Weekly Current Affairs (15th to 21st August 2024) | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
WHO Declares Mpox a Global Public Health Emergency

On August 14, 2024, the World Health Organization (WHO) designated mpox as a "public health emergency of international concern" (PHEIC). This decision followed an observed rise in mpox cases, particularly in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) and several other African nations.
What is a PHEIC?
A PHEIC refers to a significant health event that poses risks to multiple countries, requiring a coordinated global response. It is an unusual occurrence that could spread internationally, prompting collective efforts from various nations.
Mpox Overview:
- Mpox is a viral disease first identified in humans in 1970, predominantly affecting Central and West Africa. In July 2022, the WHO had previously declared mpox a global emergency due to an outbreak that concluded in May 2023.
Current Situation:
- The DRC is facing a sharp increase in mpox cases, with more than 15,600 reported cases and 537 deaths so far this year. A new strain of the virus, called clade 1b, is rapidly spreading across the DRC and neighboring countries like Burundi, Kenya, Rwanda, and Uganda—regions where mpox had not been previously detected.
Response Efforts:
- Two vaccines have been recommended for mpox and are approved in several countries. The WHO has allocated $1.45 million to support immediate response efforts, with more funding anticipated as the crisis evolves. It is estimated that $15 million will be required for enhanced surveillance and preparedness.
More About Mpox:
- Mpox, formerly known as monkeypox, is a viral illness primarily found in Central and West Africa. Initially discovered in monkeys in 1958, the disease predominantly spreads through rodents. Symptoms include fever, rash, and swollen lymph nodes, resembling smallpox but with a shorter incubation period of 7-14 days. Mpox can be transmitted between humans via respiratory droplets and bodily fluids. In 2022, the WHO declared mpox a public health emergency, and a smallpox vaccine can offer some level of protection.
International Health Regulations (IHR):
- The International Health Regulations (IHR), first established in 1969 and updated in 2005, aim to bolster global health security by managing disease outbreaks. The IHR applies to 196 countries, including all WHO member states, and mandates reporting of certain diseases within 24 hours. The IHR also advocates for a "One Health" approach, integrating human, animal, and environmental health. These regulations offer guidelines for emergency response and public health readiness, with compliance assessed through annual reporting.
New Blood Test Detects Alzheimer’s with 90% Accuracy

Researchers at Lund University in Sweden have developed an innovative blood test called PrecivityAD2, capable of detecting Alzheimer’s disease (AD) with approximately 90% accuracy. This breakthrough, particularly beneficial for individuals with mild cognitive impairment, enables earlier diagnosis. The findings were published in the peer-reviewed journal JAMA.
Importance of Early Detection:
- Alzheimer’s disease, the most prevalent form of dementia, affects a significant portion of the population, with one in five women and one in ten men receiving a diagnosis. Early detection is vital, as misdiagnoses still occur in 25% to 35% of cases, even among specialists. A reliable blood test streamlines this process, reducing the likelihood of incorrect diagnoses and facilitating more accurate detection.
Benefits of a Blood Test:
- Historically, diagnosing Alzheimer’s has required costly and invasive procedures like PET scans to detect amyloid and tau proteins or lumbar punctures to analyze cerebrospinal fluid. This new blood test provides a more straightforward alternative, requiring only a blood sample to deliver results.
How the Test Works:
The test detects specific proteins in the blood associated with Alzheimer’s disease. It measures the ratios of:
- Phosphorylated-tau217 (p-tau217) to non-phosphorylated-tau21
- Two forms of amyloid-beta (AB42 and AB40)
These proteins are key markers of Alzheimer’s pathology and contribute to the test's high accuracy in diagnosing the disease.
Clinical Validation:
- In a study involving 1,213 patients undergoing cognitive evaluations, nearly half showed signs of Alzheimer’s disease. The new blood test demonstrated superior accuracy compared to traditional diagnostic methods, achieving 91% accuracy versus 73% for dementia specialists and 61% for primary care physicians. As further research confirms its effectiveness, this blood test has the potential to transform Alzheimer’s diagnosis and treatment, making it more affordable and accessible, especially in regions lacking advanced diagnostic tools.
More About Alzheimer’s Disease:
- First identified in 1906, Alzheimer’s disease currently affects around 50 million people globally and accounts for 60-80% of dementia cases. Contrary to popular belief, Alzheimer’s is not a normal aspect of aging. Risk factors include genetics, head injuries, and cardiovascular conditions. The disease is characterized by the presence of beta-amyloid plaques and tau tangles in the brain. While there is no cure, early detection and lifestyle adjustments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
ISRO Launches SSLV-D3-EOS-08 Mission

The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully launched the SSLV-D3-EOS-08 mission, which deployed a small Earth observation satellite. This mission follows the success of the earlier SSLV-D2-EOS-07 mission, launched in February 2023.
