Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Question Answers - Control and Coordination
Q1: Define ‘reflex action’.
Ans: It is an automatic, spontaneous, and immediate involuntary response to a stimulus controlled usually by the spinal cord. e.g. knee jerk movement.
Q2: Name the largest cell in the human body.
Ans: Nerve cell (Neuron).
Q3: Give an example of a plant hormone that promotes growth.
Ans: Auxin.
 Chemical structure of AuxinQ4: What are plant hormones?
Chemical structure of AuxinQ4: What are plant hormones?
Ans: The chemical substances produced in plants that help in the growth and development of the plant, its tissues, and other plants.
Q5: Name the part of neuron
(а) where information is acquired.
(b) through which information travels an electrical impulse.
Ans: (a) Dendrite
(b) Axon
Q6: Name two tissues that provide control and coordination in multicellular animals.
Ans: Muscular tissues and nervous tissue.
Q7: Name the hormone, the secretion of which is responsible for dramatic changes in appearance in girls and boys when they approach 10-12 years of age.
Ans: Testosterone is released from the testes in males, and estrogen is released from ovaries in females.
Q8: Name the hormone that helps regulate the level of sugar in our blood. Name the glands that secrete it.
Ans: Insulin hormone secreted by the pancreas.
Q9: Name a plant hormone that inhibits growth. Write one more function.
Ans: Abscisic acid inhibits growth in plants. It also causes the closure of stomata during water stress.
Q10: A potted plant is made to lie horizontally on the ground. Which part of the plant will show:
(i) Positive geotropism
(ii) Negative geotropism
Ans:
(i) Roots will show positive geotropism.
(ii) Shoots will show negative geotropism.
Q11: Name a plant hormone that promotes growth in plants.
Ans: Auxin is a plant hormone that promotes growth and cell elongation in plants.
Q12: State one function of each of the pons and cerebellum.
Ans: Pons: Regulates rate of respiration
Cerebellum: Maintains equilibrium of the body during walking, jumping, etc.
Q13: Name a gaseous plant hormone. Give its role.
Ans: Ethylene is a gaseous hormone. It regulates fruit ripening.
Q14: How many spinal and cranial nerves are present in the human body?
Ans: Spinal nerves = 31 pairs
Cranial nerves = 12 pairs
Q15: What are meninges?
Ans: The three membranes that cover the brain to protect it are called meninges.
Q16: Define Reflex Arc.
Ans: The reflex arc is the route traversed by nerve impulses during a reflex action, moving from a receptor organ, which may be a sense organ like the eyes or skin, to the spinal cord and subsequently back to the effector organ, which could be muscles or glands.
Q17: Draw a neat diagram of a neuron.
Ans: 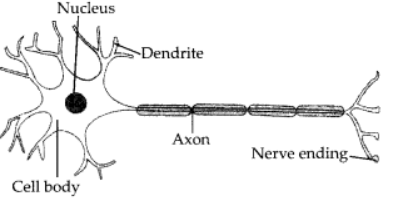 Structure of a NeuronQ18: State one example of chemotropism.
Structure of a NeuronQ18: State one example of chemotropism.
Ans: The chemotropism observed in the fertilization process of a flower involves the growth of the polleState the two types of movements seen in plants n tube towards the ovule in response to a chemical stimulus.
Q19: State the two types of movements seen in plants.
Ans:
(i) Nastic Movements.
(ii) Tropic Movements or Tropism.
Q20: Define phototropism.
Ans: Phototropism is the plant's response to light, with shoots exhibiting positive phototropism by growing towards the light, and roots showing negative phototropism by growing away from light.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Question Answers - Control and Coordination
| 1. What is control and coordination? |  |
| 2. How does the nervous system control and coordinate body functions? |  |
| 3. What are the two main types of coordination in animals? |  |
| 4. How does the endocrine system contribute to control and coordination? |  |
| 5. What is the difference between a reflex action and a voluntary action? |  |

















