Weekly Current Affairs (8th to 14th December 2024) Part - 1 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC PDF Download
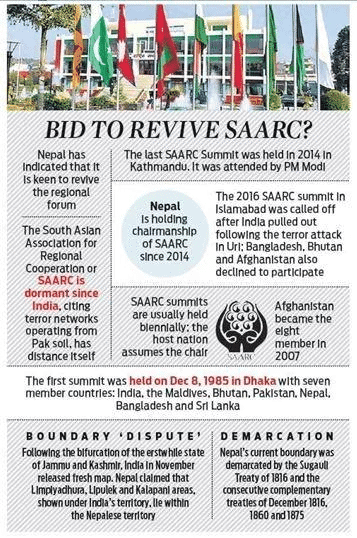
40th Charter Day of SAARC
Why in News?
- On December 8, 2024, the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) celebrated its 40th Charter Day, an annual occasion dedicated to commemorating the establishment of this regional organization.
Key Takeaways
- SAARC was officially founded in December 1985 in Dhaka, Bangladesh, with seven founding members: Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka. Afghanistan joined as the eighth member in 2007.
- The primary objectives of SAARC include promoting welfare, accelerating economic growth, and enhancing collaboration among member states.
Additional Details
- Origins of SAARC: The idea for regional cooperation in South Asia emerged at several conferences from 1947 to 1954, gaining momentum when Bangladesh's President Ziaur Rahman proposed it in 1980.
- Significance: SAARC represents 3% of the world’s land area and 21% of its population, contributing 5.21% (USD 4.47 trillion) to the global economy as of 2021.
- Scope of Cooperation: Key initiatives include the South Asian Free Trade Area (SAFTA) and the SAARC Agreement on Trade in Services (SATIS), aimed at enhancing intra-regional trade and economic interaction.
Relevance of SAARC in Today’s Context
- Platform for Dialogue: Despite challenges, SAARC remains a key platform for dialogue among South Asian countries, including India and Pakistan.
- Shared Regional Solutions: The organization has coordinated responses to issues such as pandemics and cross-border terrorism, establishing initiatives like the Covid-19 Emergency Fund.
- Economic Integration Potential: With a combined GDP exceeding USD 4 trillion and a population of nearly 1.8 billion, SAARC holds significant economic potential that can be harnessed.
- Avoiding Overdependence: Strengthening SAARC allows member nations to maintain control over their developmental paths, reducing reliance on external frameworks.
India's Contribution to SAARC

- SAARC Summits: India has hosted three major summits, showcasing its commitment to regional cooperation.
- Technological Cooperation: Initiatives like the National Knowledge Network and the South Asian Satellite have enhanced educational and technological exchanges.
- Financial Support: India's incorporation of a ‘Standby Swap’ in the Currency Swap Arrangement for SAARC members aims to bolster financial cooperation.
- Disaster Management: The Interim Unit of the SAARC Disaster Management Center in Gujarat supports policy and technical assistance across member nations.
- South Asian University: Located in India, this university fosters educational opportunities for students from SAARC countries.
Key Challenges Facing SAARC

- Political Tensions: Bilateral conflicts and strained relations, particularly involving India and Pakistan, hinder effective cooperation.
- Low Economic Integration: Intra-regional trade is only 5% of total trade, significantly lower than in other regions like the EU.
- Asymmetric Development: India's dominance can create mistrust among smaller member states, affecting collective action.
- Institutional Weaknesses: The requirement for unanimous agreement stymies decision-making, with countries like Pakistan often blocking progress.
- External Influences: China's growing role in the region complicates SAARC dynamics and challenges its effectiveness.
Way Forward
- Promoting Economic Cooperation: Operationalizing the SATIS and expanding the SAARC Development Fund for regional projects.
- Resolving Political Conflicts: Implementing mediation mechanisms and promoting Track-II diplomacy to ease tensions.
- Leveraging Sub-regional Groupings: Utilizing initiatives like BBIN and BIMSTEC to support SAARC's objectives.
- Combating Non-traditional Security Threats: Enhancing regional cooperation on counter-terrorism and disaster management.
