Weekly Current Affairs (15th to 21st July 2024) | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
China, and Russia Conduct Joint Pacific Naval Patrol
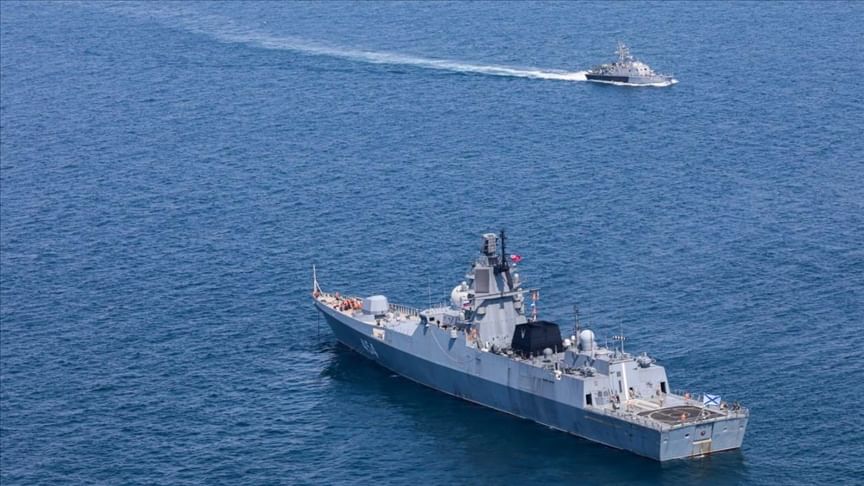

- Recently, China's defense ministry said that Russian and Chinese naval forces worked together to patrol the northern and western Pacific Ocean, which was their fourth joint naval practice. The patrols were not directed at any specific country and were unrelated to current political situations.
- China and Russia have been strengthening their military, economic, and political ties over time, especially since Russia's invasion of Ukraine in February 2022. This has led to criticism from Western countries concerning China's perceived neutrality in the conflict.
- The China-Russia alliance holds significant strategic implications, particularly in their stance against NATO. Despite tensions with NATO, both countries collaborate on military exercises to demonstrate their combined strength and foster mutual security cooperation.
- In addition to recent joint patrols, China announced further naval training with Russia near Zhanjiang, termed Joint Sea-2024. These actions were a response to criticisms from NATO and Japan regarding their burgeoning ties with Russia.
- While the China-Russia joint exercises are increasing in scale and frequency, reports suggest that their military operations are not as well-integrated as they are with NATO forces.
- Historically, the relationship between China and Russia has experienced fluctuations due to various global factors. Despite challenges, recent years have seen strengthened ties, with a focus on areas like energy, trade, and technology.
NITI Aayog Launches Hackathon for Zero-Emission Trucks
The NITI GearShift Challenge was launched by NITI Aayog in collaboration with various schools and organizations. This initiative is part of the broader e-FAST India program, which aims to promote the increased use of zero-emission trucks (ZETs) in India.
Purpose of the NITI GearShift Challenge:
- The main aim of the challenge is to inspire individuals to innovate new business approaches that facilitate the adoption of electric vehicles in India. It addresses issues in the economy, environment, and specific industries by engaging a diverse range of participants, including students, scholars, and industry professionals.
Structure of the Hackathon:
- The GearShift Challenge comprises two distinct rounds:
- Round 1: Participants present preliminary business plans that tackle specific technical, operational, or financial barriers hindering the widespread use of ZETs. These plans are supported by research.
- Round 2: Shortlisted teams refine their proposals into comprehensive business models that encompass detailed implementation plans and further research. Industry experts provide guidance on these concepts to enhance their feasibility and impact.
Significance of Transitioning to Electric Trucks:
- Transitioning to electric trucks is crucial for India's supply chain. The freight industry heavily relies on diesel fuel, significantly contributing to CO2 emissions. Shifting to electric trucks in this sector is vital for environmental preservation, air quality improvement, and ensuring sustainable energy for all. This transition aligns with global sustainability objectives.
Anticipated Outcomes:
- The NITI GearShift Challenge seeks innovative strategies to accelerate the adoption of ZETs. Its objectives include reducing pollution and positioning India as a leader in eco-friendly freight transport. The successful initiatives from the hackathon are anticipated to influence policies and inspire similar endeavors worldwide, showcasing India's commitment to environmental conservation and economic enhancement.
New High-Efficacy Malaria Vaccine Launched in Cote d’Ivoire
 The World Health Organization (WHO) gave the vaccine approval recently, and it was distributed throughout the country for the first time.
The World Health Organization (WHO) gave the vaccine approval recently, and it was distributed throughout the country for the first time.
- Development and Approvals
Novavax provided the Matrix-M adjuvant technology for the R21/Matrix-M vaccine, which was created by the University of Oxford and the Serum Institute of India (SII). The vaccine underwent rigorous testing by the WHO to ensure its efficacy and safety.
