Weekly Current Affairs (22nd to 28th February 2025) - 1 | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
World Day of Social Justice 2025

Why in News?
- The United Nations (UN) observed the World Day of Social Justice (WDSJ) on February 20, 2025, advocating against poverty, exclusion, and unemployment while promoting equality and solidarity. The 2025 theme of WDSJ, “Empowering Inclusion: Bridging Gaps of Social Justice,” focuses on inclusive policies and social protection, emphasizing the importance of “Strengthening a Just Transition for a Sustainable Future.”
Key Takeaways
- The UN promotes social justice to combat poverty and exclusion.
- The theme for 2025 emphasizes empowerment and inclusion.
What is World Day of Social Justice?
- About: It is an initiative specifically led by the International Labour Organization (ILO) to promote social justice, equality, human rights, and fair opportunities for all.
- Designated by the UN General Assembly on November 26, 2007.
Role of ILO
- The ILO adopted the Declaration on Social Justice for a Fair Globalization on June 10, 2008, in response to WDSJ.
- This declaration expands upon the Philadelphia Declaration of 1944 and the Fundamental Principles and Rights at Work of 1998.
- In 2009, the ILO launched Social Protection Floors to ensure basic social security and reduce poverty.
Social Justice in India
In India, the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment (MoSJE) is the nodal agency for uplifting vulnerable communities, including:
- Scheduled Castes
- Other Backward Classes
- Senior Citizens
- Victims of Alcoholism and Substance Abuse
- Transgender Persons
- Denotified and Nomadic Tribes (DNTs)
- Economically Backward Classes (EBCs)
- Economically Weaker Section (EWS)
Significance
- Globalization: The declaration redefined the ILO's role in globalization, ensuring it remains central to economic policies.
- Alignment with UN Goals: Supports the UN's vision of decent work, fair globalization, fundamental rights, social protections, and productive social dialogue.
- Global Stability: Social justice is essential for global peace and security, threatened by labor insecurity, inequality, and breakdowns in social contracts.
- Achieving social justice requires fundamental freedoms, human rights, and economic stability.
Challenges
- Persistent issues such as financial crises, insecurity, poverty, and exclusion continue to hinder social justice globally.
What are India’s Constitutional Provisions on Social Justice?
Preamble: Ensures social, economic, and political justice, guaranteeing equality of status and opportunity, promoting fraternity to uphold individual dignity and national unity.
Fundamental Rights:
- Article 23: Prohibits human trafficking and forced labor, making such practices punishable by law.
- Article 24: Bans child labor in hazardous occupations, protecting children’s rights to safety and education.
Directive Principles of State Policy:
- Article 38: Directs the State to reduce social and economic inequalities.
- Article 39: Ensures equal livelihood, fair wages, and protection from exploitation.
- Article 39A: Guarantees free legal aid for disadvantaged people.
- Article 46: Mandates special educational and economic promotion for SCs, STs, and weaker sections to prevent discrimination.
What are Initiatives for Ensuring Social Justice in India?
- PM-AJAY: Pradhan Mantri Anusuchit Jaati Abhyuday Yojana (PM-AJAY) supports Scheduled Caste (SC) communities through skill development, income generation, and village infrastructure. It includes:
Adarsh Gram development
Grants-in-Aid for socio-economic projects
Hostel construction in higher education institutions - SRESHTA: Scheme for Residential Education for Students in High Schools in Targeted Areas (SRESHTA) funds top CBSE/State Board schools for SC students in classes 9-12 and supports NGOs to run residential and non-residential schools and hostels.
- Purple Fests: Festival of Inclusion that fosters inclusion, dignity, and equal opportunities for persons with disabilities (Divyangjan).
- NAMASTE: National Action for Mechanized Sanitation Ecosystem (NAMASTE) ensures safety, dignity, and sustainable livelihood for sanitation workers in urban India, expanded to include waste pickers as a target group from FY 2024-25.
- SMILE: Support for Marginalized Individuals for Livelihood and Enterprise (SMILE) scheme aims at rehabilitating transgender individuals and persons engaged in begging, creating a Begging-free India. It is currently implemented in 81 cities, with 7,660 beggars identified and 970 rehabilitated as of November 2024.
- PM-DAKSH Yojana: Pradhan Mantri Dakshta Aur Kushalta Sampann Hitgrahi (PM-DAKSH) provides free skill training to SCs, OBCs, EBCs, DNTs, and Safai Karamcharis for economic empowerment.
- Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyan (NMBA): Aims for a drug-free India by targeting 272 high-risk districts through supply control, awareness, and treatment initiatives. Since its launch on August 15, 2020, NMBA has reached 13.57 crore people, with 4.42 crore youth and 3.85 lakh educational institutions participating.
India’s efforts towards social justice are rooted in constitutional provisions and targeted schemes addressing socio-economic disparities. By promoting inclusive policies, skill development, and rehabilitation programs, the government aims to uplift marginalized communities with dignity, equity, and sustainable livelihoods, aligning with global commitments to social justice and empowerment.
Mains Question:
- How do constitutional provisions in India support social justice? Discuss with examples of key government initiatives.
Climate Risk Index 2025
Why in News?
- The international environmental think tank Germanwatch has released the Climate Risk Index (CRI) 2025, which highlights the vulnerabilities of countries to extreme weather events.
Key Takeaways
- The CRI ranks countries based on their vulnerability to extreme weather events, assessing human and economic losses caused by climate-induced disasters.
- It has been released annually since 2006, covering data from the past 30 years.
- Between 1993 and 2022, over 765,000 lives were lost, resulting in economic losses of USD 4.2 trillion.
- Floods, droughts, and storms were the leading causes of global displacement.
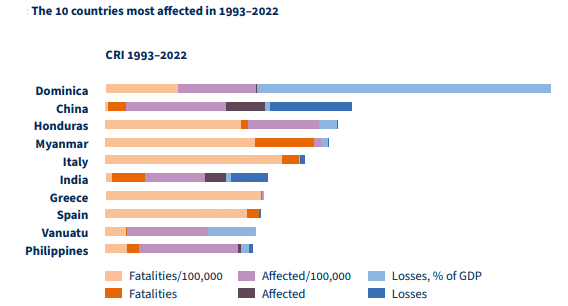
- Dominica, China, and Honduras were the top three countries affected by extreme weather events from 1993 to 2022.
- In 2022, Pakistan, Belize, and Italy were the most affected countries.
- Seven of the ten worst-affected countries are classified as low- and middle-income countries (LMICs).
Impact on India
- India ranked as the most affected country from 1993 to 2022, accounting for 80,000 fatalities (10% of global fatalities) due to extreme weather events.
- The country experienced severe floods in 1993, 2013, and 2019, intense heatwaves reaching ~50°C in years such as 1998, 2002, 2003, and 2015, and destructive cyclones like Gujarat (1998), Odisha (1999), Hudhud (2014), and Amphan (2020).
Key Challenges Related to Climate Change Mitigation Strategies
- Historical Responsibility vs. Future Emissions: High-income nations, despite their historical emissions, demand greater climate responsibility from emerging economies like India and China, leading to tensions over burden-sharing and climate finance commitments.
- Global Temperature Breach: The 1.5°C threshold was breached for a full year in 2024, exposing inadequate mitigation efforts.
- Weak Climate Commitments: Many countries are not updating their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs), creating a gap between promises and action.
- Insufficient Climate Finance: The USD 300 billion annual funding for developing nations is inadequate, and delays in operationalizing the Loss and Damage Fund hinder support for climate-vulnerable countries.
Key Suggestions to Combat Climate Change
- Enhanced Climate Finance: Greater financial and technical support is needed for vulnerable countries to adapt and manage climate-induced losses and damages.
- Strengthening Mitigation Efforts: Nations must scale up their efforts to restrict global warming to 1.5°C or lower.
- Accountability of High-Income-High-Emission Countries: Developed nations must expedite their mitigation actions to curb rising human and economic costs.
- Call for Urgent Climate Action: Timely action in adaptation and mitigation is needed to avoid escalating climate-related losses in the future.
The findings of the Climate Risk Index 2025 underscore the urgent need for global cooperation and commitment to combat the escalating impacts of climate change, particularly for the most vulnerable nations.
Detection of Most Energetic Neutrino
Why in News?
- Scientists have successfully detected the highest-energy neutrino ever recorded, utilizing the KM3NeT (Cubic Kilometre Neutrino Telescope) observatory located in the Mediterranean Sea. This neutrino was found to be 30 times more energetic than any previously observed neutrino, 1015 times more energetic than photons, and 10,000 times more powerful than particles produced by the Large Hadron Collider, the largest particle accelerator in the world.
