Weekly Current Affairs (8th to 14th November 2024) | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
Neft Daslari: The World’s Oldest Offshore Oil Platform

Neft Daslari: A Brief Overview
- Neft Daslari, also known as Oil Rocks, is the oldest offshore oil platform in the world.
- It is located about 100 kilometers from Baku, the capital of Azerbaijan.
- The platform has been a subject of interest for many years due to its historical significance and ongoing environmental concerns, especially with the upcoming COP29 climate conference.
Historical Background
- Neft Daslari was built in the late 1940s during the Soviet Union era.
- It started as a basic drilling rig but gradually expanded into a large network of oil wells and production facilities.
- The platform includes over 100 miles of bridges connecting different structures.
- At its peak, Neft Daslari accommodated more than 5,000 workers.
Current Workforce and Operations
- The current number of employees at Neft Daslari is less than 3,000.
- Workers operate on a rotation schedule of 15 days, managing the platform in increasingly challenging sea conditions.
- Oil production has significantly decreased, averaging under 3,000 tonnes per day.
Environmental Concerns
- Neft Daslari has been plagued by environmental issues, including pollution and oil spills in the Caspian Sea.
- Mirvari Gahramanli, head of the Oil-Workers Rights Protection Organisation, has highlighted problems such as untreated wastewater and oil discharge into the sea.
- The state-run oil company, SOCAR, has pledged to tackle these issues and take action against polluters.
Impact on Azerbaijan’s Oil Industry
- Neft Daslari’s contribution to Azerbaijan’s oil industry is shrinking as production continues to decline.
- Once a major contributor, the platform now accounts for a small portion of the country’s oil output.
- Its diminishing significance is leading to discussions about its future role.
Future Possibilities
- Experts propose that Neft Daslari could be repurposed from an oil production site to a tourist destination or museum.
- This transition would recognize its historical importance in offshore oil exploration.
- Filmmaker Marc Wolfensberger believes the platform has potential beyond just oil production.
Neft Daslari as a Symbol
- With COP29 on the horizon, Neft Daslari symbolizes the environmental costs associated with the fossil fuel industry.
- Its decline prompts important questions about the future of offshore oil and the necessity for sustainable practices.
- Environmental advocates are concerned about the long-term impacts of ongoing operations at Neft Daslari.
- The platform’s legacy is linked to both the history of oil exploration and the pressing need for environmental conservation.
- The future of Neft Daslari will depend on how well these environmental concerns are addressed.
Zimbabwe Launches Second Satellite ZIMSAT-2
Zimbabwe has successfully launched its second satellite, ZIMSAT-2, marking a significant milestone in the country's space program. The satellite was launched from the Vostochny Cosmodrome in Russia, following the deployment of Zimbabwe's first satellite, ZimSat-1, in November 2022.
The Launch Details
- ZIMSAT-2 is a low Earth observation satellite that was launched aboard the Soyuz-2.1 spacecraft at 1 AM.
- The launch was a collaborative effort between the Zimbabwe National Geo-Spatial and Space Agency (ZINGSA) and Southwest State University in Russia.
Satellite Capabilities
- ZIMSAT-2 is equipped with a high-resolution multispectral camera designed to support various applications such as:
- Agriculture
- Resource exploration
- Environmental monitoring
- These capabilities are expected to enhance Zimbabwe's ability to manage its natural resources effectively.
Initial Success and Functionality
- The Ministry of Higher and Tertiary Education, Innovation, Science and Technology Development confirmed that ZIMSAT-2 is now in orbit.
- Initial telemetry data indicate that all subsystems are functioning optimally, reinforcing Zimbabwe's commitment to advancing space technology.
Impact on National Development
- The launch of ZIMSAT-2 represents a milestone in Zimbabwe's journey into space technology, underscoring the nation's commitment to scientific research and innovation.
- The satellite is expected to improve agricultural capabilities, enhance environmental monitoring, and aid in disaster management and resource mapping.
Capacity Building in Zimbabwe
- The development of ZIMSAT-2 has contributed to capacity building in Zimbabwe, with local engineers actively involved in its design and construction.
- For ZIMSAT-1, Zimbabwe had two master's graduates and one PhD graduate involved, while PhD students currently studying in Russia contributed to ZIMSAT-2.