- Reforming Institutional Mechanisms: Considering weighted voting to prevent single-country vetoes and strengthening the SAARC Secretariat.
- Encouraging Youth Participation: Fostering exchanges and programs that engage South Asia’s youth in regional development.
In conclusion, despite facing various challenges such as political tensions and economic integration issues, SAARC remains a vital platform for regional cooperation. India's leadership can play a significant role in enhancing the organization's potential, focusing on economic collaboration, resolving political conflicts, and fostering partnerships within the region.
Mains Question:
- Discuss the role of SAARC in promoting regional cooperation in South Asia. What challenges hinder its effectiveness in achieving economic integration?
Ninetyeast Ridge
Why in News?
- A recent study published in Nature Communications reveals that the Ninetyeast Ridge, the Earth's longest straight underwater mountain chain, was formed by a moving hotspot. This challenges the earlier belief that it originated from a stationary hotspot and provides new insights into Earth’s tectonic processes, including age estimates of the Ninetyeast Ridge.
Key Takeaways
- Formation by a Moving Hotspot: The Ninetyeast Ridge, a 5,000 km-long underwater mountain chain located in the Indian Ocean, was formed by the Kerguelen hotspot, which moved several hundred kilometers within the Earth's mantle.
- Age Estimates: High-precision dating of mineral samples indicates that the ridge formed between 83 and 43 million years ago.
- Impact on Tectonic Models: This study aids in reconstructing Earth’s tectonic history and emphasizes the importance of understanding mantle dynamics and hotspot movement to better predict natural disasters.
Additional Details
- About the Ninetyeast Ridge: It is a linear aseismic ridge named for its alignment with the 90 meridian east, stretching approximately 5,000 kilometers from the Bay of Bengal in the north to the Southeast Indian Ridge (SEIR) in the south.
- The northern segment features massive volcanoes, while the southern part is tall and continuous, with the middle section comprising small seamounts and straight segments. It effectively divides the Indian Ocean into the West Indian Ocean and the eastern Indian Ocean.
- Formation Process: The widely accepted hotspot theory suggests that as the Indo-Australian plate moved north, it passed over the Kerguelen hotspot, leading to the ridge's formation. This process ceased due to a reorganization of tectonic plate boundaries, and ongoing research continues to investigate this theory.
- Composition: The ridge is primarily composed of Ocean Island Tholeiites (OIT), a type of sub-alkaline basalt rock, with the southern part being younger (43.2 million years) compared to the northern part (81.8 million years).
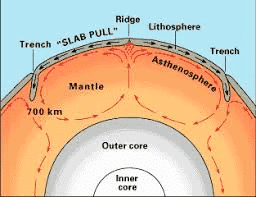
What is the Geological Significance of a Hotspot?

- A hotspot is an area where hot plumes of molten rock (magma) rise from deep within the Earth's mantle, potentially forming volcanoes as they reach the surface.
- Unlike most volcanic activity, hotspot volcanism occurs within tectonic plates, driven by stationary plumes rather than by tectonic plate boundaries.
- Hotspot Track: As tectonic plates move over a hotspot, active volcanoes form above the plume while older ones are carried away, creating a chain of islands or seamounts. An example is the Hawaiian Islands, where the Island of Hawaii is the youngest and most active.
How Do Hotspots Impact Tectonic Plates and Natural Disasters?
- Hotspot Influence on Tectonic Plates: The sequence of volcanic islands provides evidence for plate motion and allows scientists to estimate plate speed.
- Hotspots are linked to geothermal features like geysers, offering insights into tectonic plate movements.
- Rifting and Continental Breakup: Hotspots can contribute to continental rifting, weakening the lithosphere and causing it to break apart, as seen in the East African Rift.
- Mantle and Hotspot Influence on Natural Disasters:
- Earthquakes can occur as mantle plumes and tectonic plates move, highlighting the need for early warning systems.
- Tsunamis can be triggered by underwater earthquakes and volcanic eruptions; understanding mantle dynamics can help predict these events.