- Manufacturing and Distribution
The vaccine is highly effective and requires only a small dose, enabling rapid mass production. Currently, 25 million doses have been manufactured, with plans to increase production to 100 million doses annually. Each dose costs less than USD 4.
- Rollout and Impact
Cote d'Ivoire led the way in using the R21/Matrix-M vaccine, aiming to vaccinate around 250,000 children aged 0 to 23 months in 16 regions. Malaria claims approximately four lives daily in the country, mostly children, and this vaccine has the potential to significantly reduce that toll. Additionally, other countries like Ghana, Nigeria, Burkina Faso, and the Central African Republic have also approved the vaccine. The introduction of R21/Matrix-M and another vaccine, RTS,S, is expected to save tens of thousands of lives annually. By 2024, with support from Gavi, 15 African nations intend to implement this vaccine, safeguarding approximately 6.6 million children over a two-year period.
- About Serum Institute of India
The Serum Institute of India, established by Cyrus Poonawalla in 1966, is the largest vaccine manufacturer globally in terms of doses produced. Headquartered in Pune, India, it initially focused on immunobiologicals. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the institute played a crucial role by mass-producing the Covishield vaccine, a variant of the Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine. Noteworthy, the institute also develops vaccines for various diseases like polio, diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, BCG, r-Hepatitis B, measles, mumps, and rubella. Its Pune facility stands as the largest vaccine factory worldwide concerning doses produced and sold internationally.
INS Delhi Wins Best Ship of Eastern Fleet 2024

On July 14, 2024, in Visakhapatnam, the Fleet Awards Function celebrated the success of the Eastern Fleet. INS Delhi was recognized as the top ship.
Acknowledgment of Excellence:
- Every year, outstanding ships are honored at the event. INS Kavaratti was lauded as the best in its category. INS Shivalik, INS Sumedha, and INS Sumitra were commended for their dedication.
Guests of Honour:
- Vice-Admiral Rajesh Pendharkar, the Chief Guest, and Rear Admiral Rajesh Dhankhar, highlighted the collaborative efforts of the fleet.
Operational Achievements and Activities:
- The Eastern Fleet remained busy safeguarding naval interests in the Indian Ocean Region through various operations and drills.
Cultural Celebrations:
- Besides official proceedings, a cultural program fostered unity, boosted morale, and commemorated the Indian Navy's rich heritage.
About INS Delhi:
- INS Delhi, a guided-missile frigate, was inducted into the Indian Navy in 1997. Built by Mazagon Dock Limited, it is a formidable vessel armed with advanced weaponry and electronic systems.
National Quantum Mission – Current Updates (July, 2024)
 India initiated the National Quantum Mission in 2022 with a budget of Rs 6,000 crore, equivalent to $0.75 billion. The country is actively investing in quantum technology to address challenges in energy, healthcare, and other sectors. India aims to accelerate its progress in quantum sciences to compete with leading nations like China and the US, leveraging its existing strong foundation in the field.
India initiated the National Quantum Mission in 2022 with a budget of Rs 6,000 crore, equivalent to $0.75 billion. The country is actively investing in quantum technology to address challenges in energy, healthcare, and other sectors. India aims to accelerate its progress in quantum sciences to compete with leading nations like China and the US, leveraging its existing strong foundation in the field.
Understanding Quantum Technologies
- Quantum technologies utilize the peculiar behaviors of subatomic particles such as electrons, which can exist in multiple locations simultaneously (superposition) and be interconnected over significant distances. These characteristics, demonstrated in various experiments, are now applied in practical applications like quantum computing, communications, sensors, and materials.
The Scale of Global Investment and Competitiveness
- When it comes to quantum science, China and the US are outpacing India in terms of investment and output. China's investment amounts to around $15 billion, while the US invests approximately $3.75 billion, surpassing India's current spending. Additionally, these nations engage in more research and patent activities than India, intensifying competition in this domain.
India’s Current Status and Potential
- Despite the challenges, India possesses a substantial base for quantum education. The country boasts more students studying quantum-related subjects than China and the US combined. Moreover, India houses robust research teams led by 110 to 145 esteemed scientists. Notably, Indian experts excel in specific areas like quantum communications and sensing, suggesting the potential for India to bridge the technological and innovation gap in these fields.
Strategic Steps Ahead
- The inception of the National Quantum Mission signals a deliberate and earnest effort to enhance India's proficiency in quantum technologies. To advance toward this objective, India should actively encourage youth to pursue careers in science, fostering a dedicated community of quantum scientists akin to its achievements in atomic energy and space science. This strategic initiative aims to nurture an ecosystem that can eventually establish technological leadership and yield substantial economic benefits. India aspires to rival or surpass global competitors in quantum technologies by leveraging its existing strengths, emphasizing strategic planning, and fostering collaborations with other nations.