Economic Development Potential
- Dr. Painos Gweme, the Coordinator of ZINGSA, highlighted the economic benefits of ZIMSAT-2, stating that the satellite will provide valuable data and insights crucial for Zimbabwe's economic development, particularly in agriculture and mining sectors.
Future Prospects
- The successful launch of ZIMSAT-2 sets a precedent for future space initiatives in Zimbabwe, opening doors for further collaboration in space technology.
- The experience gained from this project will enhance Zimbabwe's capabilities in satellite development and utilization.
Poorvi Prahaar: India Launches Major Tri-Services Exercise
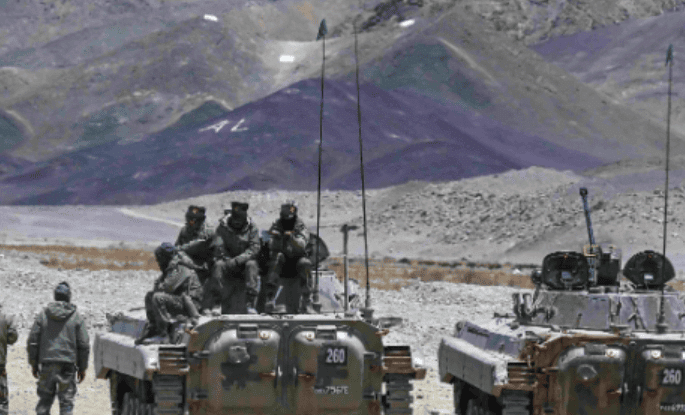

Context of the Exercise
- The exercise comes after the recent withdrawal of Indian and Chinese troops in eastern Ladakh, specifically at Depsang and Demchok.
- Ongoing negotiations aim to reduce troop presence in the region and discuss the restoration of patrolling rights in the Yangtse area of the Tawang sector.
Army Participation
- The Indian Army will showcase its capabilities by deploying various units, artillery guns, Light Combat Helicopters (LCH), and Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs).
- The focus will be on demonstrating operational readiness and the Army's preparedness for joint operations.
Air Force Involvement
- The Indian Air Force (IAF) will play a crucial role by deploying advanced fighter jets such as the Su-30 MKI and Rafale, along with transport aircraft like the C-130J Super Hercules.
- Operations will be supported by air bases in Kolkata, Hashimara, Paanagarh, and Kalaikunda.
Naval Contributions
- The Indian Navy will contribute to the exercise with the participation of MARCOS commandos, who specialize in maritime operations.
- Their involvement highlights the importance of naval capabilities in joint operations and enhances the exercise's overall scope.
Objectives of the Exercise
- To test and strengthen the synergy among the Indian Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- To enhance operational preparedness and boost India’s defence posture, particularly in the eastern sector.
- To improve inter-service collaboration, which is crucial given the regional security challenges.
Strategic Significance
- The exercise is strategically important for India, especially amid rising tensions with China.
- It demonstrates India’s commitment to maintaining peace and stability in the region while acting as a deterrent against potential aggression.
Future Implications
- The outcomes may shape future military strategies and enhance inter-service coordination for more effective crisis responses.
- Continued dialogue with China will be essential for long-term stability in the region despite the exercise's assertive posture.
