Weekly Current Affairs (15th to 21st February 2025) - 2 | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| India-Qatar Strategic Partnership |

|
| Microfinance Sector in India |

|
| 22nd Foundation Day of NCST |

|
| Draft UGC Regulations 2025 |

|
| India-Argentina Lithium Partnership |

|
| DDoS Cyber-Attack |

|
India-Qatar Strategic Partnership
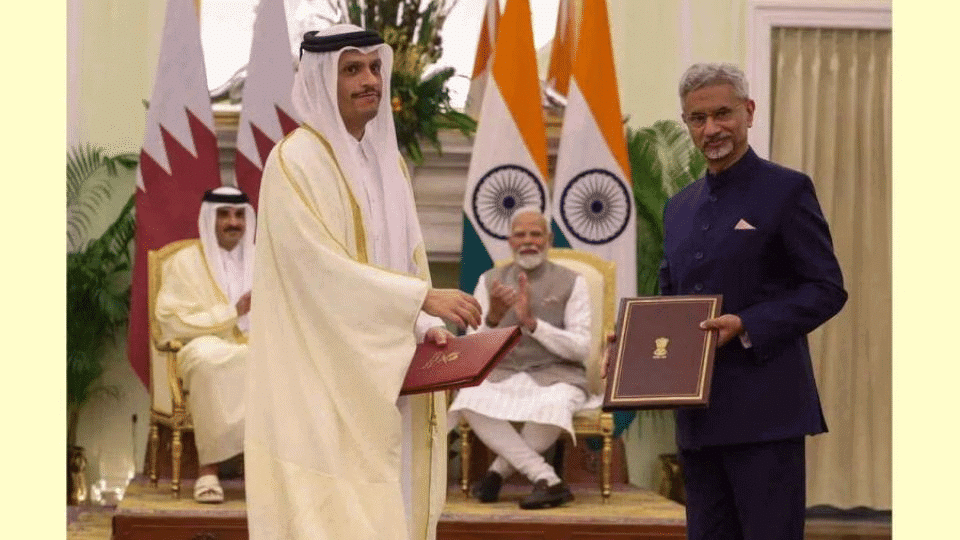 Why in News?
Why in News?
- Sheikh Tamim Bin Hamad Al Thani, the Amir of Qatar, recently visited India to strengthen bilateral relations, focusing on key areas such as trade, energy, and investment. Both nations have set a goal to double their trade to USD 28 billion and enhance Qatari investments in India.
Key Takeaways
- Elevation to Strategic Partnership: India and Qatar have upgraded their bilateral relationship to a strategic partnership to enhance cooperation in trade, investment, energy, and security.
- Target for Bilateral Trade: The two countries aim to increase bilateral trade from USD 14 billion to USD 28 billion by 2030.
- Qatar’s Investment Commitment: Qatar’s sovereign wealth fund has invested USD 1.5 billion in India and pledged an additional USD 10 billion in infrastructure, renewable energy, and emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning.
- Avoidance of Double Taxation: A revised agreement was exchanged to promote economic and financial collaboration.
- Status of Free Trade Agreement (FTA): Ongoing discussions focus on negotiating a FTA between India and the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), which includes Qatar.
- Infrastructure: Talks included operationalizing India’s Unified Payment Interface (UPI) in Qatar and expanding the presence of Qatar National Bank in India through GIFT (Gujarat International Finance Tec-City).
- Israel-Palestinian Conflict: India reiterated its support for a two-state solution.
Additional Details
- Energy Cooperation: In FY 2022-23, Qatar was India’s largest supplier of Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG), providing over 48% of total LNG imports and being the top supplier of liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) with 29% of imports. This energy partnership is crucial as India shifts towards cleaner energy sources.
- Strategic Cooperation: Qatar plays a vital role in India’s “Look West” policy, enhancing ties with GCC countries to bolster energy security and trade.
- Geopolitical Significance: Qatar acts as a mediator in significant geopolitical issues, such as the Afghanistan and Israel-Palestine conflicts, allowing India to engage indirectly in regional matters.
- Counterterrorism Cooperation: India and Qatar share interests in combating terrorism, with Qatar's strategic location facilitating collaboration on counterterrorism and maritime security.
This partnership signifies a robust collaboration between India and Qatar, highlighting the importance of mutual cooperation in various sectors to achieve shared economic and strategic goals.
