full employment mean in the context of economics? |  |
Ans. Full employment is a situation where all individuals who are willing and able to work at the prevailing wage rates are able to find employment. It does not mean zero unemployment, but rather a level of unemployment that is considered natural due to factors such as frictional and structural unemployment.
| 3. How do changing employment patterns impact the economy? |  |
Ans. Changing employment patterns can affect the economy in various ways, such as altering the demand for certain goods and services, influencing wage levels, and impacting overall economic productivity. For example, a shift from manufacturing to service-based industries can lead to changes in the distribution of income and employment opportunities.
| 4. What factors contribute to fluctuations in employment levels within an economy? |  |
Ans. Fluctuations in employment levels can be influenced by a variety of factors, including changes in consumer demand, technological advancements, government policies, global economic conditions, and shifts in the business cycle. These factors can lead to changes in the level of job creation and destruction within the economy.
| 5. How does the concept of the labour force participation rate relate to measuring employment trends? |  |
Ans. The labour force participation rate is a key indicator used to measure the proportion of the working-age population that is either employed or actively seeking employment. Changes in the labour force participation rate can provide insights into trends in employment and can help policymakers assess the overall health of the labour market.
Related Searches















