Verb | English Grammar Class 5 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is a verb? |

|
| Types of Verbs |

|
| Different Categories of Verb |

|
| Verb Forms |

|
What is a verb?
A verb is a word or group of words that express an action, event, or state. It's what we do, what happens, or how we are.
Verbs Referring to Actions
These verbs depict physical movements or actions.
Examples include Walking, running, talking, sitting, reading, and writing. These are the things we physically do.
Verbs Referring to Experiences or Feelings
These verbs describe emotions, sensations, or mental states without necessarily involving physical movement.
Examples encompass Love, hate, envy, belief, trust, feeling, etc. These are the things we feel or believe.
Verbs Referring to a State or Condition
These verbs describe situations or states of being.
Examples comprises Am, is, are, was, were, have, has, will be, etc. These are the conditions or states we find ourselves in.
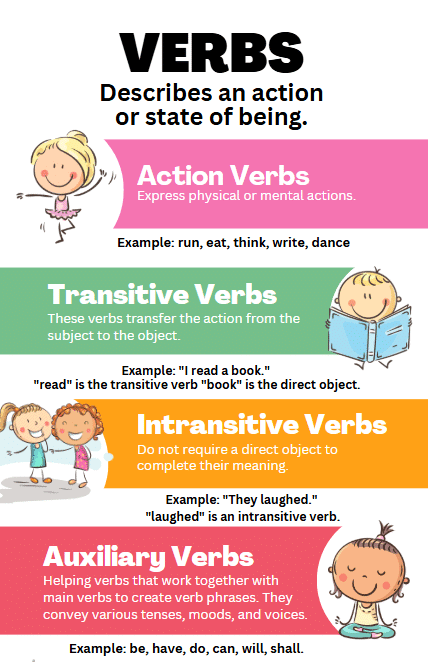
Types of Verbs
Auxiliary Verbs/Helping Verbs
Auxiliary verbs help other verbs make sense by changing their tense, mood, or voice.
Examples: Am, is, are, was, were, have, has, do, will, can.
- Remember to conjugate auxiliary verbs correctly according to the tense of the sentence.
- Some auxiliary verbs can also be used as main verbs.
- Modal verbs, a type of auxiliary verb, express possibility, probability, capability, or necessity.
Modal Verbs
Modal verbs indicate possibility, probability, capability, or necessity.
Examples: Can, could, will, would, may, might, should, must, ought to.
Phrasal Verbs
Phrasal verbs are combinations of verbs and prepositions that act as verbs.
Examples: Go by, lay off, log in, get off, run out, go all out, think through, etc.
Linking Verbs
Linking verbs connect the subject to other parts of the sentence, such as objects, adjectives, or prepositional phrases.
Examples:
1. Connecting nouns to other nouns: "Danny is my brother."
2. Connecting nouns to prepositional phrases: "The children were in the park."
3. Connecting nouns/subjects to adjectives: "Your presentation was excellent."
4. Connecting subjects/nouns to predicates using 'seem' or 'become': "This book seems interesting." "The students became bored."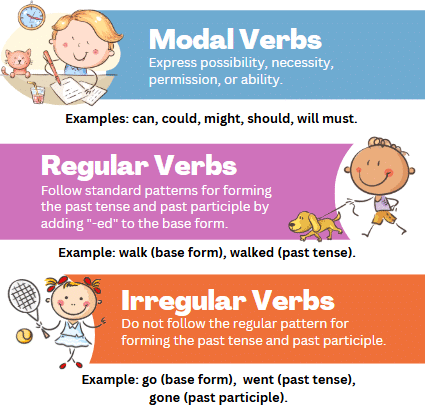
Different Categories of Verb
Regular Verbs and Irregular Verbs
Regular verbs form their past tense by adding "ed," while irregular verbs have unique past tense forms.
Examples: Regular - "searched" (search), Irregular - "found" (find), "read" (read).
Transitive Verbs and Intransitive Verbs
Transitive verbs require a direct object, intransitive verbs do not, and ditransitive verbs take both direct and indirect objects.
Examples: Transitive - "gave" (gave chocolates), Intransitive - "ran" (ran around the park).
Verb Forms
Root Verb
The raw or original form of the verb, how it originally exists in the English language, without any inflections or conjugations, is called the root verb.
Examples include Eat, Sit, Stir, Type, Read, Fry, etc.
Simple Present (Third Person Singular )
Third-Person Singular Singular form of the verb is used with third-person singular pronouns.
Example: "Kenny likes mangoes."
Present Participle
It is formed by adding "ing" to the root verb, indicating ongoing action.
Example: "Jhanvi is watching a movie."
Simple Past
The past tense form of the verb is often formed by adding "ed" or through irregular forms.
Example: "Nelson bought the car."
Past Participle
Used in perfect tense forms, it can be the same as past tense or different.
Example: "I have searched the loft."
Gerunds
Verbs with "ing" are used as nouns or with auxiliary verbs to show continuous action.
Example: "Walking every day is good exercise."
Infinitives
Verbs with "to" are used as nouns or with verbs to express purpose.
Example: "I like to dance."
Active Voice and Passive Voice
Active voice: Subject acts, passive voice: subject receives the action.
Example: Active - "The doctor checked the patient."
Passive - "The patient was checked by the doctor."
Conjugating Verbs in English - Tense Forms:
Verbs change form to represent present, past, and future and can be simple, continuous, perfect, or perfect continuous.
|
37 videos|288 docs|53 tests
|
FAQs on Verb - English Grammar Class 5
| 1. What is the importance of verb and tense in language learning? |  |
| 2. How many verb tenses are there in the English language? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between simple past and past continuous tense? |  |
| 4. How can I improve my understanding and usage of verb tenses? |  |
| 5. What are some common mistakes to avoid when using verb tenses? |  |





