Microfinance Sector in India
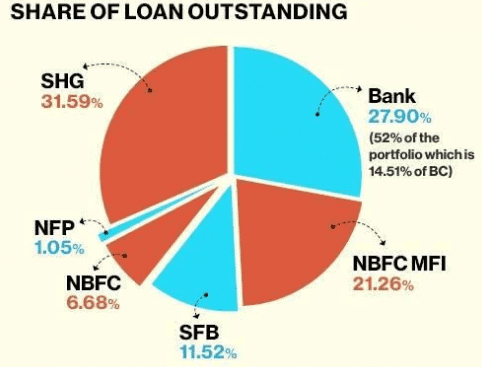
Why in News?
- The microfinance sector in India has been instrumental in advancing financial inclusion by providing credit to underserved households. Nonetheless, increasing concerns regarding rapid credit expansion highlight the necessity for more robust regulations and responsible lending practices.
Key Takeaways
- Microfinance Institutions (MFIs) provide essential financial services to those lacking access to traditional banking.
- The sector is regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) under the NBFC-MFI framework established in 2014.
- As of March 31, 2024, the sector consists of 168 MFIs serving over 3 crore clients with a loan portfolio of Rs 4.33 lakh crore.
Additional Details
- Microfinance Institutions (MFI): These are financial entities that extend small loans and other financial services to individuals without access to banking facilities, aiming to empower low-income and unemployed individuals and promote financial inclusion.
- Regulatory Framework: MFIs are governed by the RBI's NBFC-MFI framework, which includes provisions for client protection, borrower safeguards, and credit pricing.
- Challenges Faced by MFIs:
- Profitability and Economic Sustainability: Many MFIs rely on subsidies, face high operational costs, and only a fraction are truly profitable post capital expenses.
- Regulatory Gaps: Inadequate documentation and delayed credit bureau data hinder accurate evaluations, especially by unregulated lenders.
- Rising Competition: Increased players in the sector lead to greater credit supply without stringent due diligence.
- Poor Model Selection: MFIs primarily use the SHG or JLG models, which may not effectively address the needs of borrowers.
- Gender Bias: Women encounter significant barriers in accessing financial services, being 15-20% less likely than men to have a bank account.
- Government Schemes Related to Microfinance:
- Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY)
- Self-Help Group (SHG) - Bank Linkage Program
- Credit Guarantee Fund for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE)
- Proposed Reforms for Sustainable Growth:
- Strengthening Credit Assessment with standardized household income evaluations and enhanced liability tracking.
- Enhancing Borrower Identification through Aadhaar-based KYC processes.
- Adopting need-based lending models that cater to borrower requirements rather than standardized approaches.
- Promoting gender-inclusive financing to improve women's access to financial services.
- Conducting robust impact assessments of microfinance initiatives to gauge their effectiveness in poverty alleviation.
In conclusion, while the microfinance sector in India has made significant strides in promoting financial inclusion, it faces numerous challenges that necessitate regulatory reforms and innovative lending practices to ensure its sustainable growth.
22nd Foundation Day of NCST