Anti-Terror Conference 2024
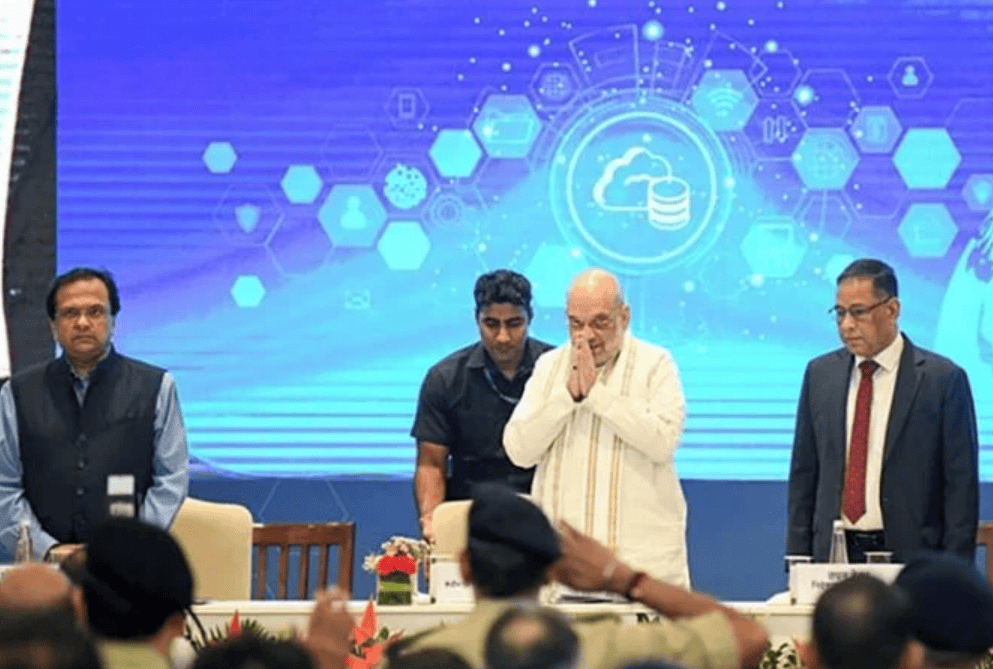

Context of Terrorism Today
- Terrorism has become a borderless issue, operating in an invisible manner that makes traditional countermeasures less effective.
- Governments around the world are increasingly challenged in identifying and responding to these threats, highlighting the need for a proactive approach.
- Union Home Minister Amit Shah emphasized the importance of advanced technology and effective training in combating modern terrorism during the Anti-Terror Conference 2024.
National Counter Terrorism Policy
- A National Counter Terrorism Policy and Strategy will be formulated to guide future actions against terrorism.
- The policy aims to ensure a coordinated response among various agencies, focusing on proactive measures and strategic planning.
Role of State and Central Agencies
- The fight against terrorism is primarily the responsibility of state authorities.
- State police play a crucial role in combating terrorism, with central agencies providing support through intelligence and resources.
- Collaboration between state and central forces is essential for effective counter-terrorism efforts.
Zero-Tolerance Policy
- Prime Minister Modi’s zero-tolerance approach to terrorism is gaining international recognition and reflects India’s firm commitment to combating terrorism.
- This policy has significantly shaped India’s internal security framework, with a strong focus on maintaining peace and security.
Tribute to Fallen Officers
- Union Home Minister Amit Shah paid tribute to over 36,000 police officers who lost their lives in the line of duty, highlighting their sacrifices in upholding national security.
- This recognition underscores the risks faced by law enforcement personnel in the fight against terrorism.
Objectives of the Conference
- The Anti-Terror Conference aims to promote coordinated action and implement a ‘Whole of Government’ approach to counter-terrorism.
- It seeks to generate insights for future policy development and emphasizes the importance of collaboration among stakeholders for effective counter-terrorism strategies.
- The focus on training and technology will be pivotal in shaping future counter-terrorism efforts, with policymakers prioritizing adaptive strategies to address emerging threats.
- Continuous evaluation and adjustment of tactics will be necessary to create a resilient security framework.
One Rank One Pension Scheme Marks Ten Years

10 Years of OROP: Ensuring Fair Pensions for Veterans
- The One Rank One Pension (OROP) Scheme, aimed at providing equitable pension payments to Ex-servicemen, has reached a significant milestone with its 10th anniversary since implementation.
- Introduced by the Government of India, OROP ensures fairness for veterans by guaranteeing equal pensions for those retiring at the same rank and service length, regardless of their retirement date.
Financial Impact of OROP
- The financial implications of the OROP scheme are substantial, with costs exceeding ₹4,468 crore for the current financial year.
- This figure reflects the Government’s commitment to supporting its veterans, with the Ministry of Defence prioritizing fund allocation for this scheme.
Disbursement to Pensioners
- On 30th September this year, the Government disbursed over ₹895 crore to Armed Forces pensioners, showcasing the efficiency of the scheme’s implementation.
- This timely disbursement ensures that veterans receive their entitled benefits without delay.