Mains Question:
- Examine the role of hotspots in plate tectonics and their impact on the formation of volcanic islands.
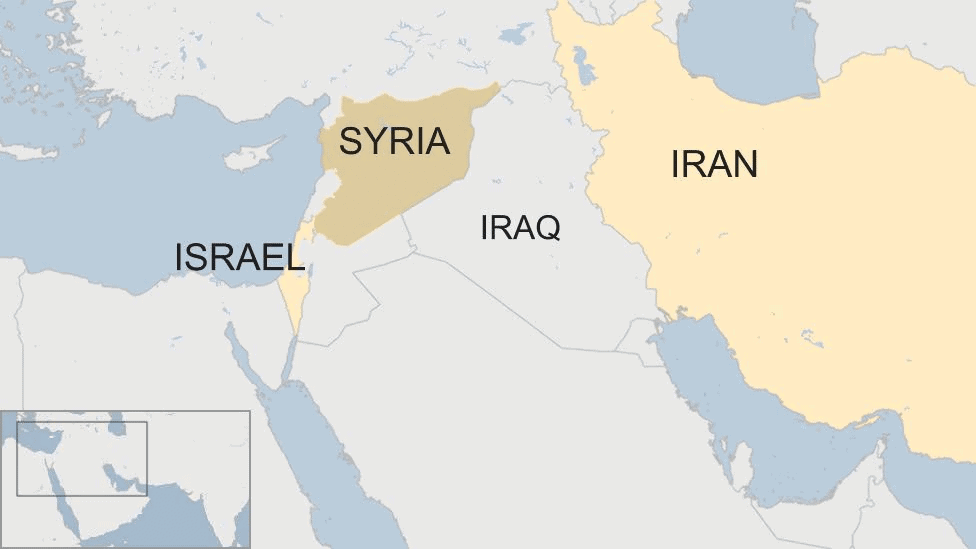
Syrian Civil War and Future of Syria
Why in News?
- Recently, Syrian rebels, led by the Islamist militant group Hayat Tahrir al-Sham (HTS), have claimed control of Homs, Syria’s third-largest city, marking a significant setback for President Bashar al-Assad's regime. This development, occurring amidst the ongoing civil war, raises serious concerns regarding the future of Syria, as it faces increasing challenges from various rebel factions.
Key Takeaways
- Syria has been ruled by the Assad family since 1971, with Bashar al-Assad continuing the authoritarian legacy of his father.
- The Arab Spring in 2011 sparked protests against Assad's rule, leading to violent repression and the rise of armed conflict.
- Multiple rebel factions, including HTS and the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF), have emerged, complicating the conflict.
- Foreign influences, particularly from Russia, Iran, the US, and Turkey, have significantly shaped the dynamics of the conflict.
- The future of Syria remains uncertain, with ongoing instability and humanitarian crises affecting millions.
Additional Details
- Historical Context: Since 1971, Syria has been under the control of the Assad family. Hafez al-Assad ruled until 2000, followed by his son Bashar al-Assad, who has maintained a tight grip on power.
- Arab Spring Uprising: The Arab Spring, a series of pro-democracy protests that began in 2011, led to widespread civil unrest in Syria, driven by dissatisfaction over unemployment, economic inequality, and corruption.
- Rise of Rebel Factions: Key groups include HTS, which aims to establish Sunni rule, and the SDF, focused on Kurdish autonomy. The Free Syrian Army (FSA) opposes both Assad and Kurdish forces.
- Foreign Influence: Russia and Iran have provided crucial support to Assad, while the US and Turkey have backed opposition forces, complicating the geopolitical landscape.
- India’s Approach: India has maintained friendly relations with Syria, emphasizing the need for a peaceful resolution to the conflict, while supporting humanitarian efforts.
The conflict in Syria has created one of the largest humanitarian crises in history, displacing millions and leading to significant geopolitical instability. The implications of the conflict extend beyond Syria, affecting regional dynamics and global security. As the situation evolves, India's historical ties to Syria and its strategic interests in the region will require careful navigation to ensure stability and protect its citizens.
