Unit Test(Solutions): Nutrition in Plants | Science Class 7 (Old NCERT) PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
M.M: 30
Attempt all questions.
Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
Question numbers 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each.
Q1: Which of the following describes the mode of nutrition in saprotrophs?
(i)They make their food using sunlight and carbon dioxide.
(ii)They obtain nutrients from dead and decaying organic matter.
(iii)They feed on other living organisms.
(iv)They trap insects and digest them for nutrients.
Ans:(ii)
Saprotrophs, such as fungi, absorb nutrients from dead and decaying matter. This mode of nutrition is known as saprotrophic nutrition. Unlike autotrophs that use sunlight, saprotrophs rely on organic material for their sustenance.
Q2: Fill in the blank: Plants that synthesise their own food are called _________. (1 Mark)
Ans: Autotrophs
Q3: Match the following:
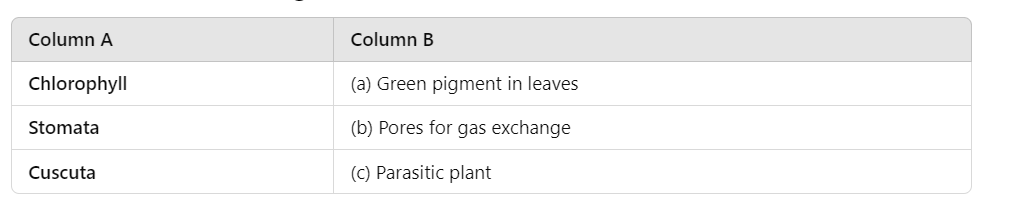
Ans: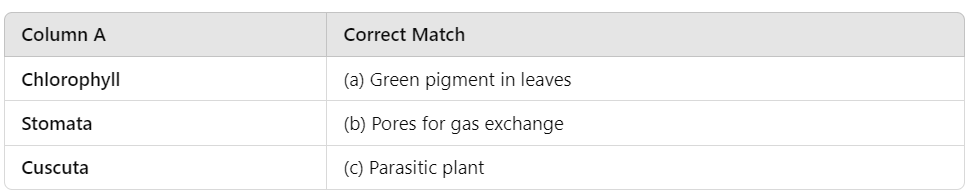
Q4: Cuscuta, Mushroom, Rose plant, Pitcher plant – which one is the odd one out and why?
Ans: The odd one out is the Rose plant.
The Rose plant is an autotroph, meaning it can produce its own food through photosynthesis using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide. On the other hand, Cuscuta is a parasitic plant that depends on a host for nutrition, Mushroom is a saprotroph that feeds on dead and decaying matter, and Pitcher plant is an insectivorous plant that traps and digests insects for nutrients. Therefore, the Rose plant is different from the others as it is the only autotrophic organism in this group.
Q5: True or False: Symbiosis is a relationship where two organisms live together and both benefit from each other. (1 Mark)
Ans: True
In a symbiotic relationship, both organisms benefit from each other. For example, Rhizobium bacteria live in the roots of leguminous plants, providing them with nitrogen, while the plant offers the bacteria food and shelter.
Q6: Why do plants need nitrogen, and how do they obtain it? (2 Marks)
Ans: Plants need nitrogen to synthesise proteins and other important compounds. They obtain nitrogen from the soil, where certain bacteria (like Rhizobium) convert atmospheric nitrogen into a usable form, or through the use of nitrogen-rich fertilisers.
Q7: How does the pitcher plant obtain nutrients? (2 Marks)
Ans: The pitcher plant traps and digests insects to obtain nutrients. The apex of the leaf forms a pitcher-like structure, and when an insect falls into it, digestive juices break it down, allowing the plant to absorb the nutrients.

Q8: How do algae prepare their food, and why are they green? (2 Marks)
Ans: Algae contain chlorophyll, which gives them a green color. Like green plants, they prepare their food through photosynthesis by using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide.
