What is Rankine's Formula? | Civil Engineering Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Rankine Formula for Columns? |

|
| Alternate Form of Rankine Formula |

|
| What is Rankine’s Constant? |

|
| Rankine Formula for Short Columns |

|
| Rankine Formula for Long Columns |

|
What is Rankine Formula for Columns?
When analyzing columns, we often consider two primary failure modes: buckling for long columns and crushing for short ones. In reality, most columns fail due to a combination of both buckling and crushing. The Rankine Gordon formula, commonly known as the Rankine formula for columns, takes into account this combined failure mode, making it applicable to all types of columns, whether long or short.
The Rankine formula expresses the critical load as the reciprocal of the sum of the reciprocals of the crushing load and Euler's buckling load:
1/P=1/Pc+1/Pe
Where, P = Rankine's critical load
Pc = crushing load
Pe = Euler's buckling load
Explanation with Examples: To understand the Rankine formula better, consider a scenario where you have a slender column supporting a heavy load. If the column is long, it might buckle under the compressive force. On the other hand, if the column is short, it may crush due to the excessive load. The Rankine formula accounts for both possibilities, providing a comprehensive approach to determining the critical load for columns.
Application in Engineering: Engineers use the Rankine formula to assess the stability of columns in various structures, such as buildings, bridges, and support beams. By calculating the critical load based on crushing and buckling considerations, engineers can design columns that withstand the expected loads without failing.
Alternate Form of Rankine Formula
When we substitute the values of the crushing load Pc and Euler's buckling load Pe into the Rankine formula discussed earlier, we derive an alternative representation of the Rankine formula for columns. The general form of the Rankine formula is:1/P = 1/Pc + 1/Pe
P = (Pc * Pe) / (Pc + Pe) ... (i)
The crushing load Pc can be expressed as:
- σc = ultimate crushing stress
- A = cross-sectional area of the column
According to Euler's theory, the buckling load Pe can be defined as:
- E = Young's modulus of elasticity
- I = moment of inertia
- Le = effective length of the column
- λ = slenderness ratio of the column
By substituting Pc and Pe into equation (i), we obtain:
P = σc * A / [1 - (σc * λ^2 / (π2 * E * A))]
P = σc / [1 - (αλ2)]
Here, α represents Rankine's constant and is given by α = σc / (π2 E).
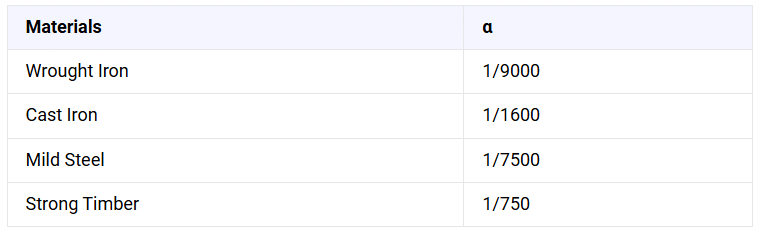
What is Rankine’s Constant?
- We previously introduced the concept of Rankine constant while exploring the alternative form of the Rankine formula. The Rankine constant, symbolized by 𝑎, is expressed as 𝛼 = σc / π2E.
- The Rankine constant varies for different materials. Below is a table listing the Rankine constants for some materials commonly used in column construction:

Rankine Formula for Short Columns
- This section delves into the modifications required for the Rankine formula concerning the critical load when dealing with short columns. Short columns possess a reduced effective length.
- Euler’s equation for the buckling load is represented as
 . With a smaller effective length (Le), the buckling load (Pe) significantly increases.
. With a smaller effective length (Le), the buckling load (Pe) significantly increases. - In the Rankine formula for columns, the value of (1/Pe) becomes negligible due to the diminutive effective length. Consequently, the Rankine formula for the critical load simplifies to 1/P = 1/Pc., leading to P = Pc.
- Hence, for short columns, the Rankine critical load equals the crushing load.
Rankine Formula for Long Columns
- A long column's effective length is larger, resulting in a minimal buckling load (Pe), as per Euler’s formula.
- In Rankine's column formula, (1/Pe) surpasses (1/Pc), thus (1/Pc) can be disregarded.
- The Rankine critical load simplifies to 1/P = 1/Pe and P = Pe.
- Conclusively, the Rankine critical load for long columns equals Euler’s buckling load.
|
350 videos|464 docs|2 tests
|
|
350 videos|464 docs|2 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
 . With a smaller effective length (Le), the buckling load (Pe) significantly increases.
. With a smaller effective length (Le), the buckling load (Pe) significantly increases.