Supreme Court Guidelines on Death Penalty and Mercy Petitions
Why in News?
- Recently, the Supreme Court of India has released comprehensive guidelines designed to streamline the execution of death sentences and the processing of mercy petitions. This initiative was prompted by the Supreme Court's decision to uphold the Bombay High Court's ruling in the case of Purshottam Dashrath Borate vs Union of India (2019), which commuted the death penalty of two convicts in the 2007 Pune BPO gang-rape and murder case to a 35-year life term due to excessive delays in execution.
Key Takeaways
- The establishment of dedicated cells in states and union territories to manage death penalty cases and mercy petitions.
- Mandatory electronic communication for efficient processing of petitions and information sharing.
- Implementation of a 15-day gap between the issuance of an execution warrant and its execution.
Additional Details
- Establishment of Dedicated Cells: The Supreme Court directed the creation of dedicated cells within Home or Prison Departments to handle death penalty and mercy petition cases efficiently. These cells will be overseen by a designated officer responsible for ensuring compliance with legal standards.
- Information Sharing: Prison authorities are required to forward mercy petitions along with relevant convict details, including their background and incarceration history, to the dedicated cell without unnecessary delays.
- Execution Warrant Protocol: A 15-day mandatory notice period will be enforced between the issuance of an execution warrant and its execution, ensuring that convicts are informed of their rights and legal assistance is provided if requested.
- State Government Responsibility: The State Government must seek an execution warrant promptly once the death penalty becomes final.
The Supreme Court's guidelines aim to reduce delays in the judicial process related to capital punishment and enhance accountability and fairness. By establishing structured procedures and clear responsibilities, these guidelines strive to uphold constitutional rights and ensure timely justice in death penalty cases.
UNCCD's Drought Atlas
Why in News?
- At the UNCCD COP16 in Riyadh, the UN Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD) and the European Commission's Joint Research Centre launched the World Drought Atlas, a comprehensive global publication focused on drought risks and potential solutions.
Key Takeaways
- Drought is a systemic risk that impacts multiple sectors worldwide.
- By 2050, it is projected that 75% of the global population could be affected by drought if current trends continue.
- In 2022 and 2023, approximately 1.84 billion people (about 1 in 4 globally) experienced drought, with 85% of those affected living in low- and middle-income countries.
- The economic costs of drought damages are significantly underestimated, currently amounting to USD 307 billion annually, which is 2.4 times the acknowledged figures.
- India is particularly vulnerable due to its reliance on monsoon rains, with around 60% of its agricultural land being rain-fed.
- The 2016 drought in Southern India was attributed to exceptionally low rainfall during both summer and winter monsoons.
- Rapid urbanization has led to water mismanagement in cities like Chennai, resulting in crises even with adequate rainfall.
Additional Details
- Drought Vulnerability in India: The Atlas highlights India's susceptibility to drought due to diverse climatic conditions and heavy reliance on monsoon rains. About 60% of agricultural land relies on rainfall, making it vulnerable to changes in precipitation patterns.
- Impact of Human Activities: The report indicates that human activities and occasional lack of rain contribute to drought and resource degradation.
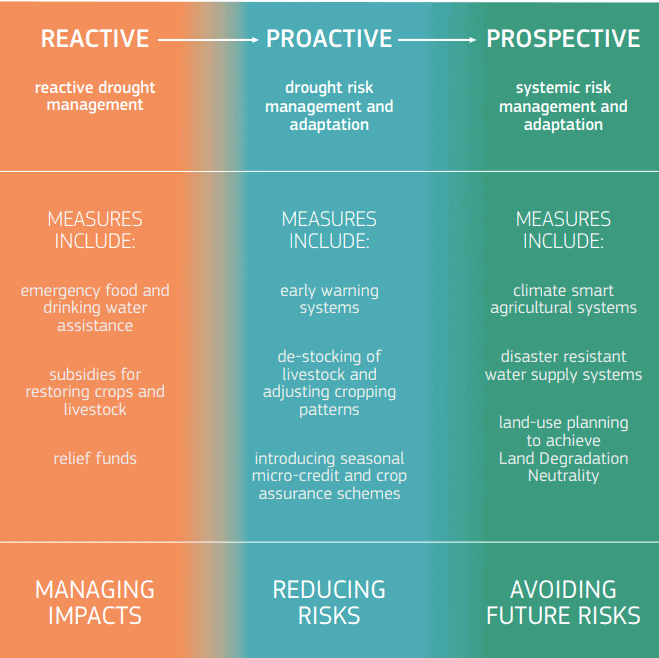
Recommendations from the World Drought Atlas

- Governance: Countries should create and implement national drought plans to improve preparedness and resilience against drought events.