Development Milestones:
The SSLV-D3-EOS-08 mission marks the third flight in ISRO's Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) series and completes the development phase of this new rocket. Earlier in 2024, ISRO conducted two other successful launches: the PSLV-C58/XpoSat mission in January and the GSLV-F14/INSAT-3DS mission in February.
Launch Details:
Initially scheduled for August 15, the launch was rescheduled to August 16 at 9:19 AM IST from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre. The SSLV rocket stands about 34 meters tall and is capable of carrying payloads of up to 500 kg into Low Earth Orbit (LEO).
Mission Objectives:
The SSLV-D3-EOS-08 mission has several key objectives:
- Building and launching a microsatellite.
- Developing instruments to support the microsatellite.
- Incorporating new technology for future satellite missions.
Satellite Specifications:
The Earth Observation Satellite launched during this mission:
- Weighs approximately 175.5 kg.
- Consumes 420 watts of power.
- Is built on the Microsat/IMS-1 bus.
- Has a mission life of one year, launched aboard the SSLV-D3 rocket.
Payload Details:
The satellite is equipped with three primary instruments:
- Electro-Optical Infrared Payload (EOIR): Captures images using infrared light for surveillance, disaster monitoring, and environmental studies.
- Global Navigation Satellite System-Reflectometry Payload (GNSS-R): Utilizes GPS signals to study ocean winds, soil moisture, and detect floods.
Croatia to Reintroduce Compulsory Military Service
 Croatia has announced plans to reinstate two months of compulsory military service beginning January 1, 2025. This decision comes in response to growing tensions in Europe, particularly due to Russia’s actions in Ukraine and increased military activity in the Balkans, a region with a history of conflict.
Croatia has announced plans to reinstate two months of compulsory military service beginning January 1, 2025. This decision comes in response to growing tensions in Europe, particularly due to Russia’s actions in Ukraine and increased military activity in the Balkans, a region with a history of conflict.
Background on Conscription in Croatia:
- Mandatory military service in Croatia was suspended in 2008, transitioning to a volunteer-based military system. However, given the current geopolitical situation, the Croatian government has decided to restore conscription to bolster national defense.
Government Justifications:
- Croatian Defence Minister Ivan Anusic stated that the government aims to strengthen the country’s military capabilities. This includes increased investments in soldiers and continued modernization of the Armed Forces, aligning with NATO’s objectives.
Regional Implications:
- Croatia’s decision mirrors a broader trend across Europe, with nations like Latvia also reinstating conscription due to security concerns. Serbia, a key rival of Croatia, is contemplating similar measures, potentially leading to an arms race in the region. The reintroduction of compulsory service is a strategic step for Croatia to enhance national security amid growing instability, ensuring preparedness for future challenges.
About Compulsory Military Service:
- Mandatory military service, or conscription, is enforced in more than 60 countries. For example, Switzerland requires men to undergo military training, with an option for civil service, while in Israel, both men and women are obligated to serve from the age of 18. South Korea maintains conscription due to regional threats, and countries like Sweden have reintroduced it in response to changing global security dynamics.
About NATO:
- NATO, established in 1949, initially consisted of 12 member countries and was created to counter Soviet influence. Its core principle of “Collective Defense” states that an attack on one member is considered an attack on all, a principle invoked only once after 9/11. NATO, headquartered in Brussels, Belgium, has expanded to 31 members as of 2023 and regularly conducts joint military exercises to enhance cooperation and defense capabilities.
Government Finalizes Tender for 1,000 GPUs Under IndiaAI Mission

The Indian government is advancing the IndiaAI Mission with the finalization of a plan to procure 1,000 graphics processing units (GPUs), which are essential for supporting start-ups, researchers, and public agencies in building AI computing capabilities.
Key Objectives of the IndiaAI Mission:
- The mission, with a budget of ₹10,370 crore, aims to utilize over 10,000 GPUs to develop AI models with more than 100 billion parameters. These models will be designed to function with major Indian languages and will focus on key sectors like healthcare and agriculture. Winning bidders must provide AI computing time immediately: 100 hours within the first day, 500 hours within two days, and over 500 hours within a week. This infrastructure will help meet the growing demand for AI by providing easier access to computing resources.