Beneficiaries of the Scheme
- Currently, the OROP scheme benefits more than 25 lakh Armed Forces pensioners, including both retired personnel and their family pensioners.
- The broad reach of the scheme underscores its importance in providing financial security to veterans and their families.
Pension Revisions
- Pensions under the OROP scheme are revised every five years, with the latest revision taking effect in July of this year.
- This regular update ensures that pensions remain relevant and adequate, reflecting changes in living costs and inflation to safeguard the purchasing power of pensioners.
Future of OROP
- The future of the OROP scheme looks promising with continuous Government support and ongoing evaluations to adapt the scheme to evolving needs.
- OROP has transformed the pension landscape for Ex-servicemen, establishing a precedent for fairness and equality in pension distribution.
- The scheme stands as a testament to the nation’s respect for its armed forces, with ongoing support and enhancements likely to reinforce this commitment in the years to come.
India Achieves WOAH Reference Laboratory Status

India’s Progress in Animal Health
- India’s Department of Animal Husbandry & Dairying is making significant improvements in animal health.
- The Indian Council of Agricultural Research-National Research Centre on Equines (ICAR-NRC Equine) has been recognized as a World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH) Reference Laboratory for Equine Piroplasmosis.
Significance of the Achievement
- Being designated as a WOAH Reference Laboratory is a prestigious honor for India.
- It showcases India’s commitment to meeting international standards in animal health research and diagnostics.
- This recognition boosts India’s reputation globally and reinforces its leadership in addressing critical animal health issues.
Equine Population in India
- India has around 0.55 million equines, including 0.34 million horses and ponies, 0.12 million donkeys, and 0.08 million mules.
- Key states with high equine populations are Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Haryana.
- Equines are essential for various livelihoods and industries across India.
Responsibilities of ICAR-NRC Equine
- As a WOAH Reference Laboratory, ICAR-NRC Equine will offer advanced diagnostic services, share technical expertise, and lead research on equine piroplasmosis.
- This role enhances India’s ability to collaborate internationally in animal health efforts.
Other WOAH Reference Laboratories in India
- ICAR-NRC Equine is the fourth laboratory in India’s animal husbandry sector to receive WOAH Reference status.
- Other recognized laboratories include:
- ICAR-National Institute of High Security Animal Disease, Bhopal (Avian Influenza)
- Veterinary College, Karnataka Veterinary Animal and Fisheries Sciences University, Bangalore (Rabies)
- ICAR-National Institute for Veterinary Epidemiology and Disease Informatics, Bangalore (PPR and Leptospirosis)
Future Announcements
- The official recognition of ICAR-NRC Equine will be announced at the 92nd WOAH General Session in May 2025, marking a significant step in India’s animal health improvement journey.
Understanding Equine Piroplasmosis
- Equine piroplasmosis is caused by protozoan parasites like Babesia caballi and Theileria equi and affects horses, donkeys, mules, and zebras.
- The disease is a serious threat to animal health and has significant economic impacts.
- In India, the seroprevalence rate ranges from 15-25%, with some high-risk areas reporting up to 40%.
Diagnostic Innovations for Equine Piroplasmosis
- The Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying (DAHD) is focusing on developing advanced diagnostic tools to fight equine piroplasmosis.
- New diagnostic methods being prioritized include: ELISA tests using recombinant antigensIndirect Fluorescent Antibody TestsPolymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) tests for antigen detection
- These innovations are crucial for the early detection and control of equine piroplasmosis.
Economic Impact of Equine Piroplasmosis
- Equine piroplasmosis can lead to severe economic losses by affecting equine productivity, health, and mobility.
- Restrictions on the movement and export of affected equines can exacerbate these losses.
- Therefore, establishing rigorous control measures is essential to protect the equine industry in India.
India Advances Cross-Border Electricity Initiatives
- India is in talks with several countries, including Oman, the UAE, Saudi Arabia, the Maldives, and Singapore, to set up cross-border electricity transmission lines.
- This initiative is part of the "One Sun One World One Grid" (OSOWOG) program, launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in 2018, aiming to create a global interconnected grid for renewable energy.