- Strengthening international collaboration is crucial for sharing knowledge, resources, and best practices in managing drought risks.
- Developing financial mechanisms, such as microinsurance for smallholder farmers, can provide essential safety nets for vulnerable populations.
- Land Use Management: Sustainable agricultural practices like reforestation and soil conservation are vital for enhancing resilience to drought.
- Management of Water Supply and Use: Investments in infrastructure for water management, including wastewater reuse and groundwater recharge systems, are necessary to improve water security during droughts.
In conclusion, the UNCCD's Drought Atlas underscores the urgent need for comprehensive strategies to tackle the multifaceted challenges posed by drought, particularly in vulnerable regions like India. Enhanced governance, sustainable land use, and improved water management are essential for building resilience against future drought events.
Mains Question:
- Discuss how socio-economic factors influence drought resilience in India and suggest actionable strategies for improving preparedness against future droughts.
Surge in Agricultural Employment
Why in News?
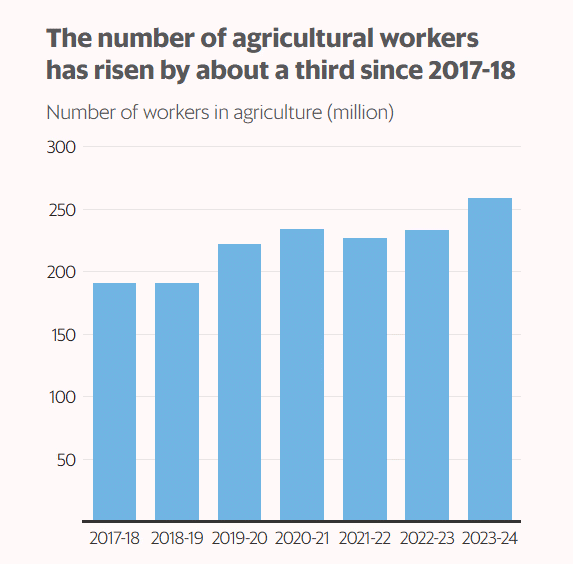
- The number of Indians engaged in agriculture has significantly increased by 68 million from 2017-18 to 2023-24. This marks a reversal from the previous trend of workforce decline in the sector, primarily driven by women workers and concentrated in economically weaker states. However, this trend raises concerns regarding structural challenges within the labor market.
Key Takeaways
- 68 million increase in agricultural workers from 2017-18 to 2023-24.
- Majority of the increase attributed to women workers.
- Growth concentrated in economically weaker states such as Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and Madhya Pradesh.
- Concerns regarding the structural challenges in the labor market.
Additional Details
- Economic Reversal: Following a decline of 66 million agricultural workers between 2004-05 and 2017-18, India has experienced a notable increase in agricultural employment, indicating a reversal of this trend.
- Impact of Covid-19 Pandemic: Many workers from urban informal sectors returned to family farms during lockdowns, and this trend continued even post-recovery.
- Employment Dynamics: Agriculture serves as a fallback option due to insufficient non-agricultural job opportunities, with women accounting for a significant portion of the increase.
- Economic Conditions in Key States: The rise in agricultural employment is particularly evident in states with limited employment opportunities, indicating higher demand for agricultural labor.