Key Takeaways
- The detected neutrino is unprecedented in energy levels.
- It was identified using advanced neutrino observatories.
- Neutrinos are crucial for understanding cosmic phenomena.
Additional Details
- Neutrinos: Often referred to as "ghost particles," neutrinos are electrically neutral and nearly massless subatomic particles that rarely interact with matter, enabling them to traverse immense distances through stars, planets, and galaxies without being deflected by magnetic fields.
- Sources of Neutrinos:
- Natural Sources: Includes solar neutrinos from the Sun, nuclear reactions occurring in stars, supernovae, and cosmic rays.
- Artificial Sources: Produced from nuclear reactors, radioactive decay processes, and particle accelerators.
- Big Bang Neutrinos: These are remnants from the early universe, contributing valuable insights to cosmological studies.
- Types/Flavors of Neutrinos: Neutrinos can change from one flavor to another through a process known as oscillation, which occurs due to quantum mixing.
- Significance in Astrophysics: Neutrinos are crucial for tracing high-energy astrophysical events because they travel undisturbed through the cosmos, unlike cosmic rays. Scientists employ deep-sea or ice observatories to detect neutrinos by capturing Cherenkov radiation, the detectable flash of light produced from rare interactions.
This groundbreaking discovery enhances our understanding of high-energy astrophysics and the fundamental properties of neutrinos, which play a significant role in the universe.
NEP 2020 and Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan
Why in News?
- The Union Government has withheld Tamil Nadu’s central share of funds for opposing the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
Key Takeaways
- Tamil Nadu's opposition to NEP 2020 stems from concerns over language policy and state autonomy.
- The state follows a two-language formula since 1968, contrasting with NEP's three-language mandate.
- Tamil Nadu is drafting its own State Education Policy to better fit its socio-linguistic context.
- There is a call for a pragmatic approach, suggesting that funding should be based on performance indicators rather than policy compliance.
Additional Details
- Language Policy Dispute: NEP 2020 mandates a three-language policy (Tamil, English, and a regional language), which Tamil Nadu views as an imposition of the central government's policy.
- Undermining State Autonomy: Tamil Nadu perceives the Centre's push for uniform NEP implementation as infringing on its autonomy, thereby weakening cooperative federalism.
- Call for a Pragmatic Approach: Tamil Nadu argues that central schemes like Samagra Shiksha and PM SHRI should be delinked from NEP 2020.
What is the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020?
NEP 2020 replaces the 34-year-old NEP of 1986, aiming to bridge gaps in quality, equity, and access to education at all levels.
- Developed based on the recommendations of Dr. K Kasturirangan's committee.
- Prioritizes foundational literacy, a holistic curriculum, multilingual learning, and integrates vocational and academic pathways.
Key Provisions
- Structural Reforms: Introduces a 5+3+3+4 educational structure, catering to children aged 3 to 18 years.
- Experiential Learning: Emphasizes internships, field visits, and real-world projects to connect theory with practice.
- Teacher Training: Focuses on continuous professional development to adapt to evolving educational needs.
Key Initiatives
- PM SHRI scheme: Aims to develop 14,500 ideal schools as role models.
- NIPUN Bharat Mission: Launched to ensure foundational literacy and numeracy by Grade 2.
- PARAKH: Introduced for monitoring learning outcomes.
- NISHTHA: A teacher training program aligned with NEP’s transformative goals.
Major Achievements
- Foundational Stage Curriculum: Implemented the Jadui Pitara kit to promote play-based learning for children aged 3-8.
- Regional Language Inclusion: Engineering and medical courses are now offered in regional languages, enhancing accessibility.
- Four-Year Undergraduate Program (FYUP): Over 105 universities have adopted FYUP for flexible higher education options.
- Digital Learning: PM e-VIDYA and DIKSHA platforms promote universal access to digital learning resources.
Challenges
- Integration of the 5+3+3+4 Structure: Aligning state curricula and training teachers remains a significant challenge.
- Pending Legislation: Proposed merging of UGC, AICTE, and NCTE into a single higher education regulator is still awaiting legislative action.
- Lack of Uniform Monitoring: No standardized assessment metrics exist across states to evaluate NEP's impact effectively.
What is Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan?