Why in News?
- The National Commission for Scheduled Tribes (NCST) celebrated its 22nd Foundation Day on 19th February 2025, emphasizing the Commission's critical role in safeguarding the rights of Scheduled Tribes (STs).
Key Takeaways
- The NCST was established to specifically address the distinct needs of Scheduled Tribes in India.
- The Commission plays a vital role in monitoring constitutional safeguards and advising on socio-economic development for STs.
Additional Details
- Origin and Evolution: The National Commission for Scheduled Castes (SCs) and STs was first set up in 1992. To meet the specific requirements of STs, the NCST was formed in February 2004 via the 89th Constitutional Amendment Act, which amended Article 338 and introduced Article 338A.
- Composition and Tenure: The NCST consists of a Chairperson (of Cabinet Minister rank), a Vice-Chairperson (of Minister of State rank), and three other Members (of Secretary rank), all appointed by the President. The tenure for members is three years, with the possibility of reappointment for a maximum of two terms.
- Key Functions: Under Article 338A(5), the NCST monitors protections for STs, addresses tribal rights issues, and advises on socio-economic development. It reports to the President regarding tribal welfare, suggests policy measures, and oversees ST welfare programs.
- The Commission also recommends land ownership rights for tribals, as outlined in the Forest Rights Act, 2006, and advocates for the implementation of the Panchayat (Extension to Scheduled Areas) Act, 1996 (PESA).
Challenges Regarding the NCST
- Administrative and Financial Constraints: The NCST operates under the Ministry of Tribal Affairs, which limits its financial and operational autonomy, affecting its budgeting and operations.
- Manpower Shortages: The effectiveness of the NCST is hampered by staff shortages and prolonged vacancies in key positions, which leads to delays in addressing tribal welfare issues.
- Weak Enforcement Powers: The recommendations made by the NCST are not binding, limiting its ability to enforce protective measures for STs and leading to a lack of accountability among government agencies.
- Lack of Awareness and Outreach: Many tribal individuals are unaware of their rights and the existence of the NCST, indicating a need for stronger grassroots engagement.
Way Forward
- Strengthening Legal Mandate: The NCST should be empowered to impose penalties similar to those granted to the Central Information Commission under the Right to Information Act, 2005.
- Capacity Building: Establishing a separate cadre for NCST personnel can help address staffing shortages and improve operational efficiency.
- Mandatory Consultation on Policies: Ensuring compliance with Article 338A(9) will make it mandatory for ministries and states to consult the NCST on all tribal welfare policies.
- Grievances: The NCST should establish a dedicated grievance redressal cell to address cases of violence, displacement, and human rights violations effectively.
In conclusion, the NCST plays a crucial role in advocating for the rights and welfare of Scheduled Tribes in India. Addressing its challenges and enhancing its capabilities will be vital for the effective protection of tribal rights and interests.
Draft UGC Regulations 2025
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- Recently, six states in India have requested the withdrawal of the draft University Grants Commission (UGC) Regulations for 2025. The concerns raised center around issues of federal autonomy and the standards of education within the country.
Key Takeaways
- The draft consolidates the selection process for Vice Chancellors (VCs), eliminating the involvement of State governments in their appointment.
- Universities that fail to adhere to these regulations may be excluded from UGC funding and other schemes.
- The tenure for VCs is suggested to be extended from three years to five years.
- It permits the hiring of individuals from non-academic backgrounds who possess at least a decade of senior-level experience in public administration and policy.
- Mandatory entrance examinations for undergraduate programs are proposed.
- The regulations aim to enhance collaboration between academia and industry, promote the use of Indian languages in academic publications, increase transparency, and incorporate sportspersons into teaching roles.