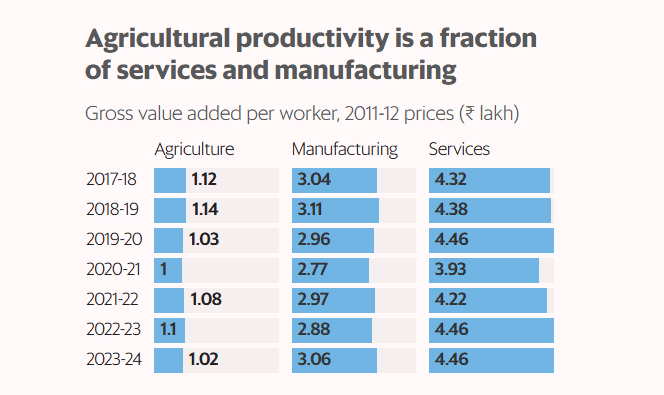
The surge in agricultural employment, while appearing beneficial, raises several concerns regarding economic transition and productivity. The shift back to agriculture, especially among women, highlights underlying issues in job creation in more productive sectors.
Concerns Regarding the Surge

- Reversal of Economic Transition: Typically, as economies develop, the workforce transitions from agriculture to manufacturing and services. India's reversal of this trend suggests mobility issues within the labor market.
- Economic Inefficiency: The rise in agricultural employment during periods of GDP growth indicates inadequate job creation in higher productivity sectors.
- Underemployment in Agriculture: Many agricultural jobs are seasonal and low-paying, which perpetuates rural poverty and limits advancement opportunities.
- Increased Informality: The surge may lead to greater informality, leaving workers vulnerable due to a lack of protections.
- Gender Disparity and Unequal Wages: Women in agriculture often earn less than their male counterparts, exacerbating gender pay gaps and undermining income stability.
Factors Contributing to Insufficient Non-Agricultural Employment
- Stagnant Manufacturing Sector: India's reliance on service sector growth has limited job creation in manufacturing, which traditionally absorbs surplus labor.
- Service Sector Growth Challenges: The polarization of the service sector limits job opportunities for low-skilled workers while high-tech sectors grow slowly.
- Skill Deficit and Education Quality: A significant number of graduates remain unemployable due to the quality of education, despite a high output of STEM graduates.
- Informal Economy: The post-pandemic shift to informal work reflects economic distress and the lack of formal employment options.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for ensuring a smoother transition for the workforce from agriculture to more productive sectors. Investments in education, skill development, and infrastructure will be essential for creating sustainable employment opportunities.
Way Forward
- Enhance Non-Agricultural Employment: Increase investments in manufacturing and service sectors to generate high-productivity jobs.
- Gender-Specific Interventions: Promote pay parity and entrepreneurship opportunities for women in agriculture.
- Increase Agricultural Productivity: Encourage mechanization and modern farming techniques to improve productivity.
- Strengthen Rural Infrastructure: Develop robust infrastructure to support growth in industrial and service sectors.
- Green Jobs: Transition to green technologies to create job opportunities in the emerging green economy.
- Implement Universal Social Security: Establish a safety net for rural workers through targeted social security schemes.
Through these strategies, India can create a more resilient workforce capable of adapting to the changing economic landscape.
Mains Question:
- Discuss the challenges faced by India in transitioning its workforce from agriculture to manufacturing and services. How can this transition be accelerated?
Inequality and the Role of Charitable Organizations
Why in News?
- Warren Buffett, who is often regarded as the greatest investor of all time, has donated over USD 52 billion to charitable causes. He emphasizes his belief that wealth should be utilized to equalize opportunities rather than perpetuate inequality. His philanthropic philosophy is closely associated with the concept of luck egalitarianism, which has ignited discussions about the effectiveness of charitable organizations in addressing the issue of inequality.
Key Takeaways
- Warren Buffett's donations highlight the role of wealth in promoting social equality.
- Luck egalitarianism suggests that inequalities arising from unchosen circumstances are unjust and should be addressed.
- Buffett's philosophy is supported by research indicating that socioeconomic factors significantly influence wealth potential.
Additional Details
- Luck Egalitarianism: This philosophy posits that inequalities stemming from factors such as birthplace or socio-economic status are inherently unjust. Buffett believes his success is attributed to both personal effort and structural advantages, such as being born into a favorable economic environment.