Maharashtra Special Public Security (MSPS) Act, 2024
 The MahaYuti government, led by the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), approved the Maharashtra Special Public Security (MSPS) Act on July 11, 2024. This legislation aimed to halt the spread of Naxalism in urban areas. The proposed law, often referred to as the "urban naxal" law, has sparked significant debate.
The MahaYuti government, led by the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), approved the Maharashtra Special Public Security (MSPS) Act on July 11, 2024. This legislation aimed to halt the spread of Naxalism in urban areas. The proposed law, often referred to as the "urban naxal" law, has sparked significant debate.
Purpose of the Bill:
- The government believes that Naxal-related activities are on the rise in cities. Deputy Chief Minister Devendra Fadnavis highlighted the role of support organizations aiding Maoist groups with logistics. The law intends to equip the government with the necessary tools to effectively manage these activities.
Comparison with Existing Laws:
- The MSPS Act shares similarities with the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act (UAPA) but proposes alternate monitoring approaches. Instead of the UAPA's tribunal system, an advisory board would confirm the identities of banned groups. The Maharashtra Control of Organized Crime Act (MCOCA) also holds significance in this context.
Key Provisions of the MSPS Act:
- The Act empowers the government to declare any group illegal and outlines four primary offenses:
- Being associated with an unlawful group.
- Raising funds for or sheltering members of a criminal group.
- Promoting or organizing illegal groups or events.
- Engaging in or plotting illicit activities. Penalties include fines and prison sentences ranging from two to seven years.
Legislative Status:
- The Bill has been introduced in the Lower House, but with the Assembly's term ending, its future is uncertain, particularly with elections on the horizon. The Bill became invalid following the conclusion of the summer session.
Opposition Response:
- Opposition figures like former Chief Minister Prithviraj Chavan have criticized the Bill as severe and ineffective, arguing that existing laws suffice to manage Naxal activities. Chavan suggests that the government aims to stifle dissent, implying that a change in government could lead to the Bill's repeal.
Asia’s First Pre-Clinical Network Facility Inaugurated in Faridabad
 Asia's first Pre-clinical Network Facility for health study was inaugurated in Faridabad, Haryana by Dr. Jitendra Singh, Minister of State for Science and Technology. This facility is a part of the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI), aiming to enhance research capabilities during epidemics.
Asia's first Pre-clinical Network Facility for health study was inaugurated in Faridabad, Haryana by Dr. Jitendra Singh, Minister of State for Science and Technology. This facility is a part of the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI), aiming to enhance research capabilities during epidemics.
What is CEPI?
- CEPI, known as the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations, is an international organization dedicated to accelerating the development of vaccines for infectious diseases. By fostering collaboration in research and funding, CEPI strives to bolster global readiness and response to epidemics.
Role of BRIC-THSTI
- The BRIC-Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI) has been designated by CEPI as a pre-clinical network laboratory due to its capability to handle Biosafety Level 3 (BSL3) pathogens. This advanced laboratory enables comprehensive testing and enhancement of medicines and treatments.
Significance of the Pre-clinical Network Facility
- This facility stands as a pioneering initiative in Asia and the ninth of its kind globally. Its establishment enhances India's preparedness for epidemics and facilitates collaborative research among international scientists, thereby strengthening responses to urgent health threats.
Experimental Animal Facility
- This facility boasts one of India's largest living spaces for small animals, accommodating approximately 75,000 mice and other creatures. It serves as a critical resource for pre-clinical investigations by providing a controlled environment for testing drugs and vaccines.
About Coalition of Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI)
- Formed in 2017, the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI) focuses on expediting vaccine development, particularly for emerging infectious diseases like Ebola and Lassa fever. CEPI operates through a collaborative framework involving governments, NGOs, and businesses to ensure equitable vaccine access during outbreaks. With a significant investment exceeding $1 billion in research and development, CEPI collaborates closely with organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO), GAVI, and the Global Fund for TB, AIDS, and Malaria.