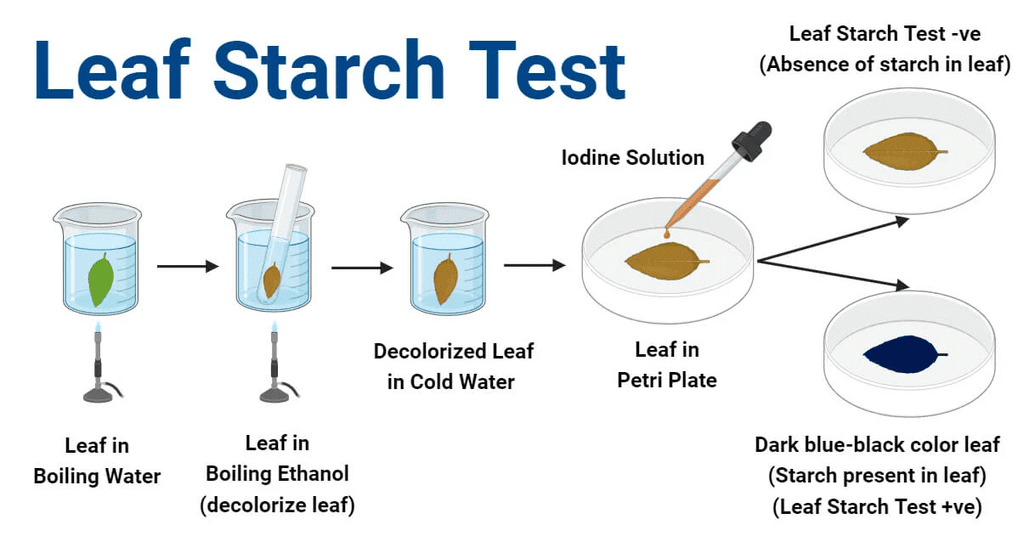
Q9: How would you test the presence of starch in leaves? (3 Marks)
Ans:
To test the presence of starch in leaves, follow these steps:
Pluck a leaf: Take a green leaf from a plant that has been exposed to sunlight for a few hours.
Boil the leaf: Boil the leaf in water for a few minutes to kill the cells and soften it.
Boil in alcohol: Then, place the leaf in alcohol (usually ethanol) and boil it in a water bath. This removes the chlorophyll, turning the leaf pale or white.
Rinse with water: After boiling in alcohol, rinse the leaf with warm water to soften it.
Apply iodine solution: Place the leaf on a flat surface and add a few drops of iodine solution to it.
Observation: If starch is present, the leaf will turn blue-black when iodine is applied. If there is no starch, the leaf will not change color, remaining a brownish-yellow.
Q10: Differentiate between autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition in plants. (3 Marks)
Ans: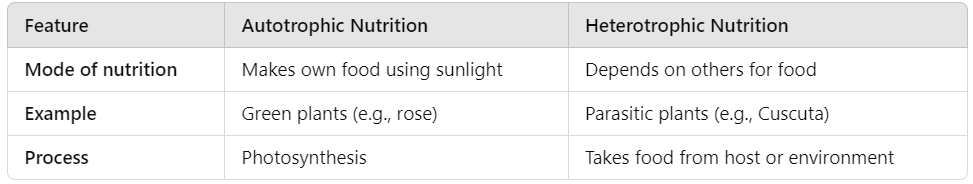
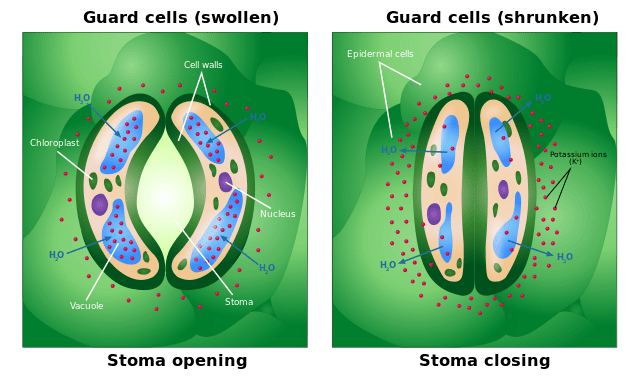
Q11: What are the roles of guard cells in the process of photosynthesis, and how do they help in regulating the exchange of gases and water loss in plants? (3 Marks)
Ans:
- Guard cells are specialized cells that surround the stomata (tiny openings) on the surface of leaves.
- They regulate the opening and closing of the stomata, controlling the exchange of gases during photosynthesis.
