Unit Test( Solutions): Integers | Mathematics (Maths) Class 7 (Old NCERT) PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
M.M.: 30
Attempt all questions.
Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
Question numbers 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each.
Q1: Which of the following is a correct example of the commutative property of addition? (1 Mark)
(i) 5 + (-3) = (-3) + 5
(ii) 7 - 2 = 2 - 7
(iii) 8 × (-1) = (-1) × 8
(iv) 9 ÷ 3 = 3 ÷ 9
Ans: (i)
The commutative property of addition means that changing the order of numbers does not change their sum. In option (i), , both expressions equal 2, demonstrating the commutative property.
Other options:
(ii) (subtraction is not commutative),
(iii) shows multiplication's commutative property,
(iv) shows division, which is not commutative.
Q2: Which property states that the sum of two integers is always an integer? (1 Mark)
(i) Associative property
(ii) Distributive property
(iii) Closure property
(iv) Commutative property
Ans: (iii)
The Closure Property for integers states that when you add, subtract, or multiply two integers, the result is always an integer. This property guarantees that performing these operations on integers will never result in a non-integer.
For example:
- (an integer),
- (an integer).
Q3: Subtract (-3) from (-8). (1 Mark)
Ans: (-8) - (-3) = -8 + 3 = -5
Q4: Find the result of multiplying (-6) by (-4). (1 Mark)
Ans: (-6) × (-4) = 24
Q5: What is the additive identity for integers? (1 Mark)
Ans: The additive identity for integers is 0 because adding 0 to any integer does not change its value.
Q6: Find three integers whose sum gives 0. (2 Marks)
Ans: One possible combination is: 5, -3, and -2.
5 + (-3) + (-2) = 5 - 3 - 2 = 0.
Q7: Simplify: (-8) × (-7) + (-10) × (-2). (2 Marks)
Ans: First product:
(-8) × (-7) = 56 (negative × negative = positive)
Second product:
(-10) × (-2) = 20 (negative × negative = positive)
Add the results:
56 + 20 = 76
Q8: Subtract the integer -15 from 9 and check if subtraction is commutative for integers. (2 Marks)
Ans: Step 1: Subtract -15 from 9
9 − (−15) = 9 + 15 = 24
Step 2: Check commutativity
Subtraction is commutative if:
a − b = b − a (for all integers a, b).
Here, take a = 9 and b = −15:
9 − (−15) = 24
(−15) − 9 = −15 − 9 = −24
Since 24 ≠ −24, subtraction is not commutative for integers.
Q9: Verify whether the following holds true for integers: (3 Marks)
(-12) × (4 + 6) = (-12) × 4 + (-12) × 6.
Ans: Left-hand side (LHS):
(-12) × (4 + 6)
= (-12) × (10)
= -120
Right-hand side (RHS):
(-12) × 4 + (-12) × 6
= -48 + (-72)
= -48 - 72
= -120
Hence, LHS = RHS, the distributive property holds true.
Q10: In a quiz, team A scored (-50), 30, and (-20) in three successive rounds. Team B scored 20, (-40), and (-10) in three successive rounds.(3 Marks)
(i) Which team has a higher score?
(ii) What is the difference in their total scores?
Ans: Team A’s score:
= (−50) + 30 + (−20)
= −50 + 30 − 20
= −40
Team B’s score:
= 20 + (−40) + (−10)
= 20 − 40 − 10
= −30
(i) Which team has a higher score?
Team A = −40
Team B = −30
Since −30 > −40,
Team B has the higher score.
(ii) What is the difference in their total scores?
Difference = (−30) − (−40) = −30 + 40 = 10
Q11: Starting from , write a series of products showing a pattern that eventually leads to the result . (3 Marks)
Ans:
Let’s observe the following products:
The pattern shows that as the multiplier decreases, the product becomes less negative, and when multiplying by a negative number, the product becomes positive. Therefore,
Q12: A shopkeeper earns a profit of ₹2 by selling one notebook and incurs a loss of 50 paise per eraser while selling erasers from old stock. (5 Marks)
(i) In a particular month, the shopkeeper incurs a loss of ₹10. During this period, the shopkeeper sold 60 notebooks. How many erasers did the shopkeeper sell in this period?
(ii) In the next month, the shopkeeper neither makes a profit nor incurs a loss. If the shopkeeper sold 90 notebooks, how many erasers did the shopkeeper sell?
Ans:
(i)
- Profit per notebook = ₹2
- Loss per eraser = ₹0.50
(i) Net loss ₹10; 60 notebooks sold
Let erasers sold = e.
Net profit = (profit from notebooks) − (loss from erasers)
⇒ 120 − 0.5e =−10
⇒ 0.5 e = 130
⇒ e = 260
(ii) No profit, no loss; 90 notebooks sold
180 −0.5e = 0
⇒0.5e = 180
⇒e = 360
Q13: The temperature at 8 AM was 12°C above zero. If it decreases at the rate of 3°C per hour, at what time will the temperature be 9°C below zero? What will be the temperature at 6 PM? (5 Marks)
Ans:
Initial temperature at 8 AM = 12°C.
The temperature decreases by 3°C per hour.
We need to find how many hours it takes for the temperature to drop from 12°C above zero to 9°C below zero.
Total temperature drop =
Now, since the temperature drops by 3°C per hour:
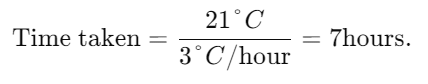
Starting at 8 AM + 7 hours =3PM.
Thus, the temperature will be 9°C below zero at 3 PM.
At 6 PM (3 hours after 3 PM), the temperature will continue to decrease:
−(3°C×3hours)=−9°C−9°C=−18°C.Thus, the temperature at 6 PM will be -18°C.
|
77 videos|386 docs|39 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test( Solutions): Integers - Mathematics (Maths) Class 7 (Old NCERT)
| 1. What are some common hobbies that involve integers? |  |
| 2. How can I use integers in my daily hobbies? |  |
| 3. Are there any educational benefits to hobbies involving integers? |  |
| 4. What are some examples of games that use integers? |  |
| 5. Can practicing hobbies that involve integers improve my math skills? |  |






