Tender Details:
- The tender allows for joint bids by groups of companies, provided that at least one partner has an annual revenue of over ₹100 crore. Bidders must comply with data localization requirements, ensuring that user data remains within India’s borders. The project will follow a public-private partnership model, with the government covering 50% of the infrastructure costs, making it more affordable to build. A total of ₹4,564 crore will be allocated specifically for developing the required computing infrastructure.
Impact on Start-ups and SMEs:
- This expansion of AI computing resources will make advanced AI technology more accessible to small and medium enterprises (SMEs) and start-ups, which often find such resources expensive and difficult to obtain. This initiative is expected to drive innovation and enhance competitiveness within India’s tech industry.
What is AI Computing Capacity?
- AI computing power has seen rapid growth, with GPUs and TPUs (Tensor Processing Units) playing a critical role. For instance, OpenAI’s GPT-3, launched in 2021, had 175 billion parameters. Training AI models is energy-intensive, but advancements in AI algorithms are improving efficiency. Supercomputers like Fugaku are often employed for AI training, and future innovations such as quantum computing may further enhance the speed and efficiency of AI.
About the India AI Mission:
- Launched in 2020, the IndiaAI Mission focuses on enhancing AI research and innovation with a strong emphasis on ethical AI usage and collaboration. India is currently ranked third globally in AI research output. The mission provides support to start-ups with funding and resources and has established the National AI Portal as a central hub for AI knowledge. It promotes AI across sectors like agriculture, healthcare, and education and works in partnership with global organizations like the Global Partnership on AI. Additionally, the mission aims to train over 1 million AI professionals by 2025, helping to upskill the workforce.
What are Graphics Processing Units (GPUs)?
- GPUs were developed in the late 1990s and revolutionized image rendering. NVIDIA’s GeForce 256 is considered the first true GPU. While GPUs are well-known for gaming, they are also critical in AI, cryptocurrency mining, and scientific research. Unlike CPUs, which have fewer cores, GPUs have thousands, enabling them to handle multiple tasks simultaneously. NVIDIA's CUDA programming model allows developers to leverage GPUs for a variety of applications. AMD’s Radeon was the first GPU to support Direct3D 11. The term "GPU" was coined by NVIDIA in 1999, underscoring its pivotal role in modern computing.
Germany Becomes 18th Member of United Nations Command in South Korea

Germany has officially joined the U.S.-led United Nations Command (UNC) in South Korea, becoming its 18th member. This step underscores Germany’s commitment to global security and its view that stability in Europe and the Indo-Pacific are interconnected.
What is the UNC?
- The United Nations Command was established in 1950 to help restore peace during the Korean War and to enforce the armistice agreement. Although created under the United Nations, the UNC operates independently and acts as a key communication channel with North Korea. It is primarily led by the U.S. military commander stationed in South Korea.
Germany's Role in the UNC:
- Germany's inclusion in the UNC enhances the command's capabilities by bringing new perspectives and resources. This move aligns with U.S. and allied efforts to bolster regional security, particularly in the face of growing challenges from authoritarian regimes.
Impact on European and Indo-Pacific Security:
- Germany views its participation in the UNC as crucial for collective security, emphasizing that peace in Europe is linked to stability in the Indo-Pacific. German Defence Minister Boris Pistorius has highlighted the importance of unity in addressing global security challenges.
Reactions from Other Countries:
- Germany’s entry into the UNC has drawn criticism from China and North Korea. North Korea sees the UNC as a U.S. tool for confrontation, while China is concerned about NATO’s expanding influence in Asia. Germany plans to reopen its embassy in Pyongyang, which was closed during the COVID-19 pandemic, and is considering its role within the UNC. Discussions are ongoing regarding the specific duties of German troops in Korea. South Korean Defence Minister Shin Won-sik has welcomed Germany’s participation, calling it a significant contribution to peace efforts on the Korean Peninsula.
Facts About Germany:
- Berlin Zoo: The world’s oldest zoo, founded in 1844, with over 19,000 animals.
- Beer: Germany is known for its beer, with approximately 1,500 varieties, regulated by the Reinheitsgebot or Beer Purity Law.
- Autobahn: Some sections of Germany’s Autobahn have no speed limit, attracting speed enthusiasts.
- Berlin Wall: The wall, a symbol of Cold War division, was dismantled in 1989.
- Oktoberfest: Munich hosts the world’s largest beer festival.
- Automotive Industry: Germany produces about 1 million cars annually, with leading brands like Volkswagen. It also has the largest economy in Europe.
Facts About the United Nations Command (UNC):
- Established: Created in 1950 during the Korean War to support South Korea against the North.
- Coalition: The UNC is not a standing army but a coalition of member states.
- Headquarters: Based in Seoul, the UNC operates under United Nations Security Council resolutions.