Overview of OSOWOG
- OSOWOG envisions a network for transferring renewable energy across borders, promoting sustainability by allowing regions with surplus solar or wind energy to help those with deficits.
- This approach optimizes resource use and minimizes the need for extensive energy storage.
India-Oman Interconnection
- A key aspect of OSOWOG is the proposed interconnection between India and Oman, involving a 1,000-km undersea power cable from Gujarat to Oman.
- This cable aims to enhance renewable energy flow and establish a secure energy exchange route.
Benefits of Cross-Border Grids
- Integrating regional grids allows better management of renewable resources like solar, wind, and hydro, which vary by region.
- Sharing these resources helps nations handle supply and demand peaks, improves grid stability, and reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
Current Electricity Exchange
- India currently exchanges about 4,100 MW of electricity with neighboring countries such as Nepal, Bangladesh, Bhutan, and Myanmar.
- This capacity is expected to increase to 7,000 MW by 2026-27 with new interconnections being developed.
Political and Regulatory Support
- The success of OSOWOG depends on political support and regional coordination, along with robust regulatory frameworks for smooth implementation.
- Countries need to collaborate to establish effective mechanisms for energy exchange.
Future Plans for Connectivity
- India is prioritizing cross-border power connectivity, with plans for interconnection with Sri Lanka as well.
- OSOWOG aims to enable countries to meet peak power demands using fewer resources, positioning renewable energy as a stable component of regional power supplies.
12th Session of the World Urban Forum (WUF12)
Urbanization Trends in Africa
- Africa is currently the least urbanised continent in the world, with urbanisation rates expected to rise from 36% in 2010 to a projected 50% by 2030. By 2050, this figure could reach 60%.
- Presently, Africa has three megacities: Cairo, Kinshasa, and Lagos. By 2050, an additional seven cities are anticipated to join this list.
- Urban solutions are becoming increasingly critical as the population living in slums continues to grow.
Housing and Informal Settlements
- Housing poses a significant challenge in Africa, with the alarming growth of informal settlements.
- These areas often lack basic services and are vulnerable to climate impacts, making urban planning essential to prevent the spread of slums in hazardous locations.
- Prioritising effective housing strategies is crucial to ensure safety and accessibility for all residents.
Climate Change and Urban Vulnerability
- Cities in Africa are particularly vulnerable to climate change, experiencing extreme weather events that disrupt livelihoods, especially in impoverished communities.
- Rising temperatures, floods, and droughts pose severe risks, with women being disproportionately affected by these climate challenges.
- Policymakers need to address these vulnerabilities to enhance urban resilience and protect vulnerable populations.
Economic Implications of Urban Growth
- Urbanisation is a driver of economic growth in Africa, with projections indicating that by 2035, the largest cities will house 21% of the continent’s population.
- However, climate risks such as rising sea levels and extreme weather threaten this growth, impacting crucial economic sectors.
- Sustainable urban planning is essential to ensure future prosperity and mitigate climate-related risks.
Collaborative Solutions for Urban Challenges
- The World Urban Forum (WUF) emphasised the importance of collaboration among stakeholders to address urban challenges effectively.
- Development partners need to work together to create innovative financing models tailored to the unique needs of African cities.
- Engaging local communities in decision-making processes is crucial for enhancing urban governance and ensuring that solutions are relevant and effective.
The Role of the World Urban Forum
- Established in 2001, the World Urban Forum (WUF) examines the impacts of rapid urbanisation and aims to promote sustainable urban development.
- The forum has been held biennially since its inception, and this year’s event highlighted Africa’s specific urban challenges, signalling a growing recognition of the need for inclusive solutions.
Future Urban Projections
- By 2042, Africa’s urban population could exceed one billion, with cities like Abidjan and Ouagadougou projected to achieve megacity status.
- Comprehensive urban planning is essential to accommodate this growth and prevent rising inequality.
- Without proper infrastructure and planning, the gap between different socio-economic groups will continue to widen.