Introduced in the Union Budget 2018-19, Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan is a comprehensive program covering education from pre-nursery to Class 12, aimed at ensuring equitable learning outcomes.
Key Features
- Integration of Schemes: It subsumes Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA), Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan (RMSA), and Teacher Education (TE).
- Sector-Wide Development Approach: Streamlines implementation across all levels instead of fragmented project-based objectives.
- Alignment with SDGs: Ensures free, equitable, and quality education, while addressing gender disparities and access for vulnerable groups.
Implementation
- Samagra Shiksha is a centrally sponsored scheme implemented through a single State Implementation Society (SIS) at the State/UT level.
- The withholding of Samagra Shiksha funds highlights the tension between the Centre and Tamil Nadu over NEP 2020. This situation reflects broader issues of federalism, linguistic autonomy, and the implementation of education policy. A collaborative approach is essential to ensure educational progress while respecting state-specific needs.
Question:
- What are the key features of National Education Policy (NEP 2020)? Critically analyze the impact of NEP 2020 on federalism.
Waste Segregation and Waste-to-Energy Plant
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The Supreme Court (SC) has highlighted the critical need for waste segregation at source and has questioned the states in the National Capital Region (NCR) regarding their adherence to the Solid Waste Management Rules (SWM Rules, 2016). The SC has also directed the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) to provide a report on the public health and environmental impacts of waste-to-energy plants.
Key Takeaways
- The SC emphasizes the importance of source segregation of waste.
- Implementation of SWM Rules, 2016 is under scrutiny.
- CPCB is mandated to assess the impacts of waste-to-energy plants.
Additional Details
- What are the Solid Waste Management Rules 2016? These rules govern the management of waste generated from various sources, including households and industries, to prevent environmental hazards.
- What is Waste Segregation at Source? This process entails identifying, classifying, and sorting waste at the point of generation to facilitate effective disposal and recycling based on its biological, physical, and chemical properties.
About Solid Waste: Solid waste constitutes any discarded material from human activities, including households and businesses. Proper management of this waste is essential to avert environmental and health risks.
Provisions in SWM Rules, 2016
Categories of Waste: Waste is categorized into three types:
- Biodegradables: Organic waste that microorganisms can decompose, such as food scraps, soiled wrappers, and paper.
- Non-biodegradables: Includes recyclable and non-recyclable items like plastic, glass, and metal.
- Domestic Hazardous Waste: Includes items like diapers, napkins, mosquito repellants, and cleaning agents.

Significance of Waste Segregation
- Prevents Contamination: Separates hazardous and non-hazardous waste, thereby reducing pollution.
- Reduces Landfill Waste: Ensures that only necessary waste is sent to landfills.
- Enhances Recycling: Improves resource recovery and minimizes the use of raw materials, enabling composting and effective waste treatment.
- Minimizes Health Risks: Aids in preventing diseases caused by medical and hazardous waste.
- Promotes Responsibility: Fosters community participation in waste management efforts.
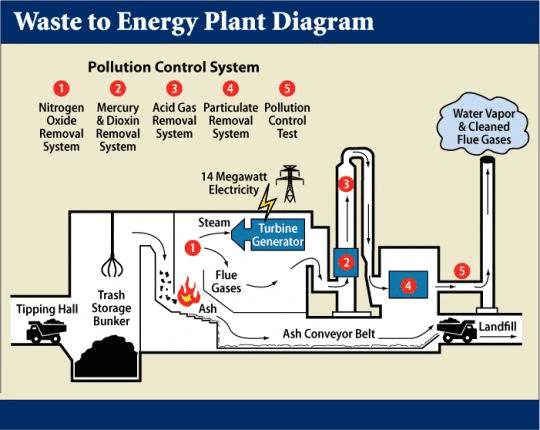
What is a Waste-to-Energy Plant?
- About: Waste-to-energy (WtE) plants convert municipal solid waste (MSW) into energy in the form of electricity, heat, or fuel through various technologies such as pyrolysis and anaerobic digestion. They also generate biogas, BioCNG, and syngas from urban, industrial, and agricultural waste.
Related Provisions in SWM Rules, 2016
- Utilization of Non-Recyclable Waste: Waste with a calorific value of 1500 Kcal/kg or more must be used for energy generation and cannot be landfilled.
- Mandatory Use of RDF: Industrial units within 100 km of a solid waste-based Refuse-Derived Fuel (RDF) plant must replace at least 5% of their fuel with RDF, which is produced from municipal and industrial waste.