- Philanthropy acts as a practical method for redistributing wealth to create equal opportunities, challenging the notion that wealth accumulation across generations is fair.
Numerous factors contribute to inequality today, including economic, technological, social, governance, and environmental aspects.
Factors Contributing to Inequality
- Economic Factors:
- Neoliberal Policies: Since the 1980s, policies promoting deregulation and privatization have concentrated wealth among a small elite, resulting in stagnant wages for the majority.
- Monopolies: The dominance of few corporations limits competition, leading to wealth accumulation by a select few, as seen with companies like Amazon and Google.
- Financialization: The growth of financial markets has disproportionately benefited investors, contributing to rising inequality where wealth is concentrated in the hands of a few.
- Technological Factors: Advances in technology tend to benefit high-skilled workers while displacing low-skilled workers, exacerbating inequality.
- Social Factors:
- Women and minority groups face systemic barriers such as wage gaps and discrimination, limiting their economic mobility.
- People with disabilities often encounter discrimination and higher healthcare costs, further entrenching inequality.
- Health Inequalities: Limited access to healthcare can lead to chronic illnesses and malnutrition, perpetuating poverty in marginalized communities.
- Governance: Policy decisions on taxation and welfare significantly influence wealth distribution, with corruption exacerbating inequality.
- Environmental Factors: Climate change disproportionately affects poorer communities, leading to environmental injustices.
Role of Charitable Organizations in Addressing Inequality

- Providing Immediate Relief: Charitable organizations offer essential services like food, shelter, and healthcare to marginalized communities.
- Social Awareness and Advocacy: These organizations raise awareness about social injustices and advocate for policy changes to promote equality.
- Wealth Redistribution: They fund programs targeting poverty alleviation and education, exemplified by initiatives from the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation.
- Supporting Long-Term Development: Organizations focus on sustainable solutions such as local entrepreneurship, empowering communities to achieve self-sufficiency.
Limitations of Charitable Organizations in Addressing Inequality

- Temporary Solution: Charitable organizations often provide short-term relief without addressing the systemic causes of inequality.
- Dependency on Individual Will: The reliance on voluntary donations from the wealthy creates inconsistency in addressing widespread issues.
- Perpetuates Status Quo: By providing support without challenging systemic issues, charities may reduce the urgency for structural reforms.
- Lack of Accountability: There is often insufficient accountability regarding the effectiveness of charitable initiatives in reducing inequality.
- Misuse of Charitable Donations: Some wealthy individuals may use charitable donations to evade taxes, undermining the intended impact of philanthropy.
Way Forward
- State-Led Redistribution: It is essential to support government-led initiatives for wealth redistribution through welfare programs and social safety nets.
- Reform Economic Policies: Implement progressive taxation and strengthen antitrust laws to prevent monopolies and ensure fair competition.
- Equity and Opportunity: Ensuring equal access to resources and technology is crucial for bridging the inequality gap.
- Rethink Corporate Practices: Encourage higher wages and better working conditions for workers to promote fair profit-sharing.
- Promote Global Cooperation: Address global inequality through international trade reforms and debt relief for poorer nations.
In conclusion, while charitable organizations play a vital role in providing immediate assistance and raising awareness about inequality, systemic change through government policies and reforms is essential for achieving lasting solutions. Wealth redistribution should prioritize addressing root causes over reliance on philanthropy alone.
|
39 videos|4279 docs|902 tests
|
FAQs on Weekly Current Affairs (8th to 14th December 2024) Part - 1 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC
| 1. What is the significance of the 40th Charter Day of SAARC in 2024? |  |
| 2. What are the key features of the Ninetyeast Ridge and its geological importance? |  |
| 3. How has the Syrian Civil War affected the future of Syria? |  |
| 4. What are the Supreme Court's guidelines on death penalty and mercy petitions in India? |  |
| 5. How can the UNCCD's Drought Atlas aid in addressing global drought issues? |  |
|
39 videos|4279 docs|902 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|

