India’s Renewable Energy Growth and Investment
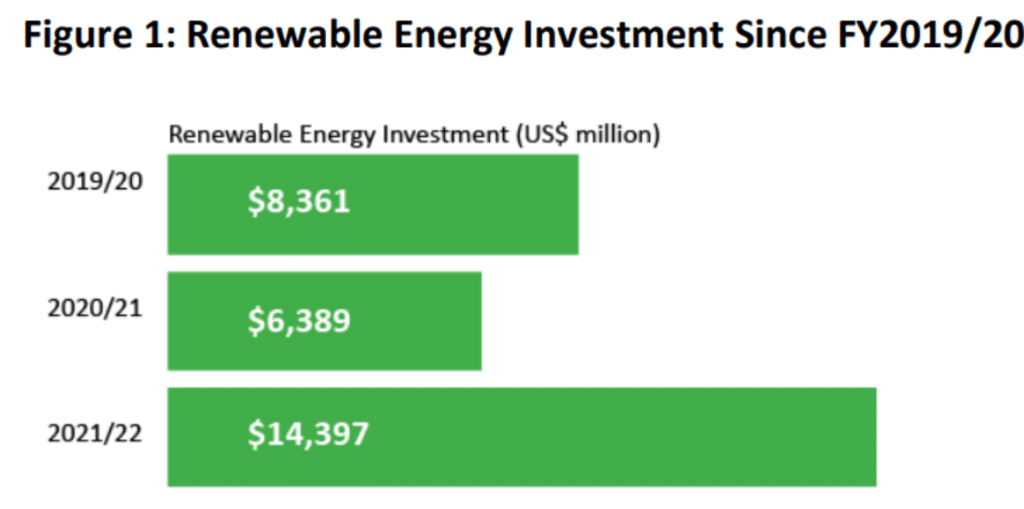
Current Capacity and Future Goals
- India has made significant progress in its renewable energy sector, recently reaching a capacity of 200 GW, with nearly 90 GW coming from solar power.
- The government aims to achieve 500 GW by 2030, requiring an annual addition of about 50 GW.
Current Capacity and Future Goals
- India’s renewable energy capacity has been expanding rapidly, with 18 GW added in FY24 and projections of 30-35 GW for FY25.
- Solar power is at the forefront of this growth, significantly contributing to the overall capacity increase.
Global Context and Competition
- Compared to global leaders, India’s solar market is still developing. In 2023, China installed 253 GW of solar capacity, while the USA added 32 GW.
- India accounted for only 3% of global capacity additions, ranking fifth. However, with increased focus, India aims to become the second-largest solar market after China.
Global Solar Market Expansion
- The global installed solar PV capacity is projected to reach 11,000 GW by 2030, requiring an investment of around US$4-5 trillion.
- Recent investments in solar PV have reached US$500 billion, with annual investments potentially nearing US$1 trillion by 2030.
Investment Opportunities in India
- India’s goal of adding 50 GW annually presents a significant opportunity for global investors, with estimated annual investments ranging from US$17-18 billion.
- This estimate covers only generation facilities, and additional investments will be needed for manufacturing solar PV modules and cells.
Investment Opportunities in India
- The majority of investments in India’s renewable sector come from debt, with domestic banks and financial institutions contributing 70-75% of the funding.
- Private equity plays a vital role in equity investments, and cumulative foreign direct investment (FDI) in renewables exceeded US$17 billion by FY24.
Role of Global Investors
- Global investors are increasingly directing capital towards infrastructure, including renewable energy.
- Public pension funds have raised their infrastructure allocation from 4.4% in 2020 to 6.57% in 2024, with the top 75 global funds investing nearly US$725 billion in infrastructure.
Alignment with Global Goals
- India’s green energy initiatives align with global sustainability targets, attracting interest from global investors.
- The solar PV industry in India is expected to have secure access to capital, positioning the sector for strong growth in the coming years.
8th International Ancient Arts Festival
Background:
- The 8th International Ancient Arts Festival and Symposium took place from November 8 to 10, 2024, at the Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts (IGNCA). The event was organized by IGNCA in collaboration with the Rays of Wisdom Society and supported by the Ministry of Culture, Government of India. It aimed to explore the connection between art, spirituality, and healing.
Exhibition:
- The festival featured an exhibition titled "Metaphysical, Symbolic, and Healing Themes in Visual Arts." This exhibition showcased artworks that delved into deep philosophical concepts and healing practices through visual art. Artists presented their interpretations of metaphysical themes, engaging visitors with the spiritual dimensions of visual arts.