Methods of WtE Conversion
- Incineration: Waste is burned at ultra-high temperatures, generating heat to produce steam for electricity.
- Gasification: Biomass is processed at high temperatures without combustion to create syngas for fuel.
- Anaerobic Digestion: Organic waste is broken down by microorganisms in an oxygen-free environment, producing biogas rich in methane.
- Fermentation and Distillation: Organic biomass is fermented and distilled to create ethanol as an alternative fuel.
- Pyrolysis: A thermo-chemical process that converts waste into clean liquid fuels through high-temperature treatment without oxygen.
- Landfill Gas Recovery: Methane and other gases from landfills are captured for energy production.
Utilization of Waste
- Waste-to-energy plants convert waste into heat and electricity, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- They help decrease landfill waste and associated environmental risks such as emissions and groundwater contamination.
- These plants facilitate resource recovery, retaining valuable materials for the circular economy.
- They contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions by diverting waste from landfills.
In conclusion, effective solid waste management through source segregation and waste-to-energy solutions is vital for sustainable urban development. While these measures provide a necessary framework, challenges such as enforcement, integration of the informal sector, and environmental concerns regarding waste-to-energy plants necessitate stricter monitoring and decentralized waste processing.
Mains Question:
- Analyze the role of waste-to-energy plants in India’s waste management strategy.
Self-Testing of HIV
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- A recent study conducted by the Indian Council of Medical Research-National Institute of Translational Virology and AIDS Research (ICMR-NITVAR) in collaboration with Mizoram University has shown the effectiveness of HIV self-testing in Mizoram, a region with a notably high prevalence of HIV.
Key Takeaways
- Mizoram has the highest HIV prevalence rate in India at 2.73%, which is 13 times the national average.
- The primary drivers of the HIV epidemic in this region are injecting drug use and commercial sex work.
- Stigma surrounding HIV testing prevents many individuals from seeking timely treatment.
- HIV self-testing enables individuals to collect blood or saliva samples and interpret their results independently using a test kit.
Additional Details
- Stigma-Free & Private: The study indicates that self-testing offers a convenient and confidential option for high-risk groups to determine their HIV status, proving to be more effective than traditional outreach campaigns, with the potential for adaptation in other regions.
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV): HIV is a virus that targets the immune system, specifically CD4 cells (a type of white blood cell). If not treated, HIV can progress to AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome), leading to increased susceptibility to various infections and cancers.
- Transmission: HIV is transmitted through direct contact with infected bodily fluids such as blood, semen, breast milk, and vaginal fluids, as well as through unprotected sexual intercourse, tattooing, and shared needles, but not through casual contact.
- Symptoms: Early symptoms may include fever and rash; later symptoms can involve swollen lymph nodes, weight loss, and diarrhea; severe symptoms can include tuberculosis, meningitis, and certain cancers (e.g., lymphoma).
- Risk Factors: Factors include having multiple sexual partners, sexually transmitted infections (STIs), and unsafe blood transfusions.
- Diagnosis: HIV can be diagnosed through rapid diagnostic tests for same-day results, self-testing kits, and confirmatory virological tests.
- Prevention: Regular HIV testing, STI screening, safe blood transfusions, and the use of sterilized needles for tattoos are crucial for prevention.
- Treatment: While there is no cure for HIV, Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) can help control the virus and must be taken daily for life to maintain health.
- Advanced HIV Disease (AHD): Defined by the WHO as a CD4 count of less than 200 cells/mm³, individuals with AHD are at a higher risk of mortality, even after beginning ART.
- Global Response: The objective is to end the HIV epidemic by 2030, in line with UN Sustainable Development Goal 3.3.
- India’s Progress: According to the India HIV Estimations 2023 report, approximately 2.5 million individuals live with HIV in India, with an adult prevalence rate of 0.2%. New infections have decreased by 44% since 2010, surpassing the global decline of 39%.
- The National AIDS Control Programme (NACP), initiated in 1992, plays a crucial role in India’s ongoing efforts to combat HIV/AIDS.
This study underscores the importance of innovative testing methods like self-testing in tackling the HIV epidemic, particularly in regions with high prevalence rates and significant barriers to traditional testing methods.
|
201 videos|842 docs|2245 tests
|
