Additional Details
- Genesis: The initiative to create a national education system in India began in 1944 with the Sargeant Report, which proposed the formation of a University Grants Committee. Established in 1945, this committee initially oversaw Aligarh, Banaras, and Delhi universities. By 1947, its responsibilities expanded to all universities.
- The 1948 University Education Commission, led by Dr. S. Radhakrishnan, recommended restructuring based on the UK model. Subsequently, in 1952, the Union Government designated the University Grants Commission (UGC) to manage grants for Central Universities and higher education institutions.
- Formally inaugurated in 1953 by Maulana Abul Kalam Azad, the UGC became a statutory body in 1956, with its head office located in New Delhi.
The proposed UGC Regulations 2025 have stirred significant debate regarding the balance of power between central and state educational authorities, as well as the impact on the quality and governance of higher education in India.
India-Argentina Lithium Partnership
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- India and Argentina have recently signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) aimed at exploring lithium resources and investment opportunities in Argentina. This collaboration is significant given Argentina's status as a major player in the global lithium market.
Key Takeaways
- Argentina is known for its vast lithium reserves.
- The country is part of the 'Lithium Triangle,' which also includes Bolivia and Chile.
- India aims to enhance its lithium supply chain through this partnership.
Additional Details
- Lithium: This element is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal often referred to as white gold. It is the lightest metal and solid element, classified as both an alkali and a rare metal.
- Lithium is extracted from ores such as petalite, lepidolite, and spodumene, as well as subsurface brines. It is highly reactive and flammable, necessitating storage in mineral oil.
- This mineral is crucial for electric vehicle batteries and renewable energy storage.
- Countries with the largest lithium reserves include Chile, China, and Australia.
- In India, significant lithium reserves have been identified in regions such as Salal-Haimna in Reasi district of Jammu & Kashmir, Koderma and Giridih in Jharkhand, and Mandya in Karnataka.
This partnership between India and Argentina is poised to strengthen India's position in the lithium market, which is essential for advancing electric vehicle technology and renewable energy solutions.
DDoS Cyber-Attack
 Why in News?
Why in News?
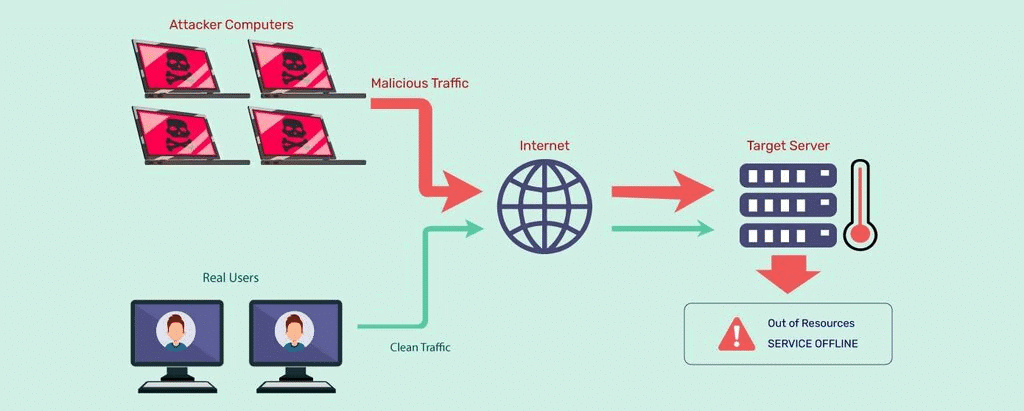
- The Kaveri 2.0 portal in Karnataka, which is responsible for property registration, experienced significant disruptions due to a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack. This attack overwhelmed the system with a flood of fake accounts and automated requests, leading to considerable downtime.
Key Takeaways
- A DDoS attack is a type of cyberattack that overwhelms a website or network with malicious traffic, rendering it inaccessible.
- DDoS attacks utilize multiple compromised systems, also known as botnets, to execute large-scale attacks.
Additional Details
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attack: This type of attack is characterized by its method of flooding a target with traffic from numerous sources, making it difficult to mitigate.
- DDoS attacks can lead to severe consequences, such as service disruption, loss of revenue, exposing cybersecurity vulnerabilities, and harming an organization's reputation.
To defend against DDoS attacks, organizations can implement various mitigation strategies including traffic filtering, rate limiting, bot detection techniques (like CAPTCHA and behavioral analysis), conducting security audits, formulating incident response plans, and employing multi-factor authentication. These measures are essential for enhancing the overall security posture against such cyber threats.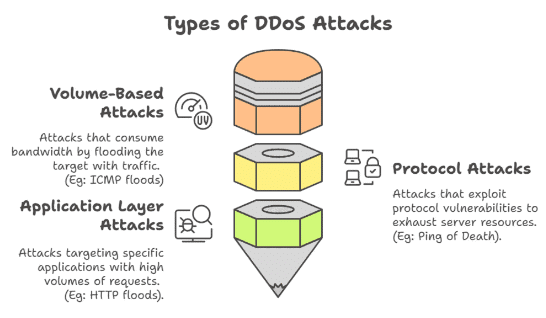
For further insights, one can explore the topic of Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks.
|
201 videos|842 docs|2245 tests
|