Two Flower Fly Species Reported from Kerala for the First Time
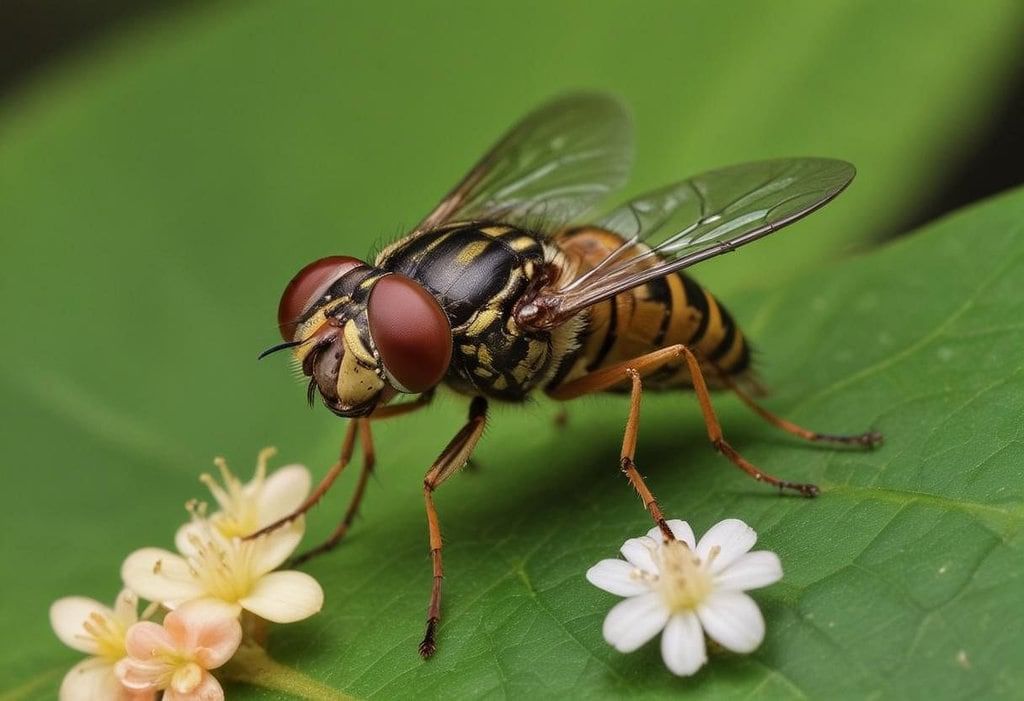 The Mesembrius Rondani genus, established in 1857, is an ancient genus with around 58 species found in different parts of the world like the Oriental, Australasian, and Afrotropical regions, as well as the Mediterranean Basin of the Palaearctic Region. These species fall under the Eristalini tribe within the Eristalinae subfamily.
The Mesembrius Rondani genus, established in 1857, is an ancient genus with around 58 species found in different parts of the world like the Oriental, Australasian, and Afrotropical regions, as well as the Mediterranean Basin of the Palaearctic Region. These species fall under the Eristalini tribe within the Eristalinae subfamily.
Research on Flower Flies by Shadpada Entomology Research Lab:
- A notable discovery was recently made by scientists from the Shadpada Entomology Research Lab (SERL) at Christ College in Irinjalakuda. Led by research scholar Athul Sankar C., along with Assistant Professor Dr. Bijoy C. and Associate Professor Dr. Shaji E.M., they identified two flower fly species, Mesembrius bengalensis and M. quadrivittatus, in the Kole wetlands and Vilagan Kunnu hillocks of Thrissur district for the first time in Kerala.
Ecological Significance of Flower Flies:
- Flower flies, part of the Syrphidae family, play a vital ecological role. They have adapted to resemble bees and wasps, which helps in their survival by repelling predators. Apart from their survival tactics, flower flies are essential as pollinators, with their larvae serving as natural pest controllers and recyclers of nutrients. Understanding their distribution and behavior is crucial due to their ecological importance.
Contribution to Entomological Studies:
- The team's findings have been published in ENTOMON, a respected entomology journal. This research not only expands Kerala's faunal list but also enriches the biological knowledge of the region. Prior to this discovery, a survey by the team had documented 59 flower fly species in Kerala, indicating a diverse ecosystem.
Research Approach and Results:
- Athul Sankar C. and his team utilized entomological techniques such as stereozoom microscopes and digital imaging to record the unique traits of these species. They've made the key features and images of these species publicly accessible, encouraging community involvement in biological research and conservation endeavors.
Implications for Conservation and Future Research:
- These discoveries are crucial for conservation efforts as they offer insights into the preferred habitats and geographic distribution of flower flies. Knowing where these species thrive can aid in formulating policies and actions to safeguard these important pollinators. The team's work also establishes a foundation for upcoming ecological and entomological studies in the region, potentially leading to more discoveries and improved environmental preservation.
About SERL (Shadpada Entomology Research Lab):
- SERL was founded on 1st August 2019 under the Department of Zoology at Christ College (Autonomous), Irinjalakuda, Thrissur, Kerala, India, under the supervision of principal investigator Dr. Bijoy C. The lab's primary focus is on conducting research and offering MSc dissertations, summer training, and PhD programs related to insect taxonomy, bio-ecology, and diversity. Additionally, the lab engages in outreach activities through identification services, short training programs, invited talks, commemorative events, and various competitions like quizzes and BioBlitz. Ongoing doctoral projects at the lab focus on the taxonomy of lesser-known insect groups such as solitary bees, cuckoo wasps, antlions, grasshoppers, flower flies, robber flies, and more.
|
164 videos|800 docs|1158 tests
|
















