Unit Test: Triangles | Mathematics (Maths) Class 10 PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
M.M. 30
Attempt all questions.
- Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
- Question numbers 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each.
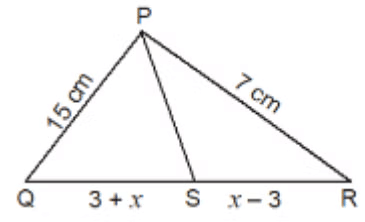
Q1. In ΔPQR, if PS is the internal bisector of ∠P meeting QR at S and PQ = 15 cm, QS = (3 + x) cm, SR = (x – 3) cm and PR = 7 cm, then find the value of x. (1 Mark)
(a) 2.85 cm
(b) 8.25 cm
(c) 5.28 cm
(d) 8.52 cm
Q2: If ABC and DEF are two triangles and AB/DE=BC/FD, then the two triangles are similar if (1 Mark)
(a) ∠A=∠F
(b) ∠B=∠D
(c) ∠A=∠D
(d) ∠B=∠E
Q3: If in two triangles ABC and PQR, AB/QR = BC/PR = CA/PQ, then (1 Mark)
(a) ΔPQR ~ ΔCAB
(b) ΔPQR ~ ΔABC
(c) ΔCBA ~ ΔPQR
(d) ΔBCA ~ ΔPQR
Q4: Write the truth value (T/F) of each of the following statements : (1 Mark)
(i) Any two similar figures are congruent.
(ii)Two polygons are similar, if their corresponding sides are proportional.
Q5: D and E are respectively the points on sides AB and AC of triangle ABC such that AB = 3 cm, BD = 1.5 cm, BC = 7.5 cm, and DE || BC. What is the length of DE? (1 Mark)
(a) 2 cm
(b) 2.5 cm
(c) 3.75 cm
(d) 3 cm
Q6: In the figure, DE // AC and DF // AE. Prove that BF/FE = BE/EC. (2 Marks)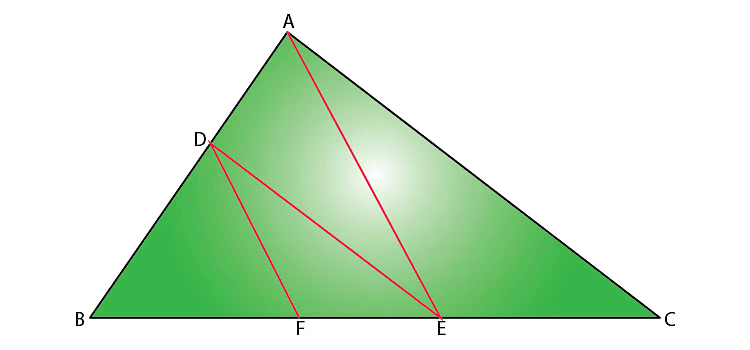
Q7: In the figure, DE || BC. Find the length of side AD, given that AE = 1.8 cm, BD = 7.2 cm and CE = 5.4 cm. (2 Marks)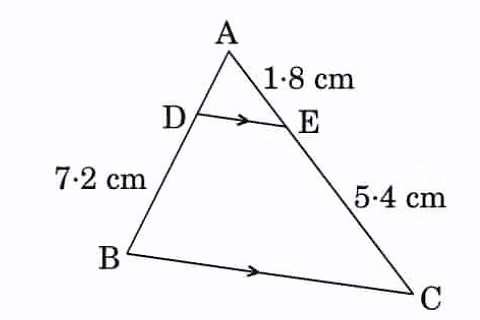
Q8: In the given figure, XY || QR,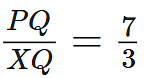 and PR = 6.3 cm, find YR. (2 Marks)
and PR = 6.3 cm, find YR. (2 Marks)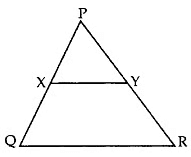
Q9: D and E are points on sides AB and AC of triangle ABC such that DE || BC. If AD = 2·4 cm, DB = 3.6 cm and AC = 5 cm, find AE. (3 Marks)
Q10: X and Y are points on the sides AB and AC respectively of a triangle ABC such that 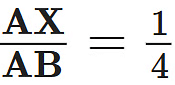 , AY = 2 cm and YC = 6 cm. Find whether XY || BC or not. (3 Marks)
, AY = 2 cm and YC = 6 cm. Find whether XY || BC or not. (3 Marks)
Q11: If a line segment intersects sides AB and AC of a ∆ABC at D and E respectively and is parallel to BC, prove that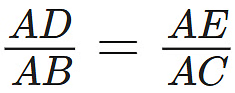 . (3 Marks)
. (3 Marks)
Q12: In the given figure, altitudes AD and CE of ∆ ABC intersect each other at the point P. Show that: (5 Marks)
(i) ∆AEP ~ ∆ CDP
(ii) ∆ABD ~ ∆ CBE
(iii) ∆AEP ~ ∆ADB
(iv) ∆ PDC ~ ∆ BEC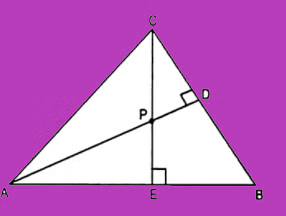
Q13: In given figure, EB ⊥ AC, BG ⊥ AE and CF ⊥ AE. (5 Marks)
Prove that:
(a) ∆ABG ~ ∆DCB
(b) 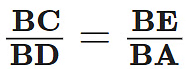
You can find the solutions of this Unit Test here: Unit Test (Solutions): Triangles
|
127 videos|584 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test: Triangles - Mathematics (Maths) Class 10
| 1. What are the different types of triangles based on their sides? |  |
| 2. How do you determine if three lengths can form a triangle? |  |
| 3. What are the types of triangles based on their angles? |  |
| 4. How do you calculate the area of a triangle? |  |
| 5. What is the Pythagorean theorem and how does it apply to right triangles? |  |

