- During photosynthesis, the stomata open to allow carbon dioxide to enter the leaf, which is used in the process to produce food.
- At the same time, oxygen, which is a by-product of photosynthesis, is released through the open stomata.
- Guard cells also play a crucial role in maintaining water balance in the plant. They close the stomata when water is scarce to prevent excessive water loss through transpiration.
- This regulation ensures that the plant can take in carbon dioxide for photosynthesis while minimizing water loss, especially in dry conditions.
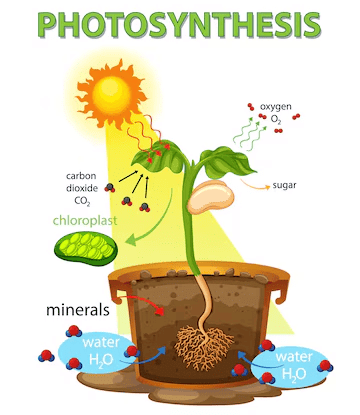
Q12: Describe the process of photosynthesis in green plants and explain its significance.(5 Marks)
Ans:
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants prepare their food using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water. It takes place mainly in the leaves of plants, which contain a green pigment called chlorophyll. Here is how the process works:
Absorption of sunlight: Chlorophyll present in the leaf cells captures energy from sunlight.
Intake of carbon dioxide: Carbon dioxide from the air enters the leaves through tiny pores called stomata. These stomata are controlled by guard cells, which open and close the pores.
Absorption of water: Water is absorbed by the plant roots from the soil and is transported to the leaves via the plant's vascular system.
Formation of glucose: In the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll, the plant converts carbon dioxide and water into glucose (a form of sugar) and oxygen.
The overall chemical equation for photosynthesis is:

This means that six molecules of carbon dioxide and six molecules of water produce one molecule of glucose and six molecules of oxygen.
Oxygen release: Oxygen, which is a by-product of photosynthesis, is released into the atmosphere through the stomata.
Significance of Photosynthesis:
- Food production: Photosynthesis is essential for the production of food (glucose), which serves as a source of energy for plants and, indirectly, for other organisms, including humans.
- Oxygen supply: The oxygen produced during photosynthesis is vital for the survival of almost all living organisms as it is used for respiration.
- Energy storage: Glucose, produced in the process, is stored in the form of starch and is used by the plant for energy during growth and reproduction. This stored energy also forms the base of the food chain.
- Maintaining balance: Photosynthesis helps maintain the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, which is crucial for sustaining life on Earth.
Without photosynthesis, life on Earth would be impossible as it is the primary process that supports the energy needs of almost all ecosystems .
Q13: Explain the role of Rhizobium bacteria in replenishing soil nutrients. (5 Marks)
Ans:
- Rhizobium is a type of bacteria that lives in the root nodules of leguminous plants (e.g., peas, beans).
- It has the ability to convert atmospheric nitrogen into a form that plants can absorb, such as nitrates.
- In exchange, the plant provides food and shelter to the bacteria, forming a symbiotic relationship.
- This process is essential because nitrogen is a critical nutrient for plant growth, but plants cannot absorb atmospheric nitrogen directly.
- Rhizobium helps maintain soil fertility by naturally replenishing nitrogen levels, reducing the need for chemical fertilisers.
- The bacteria convert nitrogen gas into a usable form, such as ammonia or nitrates, which are absorbed by plants along with water.
- Farmers benefit from this relationship by growing legumes, which help enrich the soil with nitrogen.
- This process helps promote sustainable agriculture by improving soil health.
- Rhizobium bacteria are crucial in maintaining the balance of nitrogen in the environment.
- This natural process plays a key role in the nitrogen cycle, supporting the ecosystem and plant life.

|
111 videos|286 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test(Solutions): Nutrition in Plants - Science Class 7 (Old NCERT)
| 1. What are the different modes of nutrition in plants? |  |
| 2. How do plants perform photosynthesis? |  |
| 3. What role do nutrients play in plant health? |  |
| 4. How do carnivorous plants obtain nutrients? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of mycorrhizal fungi in plant nutrition? |  |






