- Ceasefire: The command has maintained a ceasefire since 1953, though a formal peace treaty has not been signed.
- Current Commander: Major General Paul J. LaCamera leads the UNC.
- Humanitarian Efforts: The UNC also participates in humanitarian missions and disaster relief efforts in the region.
India Amends Power Export Regulations Amid Concerns Over Bangladesh's Electricity Supply

In August 2024, India revised its electricity export rules to shield Indian companies from political risks in countries like Bangladesh. The new regulations allow Indian power companies to redirect electricity back to India if there are delays in payments from the importing countries. One major company affected by this change is Adani Power, which operates a power plant in Godda, Jharkhand, supplying all its electricity to Bangladesh. Despite these regulatory updates, Adani Power has reassured that it will continue to honor its commitments to Bangladesh.
The Godda Project:
- Adani Power's plant in Godda, Jharkhand, has a capacity of 1,496 megawatts (MW), all of which is exported to Bangladesh. The project started in 2017 when Adani Power signed a 25-year Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) with the Bangladesh Power Development Board (BPDB), marking India’s first cross-border electricity supply project.
Objectives and Benefits of the Godda Project:
- The primary aim of the Godda project is to help Bangladesh enhance its electricity supply by providing cheaper, coal-based electricity to replace more expensive power generated from liquid fuels. As of June 2023, Bangladesh had an electricity generation capacity of 24,911 MW, with the Godda plant contributing approximately 6% (1,496 MW) of this total.
Criticism and Concerns:
The Godda project has faced some criticism, mainly due to the high cost of coal imported from Australia, which makes electricity more expensive for Bangladesh. Bangladeshi officials have expressed concerns about the high coal prices under the PPA. Additionally, the costs associated with maintaining the plant and its capacity contribute to the overall expense.
Why Does Bangladesh Import Power?
- Despite expanding electricity access for its population, Bangladesh continues to face challenges in securing enough fuel to run its power plants. This has resulted in many plants being underutilized. By June 2023, Bangladesh had a total generation capacity of 28,098 MW, but around 11,621 MW remained unused due to financial and logistical difficulties.
Implications of the New Rules:
- India’s updated regulations provide power companies with more flexibility, allowing them to reduce dependence on exports when facing payment issues. While this change may lead to temporary disruptions in Bangladesh’s electricity supply, experts believe that the country's long-term energy plans will remain largely unaffected.
AIM Opens Applications for Australia-India Agritech Program
The Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) has announced that it is now accepting applications from Indian and Australian startups and small businesses for the climate-smart Agritech sector of the India Australia Rapid Innovation and Startup Expansion (RISE) accelerator. This initiative aims to foster international growth and collaboration between India and Australia, particularly in the Agritech field.
Program Overview:
- The RISE Accelerator is designed to support startups and small businesses in testing and adapting their technologies for global markets. The focus is on advancing farming methods and enhancing resilience against climate change, resource limitations, and food shortages. The program seeks to back businesses developing technologies that assist farmers and improve agricultural practices, ultimately strengthening farming operations in both India and Australia.
Program Structure:
- Spanning nine months, the program combines online learning with in-person activities in India and Australia. Participants will receive in-depth market insights, personalized coaching, and mentorship from industry experts to help them adapt and thrive in the market. They will have opportunities to conduct field trials and test their technologies in real-world settings. Networking opportunities with potential partners and customers will also be provided, which are vital for business success.
Applications and Support:
- The application deadline is September 15, 2024. There are no fees to participate, and selected businesses may receive non-equity grants of up to ₹45 lakhs. Additionally, participants will have the chance to travel between Australia and India, further fostering collaboration. The program aims to address key agricultural challenges and promote innovative, effective farming practices, contributing to sustainable development in agriculture.
About Atal Innovation Mission (AIM):
- Launched by NITI Aayog in 2016, the Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) is a significant initiative aimed at encouraging innovation and supporting entrepreneurship across India. AIM focuses on creating a nurturing environment for innovation at all levels, including schools, universities, research institutions, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), and large industries.
