Unit Test(Solutions): Heat | Science Class 7 (Old NCERT) PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
Maximum Marks: 30
Attempt all questions.
Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
Question numbers 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each.
Q1: Fill in the blank: The temperature of boiling water cannot be measured by a __________ thermometer. (1 Mark)
Ans: Clinical
Q2: Which of the following is a poor conductor of heat? (1 Mark)
(i) Iron
(ii) Copper
(iii) Plastic
(iv) Aluminum
Ans: (iii)
Plastic is a poor conductor of Heat.
Q3: Match the following:
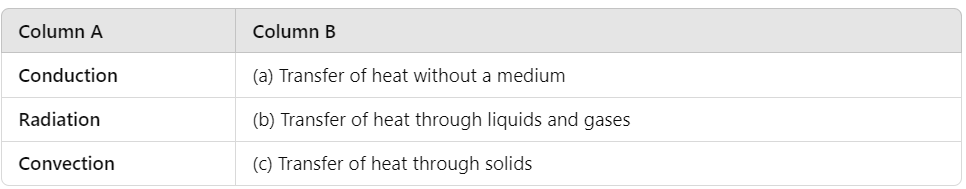
Ans:
Conduction - (c) Transfer of heat through solids
Radiation - (a) Transfer of heat without a medium
Convection - (b) Transfer of heat through liquids and gases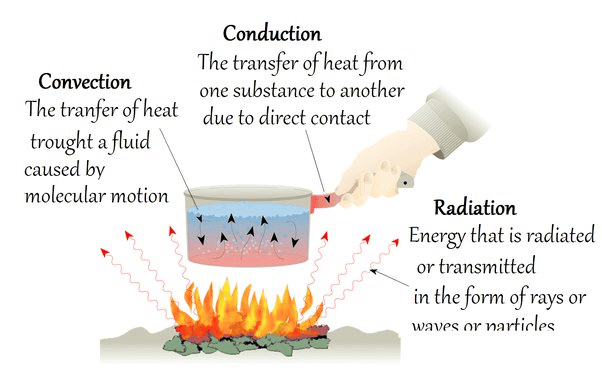
Q4: True or False: Dark-coloured clothes absorb more heat than light-coloured clothes.(1 Mark)
Ans: True
Dark-coloured clothes absorb more heat than light-coloured clothes as light coloured clothes reflect heat.
Q5: Which of the following is an example of heat transfer through convection? (1 Mark)
(i) Heating a metal rod in a flame
(ii) Boiling water in a pot
(iii) Feeling the warmth of the sun
(iv) Ironing clothes with a hot iron
Ans: (ii)
Convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids (liquids or gases). Boiling water in a pot is an example of convection, where hot water rises and cooler water sinks, creating a circulation of heat.
Q6: What precautions should be taken while using a clinical thermometer? (2 Marks)
Ans:
- Wash the thermometer before and after use, preferably with an antiseptic solution.
- Ensure the mercury level is below 35°C before using it.
- Read the thermometer by keeping the mercury level at eye level.
- Do not hold the thermometer by the bulb while reading.

Q7: Explain the difference between conductors and insulators with examples.(2 Marks)
Ans:
Q8: What happens when you dip a steel spoon in a cup of hot tea? Explain the process involved. (2 Marks)
Ans: When you dip a steel spoon in hot tea, heat is transferred from the hot tea to the spoon through the process of conduction. As steel is a good conductor, the other end of the spoon also becomes hot.
Q9: List six precautions to be taken while reading a laboratory thermometer. (3 Marks)
Ans:
- Hold the thermometer upright and ensure it is not tilted.
- Ensure the bulb is fully immersed in the substance being measured.
- The bulb should not touch the sides or bottom of the container.
- The mercury level should be steady before reading.
- Always read the thermometer at eye level.
- Do not use a laboratory thermometer to measure body temperature.
Q10: Explain the three methods of heat transfer in detail and give one example for each. (3 Marks)
Ans:
- Conduction: The process by which heat is transferred from the hotter part of a solid to the cooler part without the movement of the material itself. Example: Heat transfer through a metal rod.
