UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC > Urinary Bladder, Uterine Tubes, Vas Deferens: Clinical Anatomy
Urinary Bladder, Uterine Tubes, Vas Deferens: Clinical Anatomy | Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
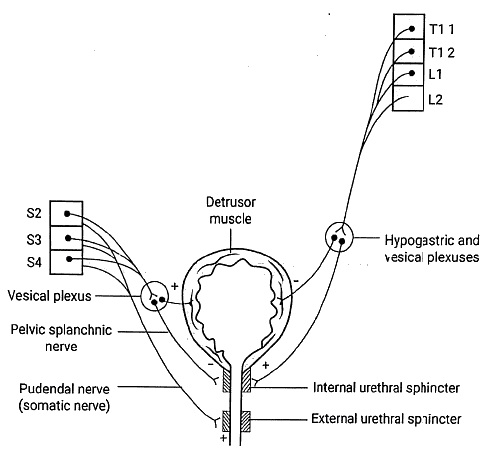
Urinary Bladder
- Bladder with trabeculations - Associated with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) and chronic obstruction.
- Bladder with an hourglass shape
- Ectopia vesicae
- Suprapubic cystotomy
- Urinary incontinence
- Bladder with automatic reflex
- Independent or autonomous bladder
Question for Urinary Bladder, Uterine Tubes, Vas Deferens: Clinical AnatomyTry yourself: Which condition is associated with a bladder showing trabeculations?View Solution
Clinical Anatomy - Uterine Tubes
- Inflammation of the fallopian tubes (Salpingitis)
- Assessments for fallopian tube patency
- Insufflation test/Rubin's test
- Hysterosalpingography
- Pregnancy occurring within the fallopian tubes (Tubal pregnancy)
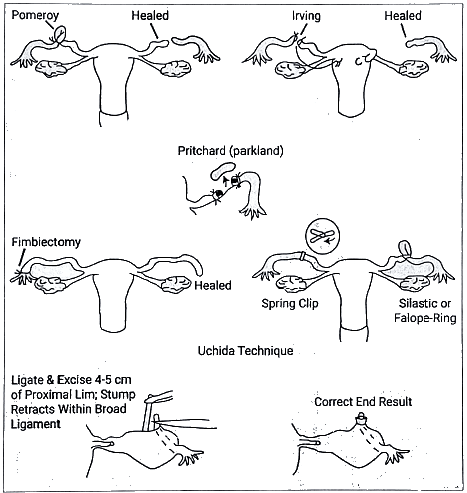
- Surgical procedure for fallopian tube sterilization (Tubectomy)

Tubectomy (sterilization)
- Coagulation using laparoscopy
- Application of tubal clip or ring
- Frimbriectomy
- Irving's procedure
- Pomeroys technique
- Uchida technique
- Pritchard or Parkland technique
[Question: 940785]
Clinical Anatomy - Vas Deferens
Vasectomy
- Couples should be advised to maintain regular contraceptive measures until the success of the operation is verified through a semen analysis performed 12-16 weeks post-surgery.
- Additionally, they should be informed about the potential for spontaneous recanalization, leading to unexpected restoration of fertility, and the chance of chronic testicular pain, which may affect up to 5% of men.
Procedure
- Vasectomy is a simple and painless procedure conducted under local anesthesia. The vasa are accessed through small bilateral scrotal incisions or a single midline scrotal incision. Measures such as burying the cut ends, fascial interposition, or reversing them can help prevent rejoining.
No-scalpel technique
- Keyhole vasectomy
- Sterility is not immediate (requires at least 30 ejaculations)
- Sperms can be stored in the reproductive tract for up to 3 months.
- Sperms are eliminated intraluminally through phagocytosis.
- The man is declared sterile after two semen analyses confirm the absence of sperm.
[Question: 940784]

The document Urinary Bladder, Uterine Tubes, Vas Deferens: Clinical Anatomy | Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
7 videos|219 docs
|
FAQs on Urinary Bladder, Uterine Tubes, Vas Deferens: Clinical Anatomy - Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is the function of the urinary bladder? |  |
Ans. The urinary bladder is responsible for storing urine produced by the kidneys until it is eliminated from the body. It expands as it fills with urine and contracts during urination to expel the urine through the urethra.
| 2. What are the uterine tubes and what is their role in reproduction? |  |
Ans. The uterine tubes, also known as fallopian tubes, are a pair of tubes that connect the ovaries to the uterus in females. Their primary role is to transport eggs released from the ovaries towards the uterus. Fertilization of the egg by sperm usually occurs in the uterine tubes.
| 3. What is the vas deferens and what is its function in the male reproductive system? |  |
Ans. The vas deferens is a long, muscular tube that carries sperm from the epididymis (where sperm is stored) to the urethra in the male reproductive system. It plays a crucial role in transporting sperm during ejaculation.
| 4. What are some common disorders or conditions that can affect the urinary bladder? |  |
Ans. Some common disorders or conditions that can affect the urinary bladder include urinary tract infections, bladder stones, bladder cancer, urinary incontinence, and interstitial cystitis. These conditions can cause various symptoms such as frequent urination, pain or discomfort, blood in the urine, and urinary urgency.
| 5. What are the possible complications associated with blockage or obstruction of the uterine tubes or vas deferens? |  |
Ans. Blockage or obstruction of the uterine tubes can lead to infertility as it prevents the fertilized egg from reaching the uterus. This can occur due to conditions such as pelvic inflammatory disease, endometriosis, or previous surgeries. Similarly, blockage or obstruction of the vas deferens can result in male infertility as it prevents the transport of sperm. This can be caused by conditions such as congenital absence of the vas deferens or scarring from infections or surgeries.

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches

