Dhangars Demand Grazing Corridors in Maharashtra
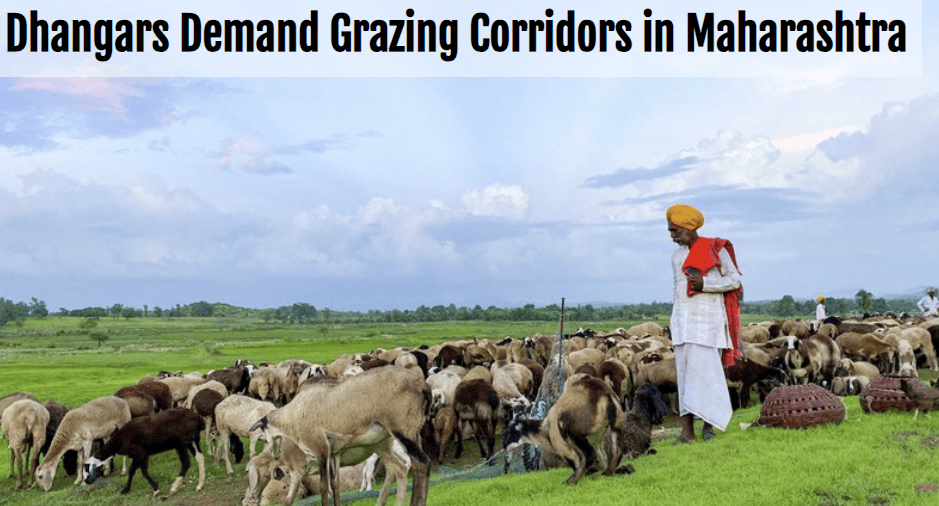
Who are the Dhangars?
- The Dhangars are a community of shepherds found in Maharashtra, Gujarat, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh. In different regions, they are also known by names such as Golla and Kuruba.
- In Maharashtra, the Dhangars are classified as Vimukta Jati and Nomadic Tribes (VJNT). For decades, they have been seeking Scheduled Tribe (ST) status, a status they believe will grant them the same benefits and recognition that “Dhangad” communities receive in other parts of India.
- The Dhangars have traditionally herded their livestock along specific routes. However, the establishment of protected forests by the forest department has led to conflicts, as walls have been erected along their grazing paths. This has resulted in the Dhangars being labeled as encroachers, facing fines and legal issues. Their traditional grazing routes are vital for both their economic well-being and cultural heritage.
- The demand for "grazing corridors" is centered around formalizing their right to graze livestock along these historical routes. The Dhangars argue that grazing by their sheep and goats does not damage the forests; instead, they believe it benefits the land.
- The Dhangars' push for grazing rights is also tied to their quest for ST status. This request has met with resistance from existing ST groups in Maharashtra, who are concerned about potentially losing their benefits.
What is the Green Ammonia Scheme?
The Indian government is launching a major auction process under the Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition (SIGHT) Scheme to promote the production of green ammonia. This initiative aims to advance India’s shift towards cleaner and more sustainable energy sources by supporting the development of green hydrogen and its associated products.
Purpose of Company Visits:- To assist companies interested in green ammonia production, the government is organizing visits to fertilizer production facilities. Scheduled from August 27 to September 10, these visits will provide companies with insights into the logistics and supply chains involved. Observing operations firsthand will help them gather crucial information for making informed bids regarding the cost of delivering green ammonia.
- Companies wishing to participate in the site visits must submit their requests to the Solar Energy Corporation of India (SECI) by August 22. The deadline for submitting bids to produce green ammonia is September 3, though an extension to this deadline is possible.
- The SIGHT Scheme, a major component of India’s National Green Hydrogen Mission, has a budget of ₹17,490 crore. It focuses on supporting the manufacture of electrolysers—devices that generate hydrogen and oxygen by splitting water with electricity—and the production of green hydrogen. The scheme is designed to promote the use of renewable energy across the country.
- The Solar Energy Corporation of India (SECI) will oversee the auction process. SECI will manage the purchase agreements between the companies producing green ammonia and the buyers, ensuring that the production and distribution are well-coordinated.
- The fertilizer industry is a major consumer of hydrogen, which is essential for producing ammonia—a key ingredient in nitrogen-based fertilizers. Major fertilizer companies, such as IFFCO, Madras Fertilisers, and Coromandel International, with a total production capacity of 739,000 tonnes per year, are expected to be the primary buyers in this auction. This initiative represents India’s first coordinated national effort to boost green ammonia production, marking a significant step towards sustainable energy and enhancing the efficiency of fertilizer production in the country.
|
164 videos|800 docs|1156 tests
|
FAQs on Weekly Current Affairs (15th to 21st August 2024) - General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce
| 1. What is the significance of WHO declaring Mpox a global public health emergency? |  |
| 2. How does the new blood test detect Alzheimer's with 90% accuracy? |  |
| 3. What is the objective of Croatia reintroducing compulsory military service? |  |
| 4. How will the Government's tender for 1,000 GPUs support the IndiaAI Mission? |  |
| 5. What role does Germany play as the 18th member of the United Nations Command in South Korea? |  |





