- Convection: The transfer of heat in liquids and gases where the warmer part of the liquid or gas moves to the cooler area. Example: Boiling water in a pot.
- Radiation: The transfer of heat without the need for a medium. Heat is transferred through electromagnetic waves. Example: Heat from the Sun reaching the Earth.
Q11: What are the differences between a clinical thermometer and a laboratory thermometer? (3 Marks)
Ans: 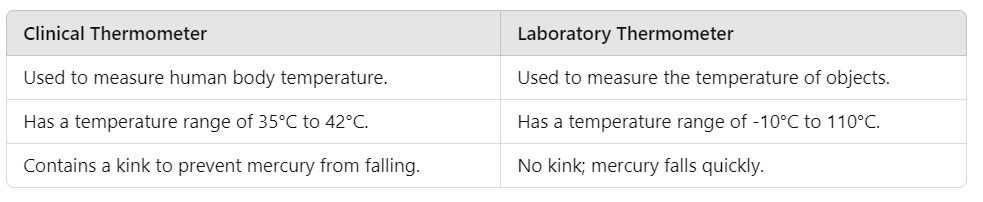
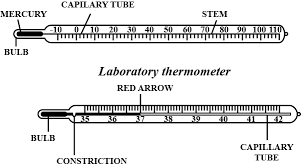 Clinical Thermometer Below oneQ12: Describe how you would perform an activity to demonstrate convection in water. (5 Marks)
Clinical Thermometer Below oneQ12: Describe how you would perform an activity to demonstrate convection in water. (5 Marks)
Ans:
Materials Required: A round-bottom flask, Water, Tripod stand, Candle or spirit lamp, Straw, Crystal of potassium permanganate (a coloured substance)
Procedure:
Fill the round-bottom flask two-thirds full with water.
Place the flask on a tripod stand to ensure it is stable and properly positioned.
Using a straw, gently place a small crystal of potassium permanganate at the bottom of the flask. The potassium permanganate is used because it has a dark purple color, which helps to visualize the movement of water.
Light a candle or spirit lamp and place it directly under the crystal of potassium permanganate, so that the area below the crystal heats up.
Observation:
- As the water around the candle heats up, it becomes less dense and begins to rise. At the same time, the cooler water from the sides, which is denser, moves down to take its place.
- You will see the purple color from the potassium permanganate forming streaks as it moves along with the water currents. This circulation of water is clearly visible because of the color, demonstrating the movement of warm water upwards and cold water downwards.
Conclusion:
This experiment demonstrates convection, the process by which heat is transferred through liquids or gases. In convection, the warmer, less dense liquid (or gas) rises while the cooler, denser liquid (or gas) sinks, creating a circulation pattern. This activity helps visualize how heat is transferred through the movement of water, which is typical in everyday situations like boiling water in a pot.
Q13: Explain in detail Sea Breeze and Land Breeze. (5 Marks)
Ans: Sea breeze and land breeze are phenomena related to the movement of air in coastal areas, caused by differences in temperature between the land and sea.
Sea Breeze:
- During the day, the land heats up faster than the sea.
- As the air above the land becomes warmer, it rises.
- The cooler air from the sea moves in to take the place of the warm air over the land.
- This cooler air from the sea is called the sea breeze.
Land Breeze:
- At night, the land cools down more quickly than the sea.
- The air above the sea stays warmer, and the cooler air from the land moves towards the sea.
- This flow of air from the land to the sea is known as the land breeze.
These breezes are common in coastal areas and are caused by the differential heating and cooling of land and water.
|
112 videos|286 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test(Solutions): Heat - Science Class 7 (Old NCERT)
| 1. What are some popular hobbies that involve heat? |  |
| 2. How can I safely engage in hobbies that involve heat? |  |
| 3. What equipment do I need for cooking as a heat hobby? |  |
| 4. Can I start heat-related hobbies on a budget? |  |
| 5. What are the benefits of engaging in heat hobbies? |  |

