Conference Focus:
- The conference revolved around the theme of "Art, Religion, and Healing." Esteemed scholars gathered to discuss the healing potential of ancient art forms and their role in spiritual expression. Topics included the relationship between religion, consciousness, spirituality, and their impact on personal and social healing.
Notable Performances:
The festival featured several cultural performances, including:
- Dr. Reela Hota's "Antar Yatra," a dance performance depicting the journey of consciousness through yogic philosophy.
- A vocal recital by Shri Shrinivas Joshi on the second day.
- A Kuchipudi dance performance by Smt. Yamini Reddy and her group, concluding the festival with a rich cultural experience.
Distinguished Guests: The event attracted notable figures such as Amita Sarabhai, Joint Secretary of the Ministry of Culture, Shri V. Srinivas, Secretary of DARPG, and Dr. Sachchidanand Joshi, Member Secretary of IGNCA. Their presence underscored the significance of the event in the arts and culture sector.
Discussion Topics: The conference featured discussions on various themes, including:
- Art and Conflict Resolution
- Healing in Baul Philosophy
- Odissi and its Universal Principles
- Drama Movement and Therapeutics These discussions aimed to uncover the therapeutic aspects of different art forms and their potential for healing and conflict resolution.
Keynote Address:
- Dr. Madhu Khanna, a Professor of Indic Religion and a Tagore National Fellow at the National Museum in New Delhi, delivered the keynote address. Her insights added depth to the discussions, with Dr. Sachchidanand Joshi serving as the special guest of honour during the inaugural session.
Cultural Impact:
- The festival highlighted the impact of religious rituals as socio-cultural art forms and examined the metaphysics of temple architecture and the epistemology of children's theatre. These discussions emphasized the relevance of ancient art in contemporary society and the integration of art and spirituality.
New Water Pollution Penalty Rules Implemented
Overview of the New Rules
- The new rules are titled Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) (Manner of Holding Inquiry and Imposition of Penalty) Rules, 2024.
- They outline procedures for inquiries and penalties related to water pollution.
- The rules empower designated officers to handle complaints and adjudicate violations.
Changes in the Water Act
- Earlier amendments to the Water Act decriminalized certain offences.
- This means that instead of facing criminal charges, violators will incur financial penalties.
- The amendments also allow the appointment of officers to adjudicate cases.
- This aims to enhance the efficiency of the enforcement process.
Authority to File Complaints
- Various authorities can file complaints regarding water pollution.
- The Central Pollution Control Board, State Pollution Control Boards, and Pollution Control Committees are involved.
- They can report contraventions related to specific sections of the Water Act.
- These sections cover the release of industrial effluents and pollutants.
Inquiry Process
- An adjudication officer is appointed to oversee the complaint process.
- This officer must hold a rank no lower than a joint secretary or secretary in state government.
- They have the authority to issue notices detailing the alleged contraventions.
- Upon receiving a complaint, the adjudication officer issues a notice to the accused party.
- The notice outlines the nature of the alleged contravention.
- The accused has the right to provide an explanation or defend themselves through legal representation.
- The inquiry aims to ensure fairness and transparency in the process.
- The inquiry process must be completed within six months.
- This timeline begins from the issuance of the notice to the accused party.
- The emphasis on a timely resolution aims to enhance accountability and compliance among industries.
Impact on Industries
- The new rules particularly affect industries that release pollutants.
- They must now navigate a more structured penalty process.
- Non-polluting ‘white’ category industries are exempt from prior permissions.
- This exemption encourages the establishment of environmentally friendly operations.
IIT Madras and ISRO Launch Research Centre for Spacecraft Thermal Management
Overview of the Collaboration
- IIT Madras is collaborating with ISRO to establish a Centre of Excellence in Fluid and Thermal Sciences.
- The focus is on improving thermal management for spacecraft and launch vehicles.
- ISRO has provided Rs 1.84 Crore as initial funding for this initiative.
- An MoU was signed on 11th November 2024 to formalize this partnership.
Objectives of the Centre
- The Centre will address thermal management challenges faced by ISRO.
- It aims to be a key research hub for spacecraft and launch vehicle thermal issues.
