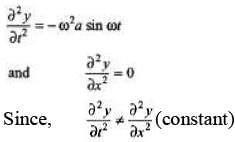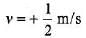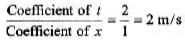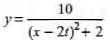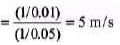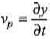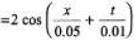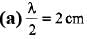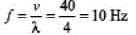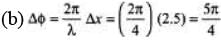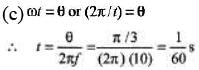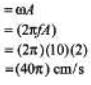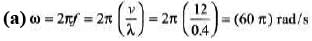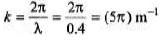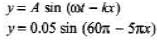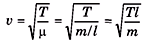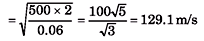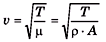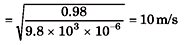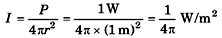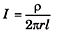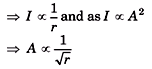DC Pandey Solutions: Wave Motion | Physics Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introductory Exercise 14.1 |

|
| Introductory Exercise 14.2 |

|
| Introductory Exercise 14.3 |

|
| Introductory Exercise 14.4 |

|
Introductory Exercise 14.1
Q.1. Prove that the equation y = a sin wt does not satisfy the wave equation and hence it does not represent a wave.
Sol.
Hence, the given equation does not represent a wave equation.
Q.2. A wave pulse is described by 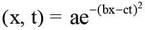 , where a, b and c are positive constants. What is the speed of this wave?
, where a, b and c are positive constants. What is the speed of this wave?
Sol.
Speed of wave
= c/b
Q.3. The displacement of a wave disturbance propagating in the positive x-direction is given by 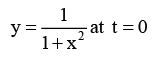 and
and 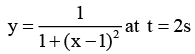
where, x and y are in metre. The shape of the wave disturbance does not change during the propagation. What is the velocity of the wave?
Sol.
At t = 0, y is maximum at x = 0.
At t = 2 s, y is maximum at x = 1 m.
Hence, in 2 s, wave has travelled 2m in positive x-direction.
= +0.5 m/s
Q.4. A travelling wave pulse is given by, 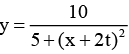
Here, x and y are in metre and t in second. In which direction and with what velocity is the pulse propagating? What is the amplitude of the pulse?
Sol. Since the coefficient of t and x are opposite signs, the wave is travelling along negative x-direction. Further,
Speed of wave =
Amplitude = maximum value of y
= 10/5 = 2m
Q.5. If at f = 0, a travelling wave pulse on a string is described by the function,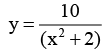
Here x and y are in metre and t in second. What will be the wave function representing the pulse at time t, if the pulse is propagating along positive x-axis with a speed of 2 m/s?
Sol. Since the wave is travelling along positive x-direction. Hence, the coefficient of t and coefficient of x should have opposite signs. Further
∴ Coefficient of t = 2 (coefficient of x) = 2 x 1 = 2 SI units.
Introductory Exercise 14.2
Q.1. The equation of a travelling wave is,
y(x, t ) 0.02 sin 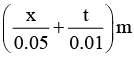
Find: (a) The wave velocity and
(b) the particle velocity at x = 0.2 m and t = 0.3 s.
Given cos θ = -0.85 where θ = 34 rad
Sol.
(a) Wave velocity =
Since, coefficient of t and coefficient of x are of same signs. Hence, wave is travelling in negative x-direction.
or
v = -5 m/s
(b) Particle velocity
Substituting x = 0.2 and t = 0.3, we have Vp = 2cos(34)
= (2) (-0.85) =-1.7 m/s
Ques 2: Is there any relationship between wave speed and the maximum particle speed for a wave travelling on a string? If so, what is it?
Sol: As we know, Wave speed,and maximum particle speed, (vp)max = wA
From these two expressions, we can see that,
(vp)max = (kA)V
Q.3. Consider a sinusoidal travelling wave shown in the figure. The wave velocity is + 40 cm/s. Find :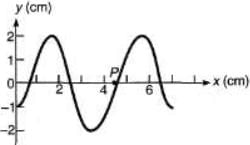
(a) the frequency
(b) the phase difference between points 2.5 cm apart
(c) how long it takes for the phase at a given posit ion to change by 60°
(d) the velocity of a particle at point P at the instant shown.
Sol.
⇒ λ = 4cm
(d) At P, particle is at mean position. So, v = maximum velocity
= 125.7 cm/s= 1.26 m/s
Further,...(i)
Sign of v1, the wave velocity is given positive.
Sign of dy/dx, slope of y - x graph is also positive.
Hence, from Eq. (i) particle velocity is negative. vp = -1.26 m/s
Q.4. Transverse waves on a string have wave speed 12.0 m/s, amplitude 0.05 m and wavelength 0.4 m. The waves travel in the + x direction and at t = 0 the x = 0 ends of the string has zero displacement and is moving upwards.
(a) Write a wave function describing the wave.
(b) Find the transverse displacement of a point at x = 0.25 m at time t = 0.15 s.
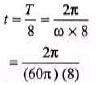
(c) How much time must elapse from the instant in part (b) until the point at x = 0.25 m has zero displacement?
Sol.
Since wave is travelling along + ve x-direction, at and kx should have opposite signs. Further at t = 0, x = 0 the string has zero displacement and moving upward (in positive direction).
Hence at x = 0, we should have Asinwt not - Asinwt. Therefore, the correct expression is
(b) Putting x = 0.2 m and t = 0.15 s in the above equation we have,
y= 0.0354 m = 3.54 cm
(c) In part (b), y = A/√2
Fromto y = 0, time taken is
= 4.2 × 10-3s = 4.2 ms
Introductory Exercise 14.3
Q.1. Calculate the velocity of a transverse wave along a string of length 2 m and mass 0.06 kg under a tension of 500 N.
Sol.
Q.2. Calculate the speed of a transverse wave in a wire of 1.0 mm2 cross-section under a tension of 0.98 N. Density of the material of wire is 9.8 × 103 kg/m3.
Sol.
Introductory Exercise 14.4
Q.1. Spherical waves are emitted from a 1.0 W source in an isotropic non-absorbing medium. What is the wave intensity 1.0 m from the source?
Sol.
Q.2. A line source emits a cylindrical expanding wave. Assuming the medium absorbs no energy, find how the amplitude and intensity of the wave depend on the distance from the source?
Sol. For line source,
|
96 videos|367 docs|98 tests
|
FAQs on DC Pandey Solutions: Wave Motion - Physics Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is wave motion? |  |
| 2. How is wave motion different from particle motion? |  |
| 3. What are the types of waves in wave motion? |  |
| 4. How is wave motion described mathematically? |  |
| 5. What are some real-life applications of wave motion? |  |