UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Geography Optional for UPSC (Notes) > Watershed Management
Watershed Management | Geography Optional for UPSC (Notes) PDF Download
Introduction
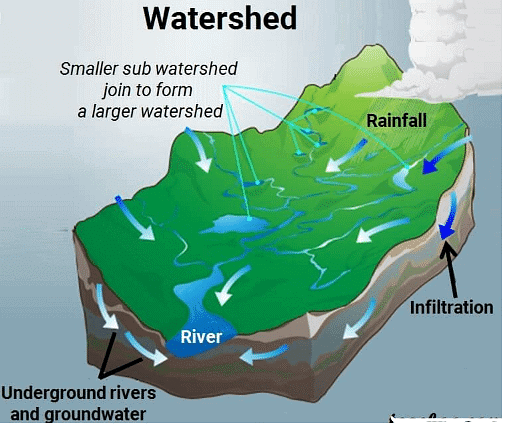
- Watershed is defined as any surface area from which rainfall is collected and drains through a common point.
- It is synonymous with a drainage basin or catchment area. In other words, watershed is a geo-hydrological unit, comprising of all land and water within the confines of drainage divide.
 Watershed Management
Watershed Management - The size of watershed may vary from a few hectares to several thousands of hectares. Watershed sizes are classified into three: micro, mini, and macro watersheds. In fact, watershed is a biological, physical, economic and social system. It is a land mass bounded vertically by the area influenced by human activities and horizontally by the water that drains into a point in the channel.
- Watershed management is the integration of technologies within the natural boundaries of a drainage area for optimum development of land, water, and plant resources to meet the basic needs of the people and animals in a sustained manner.
Principles of Watershed Management
- Utilizing the land according to its capability based on land use classification.
- Conserving as much rainwater as possible at the place where it falls i.e., in situ conservation.
- Draining out excess water with a safe velocity and diverting it to storage structure (farm ponds, tanks) for future use.
- Avoiding gully formation and putting up check-dams at suitable places to control soil erosion, to store rainwater, and recharge groundwater.
- Identifying a suitable cropping pattern for the watershed area.
- Maximizing productivity per unit area, per unit time, and per unit water.
Objectives of Watershed Management
- To effectively conserve soil, rainwater, and harness the surplus water to create water sources in addition to groundwater recharge.
- To promote sustainable farming and stabilize crop yield by adopting suitable cropping and crop management systems.
- To cover non-arable areas effectively through afforestation, horticulture, and pasture land development based on the capability of the land.
- To enhance the income of the individuals by adopting alternative enterprises.
- To restore ecological balance.
- Increasing cropping intensity and land equivalent ratio through intercropping and sequence cropping.
- Safe utilization of marginal and wastelands through alternate land-use systems such as agro-forestry.
- Ensuring sustainability of the ecosystem benefiting the man-animal-plant-land-water complex in the watershed.
- Stabilizing total income and cutting down the risk of during aberrant weather situations.
- Improving infrastructural facilities with regard to storage, transportation, and marketing.
 Pong Approach
Pong Approach
Planning For Watershed Management
- Comprehensive planning for watershed management starts with obtaining suitable maps through remote sensing techniques.
- Remote sensing provides a synoptic picture of the watershed for the characterization of natural resources, land, water, vegetation, and inter-relationship between them. Besides mapping natural resources, satellite imagery can give the estimate of the area covered by major crops, crop yield, area affected by pests and diseases and drought conditions, if any. The location of structures like check-dams, farm ponds etc., can also be delineated using satellite imagery pictures.
- Distribution patterns and assessments of the status of material resources can be obtained from satellite pictures. Comprehensive planning of various activities is then carried out. Mechanical, agronomical, agro-ecological and forestry measures of soil and rainwater conservation are then planned and implemented.
Case Study
- On July 27, 2016, rain for only two hours paralyzed the life in Gurgram (Gurgaon), with deep waterlogging. The main cause of this tragedy was ill-conceived planning. In the planning of Gurgram, Watershed Planning was ignored.
- The Firozpur-Jhikra-Delhi ridge forms the western boundary and the Delhi ridge forms the eastern boundary of this watershed. The natural drainage pattern of the city comprises of large depression and streams, tending to cover inland instead of flowing into the Yamuna.