- The initiative leverages the expertise of IIT Madras faculty in complex thermal engineering problems.
Funding and Resource Allocation
- ISRO's initial funding will cover essential infrastructure and equipment for the Centre.
- Additional resources will be allocated for consumables, maintenance, and future projects in fluid-thermal sciences.
Research Focus Areas
- The Centre will undertake advanced research in areas such as:
- Spacecraft thermal management
- Combustion instability in hybrid rockets
- Cryo-tank thermodynamics
Historical Context of Collaboration
- The collaboration builds on a long history between ISRO and IIT Madras.
- In 1985, they established the ‘ISRO-IIT M Space Technology Cell’ to promote advanced academic research.
- This new Centre of Excellence continues that legacy by focusing on critical areas of thermal science.
Anticipated Outcomes
- The collaboration is expected to lead to advancements in thermal management research.
- The Centre aims to strengthen India’s space capabilities and self-reliance in space technologies.
- Innovative solutions and research advancements are key goals of this initiative.
Taiwan’s HAWK Missiles and Ukraine’s Defence Needs

Taiwan's Defence Minister on HAWK Missiles
- Taiwan's Defence Minister, Wellington Koo, recently discussed the future of Taiwan's decommissioned HAWK anti-aircraft missiles.
- His comments came during ongoing discussions about military support for Ukraine, highlighting the role of the United States in deciding the fate of these missiles.
Background on HAWK Missiles
- The Raytheon MIM-23 HAWK system was developed during the Cold War to intercept enemy bombers.
- Over the years, the system has undergone numerous upgrades, with countries like Denmark, the Netherlands, and Norway modifying it for their needs.
- Although the HAWK is no longer in active U.S. service, it remains operational in some nations.
Taiwan's Position
- Taiwan has expressed that it no longer requires the HAWK missiles and is following established regulations for the decommissioning process.
- Defence Minister Koo emphasised that any transfer of missiles to the U.S. would occur under relevant guidelines, with the U.S. determining the next steps for the missiles.
U.S. Military Support for Ukraine
- Since Russia's invasion of Ukraine, the U.S. has provided significant military aid to Ukraine, including various weapons systems that have been phased out by Western nations.
- For example, the Netherlands has supplied F-16 fighter jets to Ukraine to enhance its defence capabilities against Russian aggression.
Taiwan's Support for Ukraine
- Taiwan has demonstrated strong moral support for Ukraine, drawing parallels between its own situation and Ukraine's challenges.
- Despite the constant threat from China, which claims Taiwan as its territory, Taiwan has not publicly announced plans to send weapons directly to Ukraine.
Upgrading Taiwan's Defence Systems
- Taiwan is actively working to enhance its missile defence capabilities, recently announcing a nearly $2 billion deal with the U.S. for the National Advanced Surface-to-Air Missile System (NASAMS).
- The NASAMS includes advanced AMRAAM Extended Range missiles, which have proven effective in Ukraine, showcasing their reliability.
HAWK's Relevance in Modern Conflict
- While the HAWK system is considered outdated, it still has certain advantages, such as the ability to engage low-altitude targets, which is useful against slow-moving drones.
- Ukraine has faced numerous drone attacks, making such capabilities valuable in modern conflict.
Future Decisions on Arms Transfers
- The decision regarding the HAWK missiles will depend on U.S. priorities and the growing need for effective air defence in the context of the ongoing conflict in Ukraine.
- Taiwan's cooperation could play a role in addressing these needs, and the evolving military landscape will influence future decisions on arms transfers.
|
164 videos|800 docs|1160 tests
|
FAQs on Weekly Current Affairs (8th to 14th November 2024) - General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce
| 1. What is Neft Daslari and why is it significant? |  |
| 2. What are the primary objectives of the Poorvi Prahaar exercise conducted by India? |  |
| 3. What is the purpose of the One Rank One Pension (OROP) scheme in India? |  |
| 4. How does India’s achievement of WOAH Reference Laboratory Status impact its veterinary sector? |  |
| 5. What are the key outcomes expected from the 12th Session of the World Urban Forum (WUF12)? |  |
