- The Delhi-Jaipur Highway No. 8 crosses several watersheds almost in the middle and blocks the natural drainage pattern from south to north. Thus, the unscientific planning of National Highway No. 8 is largely responsible for the Gurgram tragedy. It is thus, important to incorporate the watershed approach in the planning of a city.
Delineation and Codification of Watersheds
- The All India Soil and Land Use Survey Organization of the Department of Agriculture, Government of India, has finalized a nationwide system of delineation and codification of watersheds. According to this scheme various size of the watershed have been divided into:
- Basins
- Catchments
- Sub-catchments
- Watersheds
- In India, there are 35 rivers, 112 catchments, 500 sub-catchments, and 3200 watersheds. For the purpose of planning and development, the 3200 watersheds have been divided on the basis of the area into the following three categories:
- Sub-watersheds( 10,000 to 50,000 hectares)
(i) Milli-Watershed ( 1000 to 10,000 hectares)
(ii) Micro-Watershed ( 100 to 1000 hectares)
(iii) Mini-Watershed ( 1 to 100 hectares)
- Sub-watersheds( 10,000 to 50,000 hectares)
Significance of Watershed Management
- Watershed management is a comprehensive program to utilize the available water and other resources in such a way that:
- The productivity of agriculture is enhanced
- To protect and enhance water resources, moderate floods and reduce silting up of tanks and conserve rainwater for crops and thus mitigate droughts
- To utilize the natural local resources for improving cottage and small industries to improve socio-economic conditions of local people.
- The allied activities of industries are promoted
- Social forestry provides an additional source of income
- Soil erosion is checked
- Cottage industries are developed
- More employment opportunities are created
- The space available may be made more enjoyable, and ecology may be maintained in a healthy and sustainable condition.
The document Watershed Management | Geography Optional for UPSC (Notes) is a part of the UPSC Course Geography Optional for UPSC (Notes).
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
191 videos|420 docs|145 tests
|
FAQs on Watershed Management - Geography Optional for UPSC (Notes)
| 1. What is watershed management? |  |
Ans. Watershed management refers to the comprehensive and integrated management of land, water, and other natural resources within a particular watershed. It involves planning and implementing various strategies to conserve and sustainably use the resources in the watershed, such as forests, rivers, lakes, and soil, in order to maintain ecological balance and meet the socio-economic needs of the local communities.
| 2. Why is watershed management important? |  |
Ans. Watershed management is important for several reasons. Firstly, it helps in the conservation and sustainable use of water resources, ensuring their availability for various purposes such as domestic use, agriculture, and industry. Secondly, it helps in preventing soil erosion and maintaining soil fertility, which is crucial for agriculture and overall ecosystem health. Additionally, watershed management plays a vital role in mitigating the impacts of natural disasters like floods and droughts, protecting biodiversity, and supporting livelihoods of local communities.
| 3. What are the key components of watershed management? |  |
Ans. The key components of watershed management include watershed planning, soil and water conservation measures, afforestation and reforestation, rainwater harvesting, water resource development, community participation, and institutional coordination. Watershed planning involves assessing the existing conditions, identifying priority areas for intervention, and formulating strategies and action plans. Soil and water conservation measures aim to control erosion, enhance soil fertility, and improve water quality. Afforestation and reforestation help in restoring and protecting the vegetation cover, while rainwater harvesting and water resource development focus on storing and efficiently utilizing water resources.
| 4. How does watershed management contribute to climate change adaptation? |  |
Ans. Watershed management plays a crucial role in climate change adaptation. It helps in enhancing the resilience of ecosystems and communities to the impacts of climate change, such as increased frequency and intensity of floods and droughts. Through measures like afforestation, soil conservation, and water resource development, watershed management helps in improving water availability, reducing soil erosion, and maintaining ecological balance. These actions contribute to reducing vulnerability to climate change and ensuring the sustainability of natural resources.
| 5. What are some challenges in implementing watershed management? |  |
Ans. Implementing watershed management can face several challenges. Lack of awareness and understanding among local communities about the importance of watershed management may hinder their active participation. Limited financial resources and technical capacity can also be constraints in implementing comprehensive watershed management plans. Additionally, conflicting interests and lack of coordination among different stakeholders, such as government agencies, local communities, and private entities, can pose challenges in implementing integrated watershed management approaches. It is important to address these challenges through awareness campaigns, capacity building, and effective stakeholder engagement to ensure successful implementation of watershed management initiatives.
|
191 videos|420 docs|145 tests
|
Download as PDF

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches