Metals and Non-metals - 3 Class 10 Worksheet Science
Q.1. Name one metal and non-metal which exists in liquid state at room temperature? (1 Marks)
Ans. Metal – mercury, Non-metal – bromine.
Q.2. What are amphoteric oxides? Give an example. Write balanced chemical equations to justify your answer. (1 Marks)
Ans. Amphoteric oxides: Metal oxides showing both acidic and basic nature.
Example: Al2O3 / ZnO (or any other)
Al2O3 + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + 3H2O
Al2O3 + 2NaOH → 2NaAlO2 + H2O
Detailed Answer: Oxides of metals which have both acidic as well as basic behaviour are known as amphoteric oxides. Examples are aluminium oxide and zinc oxide. Amphoteric oxides react with acids as well as base to form salt and water. ZnO reacts with hydrochloric acid (acid) to form zinc chloride (salt) and water; thus acting as basic oxide.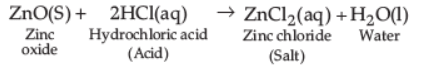
ZnO reacts with sodium hydroxide (base) to form sodium zincate (salt) and water thus, acting as acidic oxide.
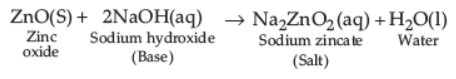
Q.3. State reason for the following : (3 Marks)
(i) Non-metals cannot displace hydrogen from the acids.
(ii) Hydrogen is not a metal, yet it is placed in the activity series of metals.
(iii) Aluminium is more reactive than iron, yet its corrosion is less than that of iron.
Ans. (i) Non-metals are electron acceptors; they cannot supply electrons so as to convert H+ ion to H2(g).
(ii) Like metals, hydrogen can lose an electron to form positive H+ ion.
(iii) Aluminium is covered with a strong protective layer of oxide which protects the metal from further corrosion.
Q.4. (a) List in a tabular form any three chemical properties on the basis of which metals and non-metals are differentiated.
(b) State two ways to prevent the rusting of iron.
Ans.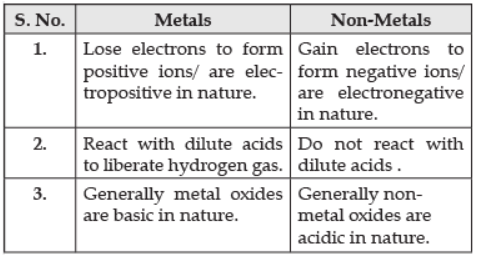
(b) (i) Painting
(ii) Oiling
(iii) Galvanization
(vi) Alloying
Q.5. Which of the following metals exist in their native state in nature? (1 Marks)
(i) Cu
(ii) Au
(iii) Zn
(iv) Ag
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Ans. (c)
Solution. Metals such as gold and silver are found as native metals.
Q.6. What is a thermite reaction? (1 Marks)
Ans. Reduction of iron oxide to iron by aluminium is called thermite reaction.
Fe2O3 + 2Al → 2Fe + Al2O3 + Heat.
Q.7. Metal X is found in nature as its sulphide XS. It is used in the galvanisation of iron articles. Identify the metal X. How will you convert this sulphide ore into the metal? Explain with equations. (5 Marks)
Ans. Metal X is Zinc: The sulphide ore is first heated strongly in supply of oxygen and changed into its oxide. This process is called roasting.
Zinc oxide is then reduced to zinc metal by heating it with carbon. This process is called reduction.
2ZnO + C → 2Zn + CO2
Q.8. In a thermite reaction, a compound of iron reacts with a metal.
(a) Name the metal used in this reaction. (1 Marks)
(b) After completion of this reaction, a metal is obtained in the molten state. Identify the metal. (1 Marks)
(c) Represent this reaction in the form of a balanced chemical equation. (1 Marks)
(d) Mention the most common use of this reaction. (1 Marks)
Ans. (a) Aluminium (Al)
(b) Iron (Fe)
(c) Fe2O3 + 2Al → 2Fe + Al2O3 + Heat.
(d) Use: To join railway tracks or cracked machine parts.
Q.9. Which method will you use to reduce the following?
(i) Oxides of less reactive metals
(ii) Oxides of moderately reactive metals
(iii) Oxides of highly reactive metals.
Explain by giving a suitable example. (3 Marks)
Ans. (i) Self-reduction
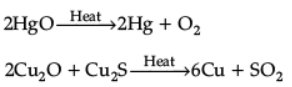
(ii) Reduction using carbon
ZnO + C → Zn + CO
Sometimes, some highly reactive metals are used as reducing agents.
Example: 3MnO2 + 4Al → 3Mn + 2Al2O3 + heat
or Fe2O3 + 2Al → 2Fe + Al2O3 + heat
(iii) Electrolytic reduction
Example: Na, Mg and Ca are obtained by electrolysis of their molten chlorides.
Q.10. (i) Write the steps involved in the extraction of pure metals in the middle of the activity series from their carbonate ores.
(ii) How is copper extracted from its sulphide ore? Explain the various steps supported by chemical equations. Draw labelled diagram for the electrolytic refining of copper. (5 Marks)
Ans. (i) (a) Calcination, (b) Reduction, (c) Purification (in the given sequence only)
(ii) Sulphide ore of copper is heated in air.
2Cu2S + 3O2 → 2Cu2O + 2SO2
2Cu2O + Cu2S → 6Cu + SO2
(Note: Full marks to be awarded even when only equations are written)
Labelled diagram of electrolytic refining of copper.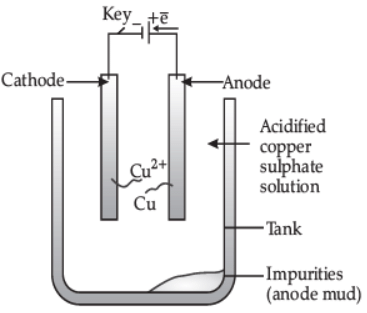
Q.11. Write balanced equations for the reaction of :
(i) Aluminium when heated in air. Write the name of the product.
(ii) Iron with steam. Name the product obtained.
(iii) Calcium with water. Why does calcium start floating in water? (3 Marks)
Ans. (i) 4Al + 3O2 → 2Al2O3, Aluminium oxide
(ii) 3Fe + 4H2O → Fe3O4 + 4H2, Ferric oxide
(iii) Ca + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + H2, because hydrogen sticks to calcium.
Q.12. You are given samples of three metals: Sodium, magnesium and copper. Suggest any two activities to arrange them in order to their decreasing reactivity. (3 Marks)
Ans. Different metals react with oxygen at different rates. e.g., Sodium (Na) and potassium (K) catch fire, if left in open. Hence, these are the most reactive metals. To prevent accidental fires, these metals are kept immersed in kerosene oil. Magnesium burns in air only by heating. So, it is less reactive than sodium and potassium. Copper (Cu) does not burn on heating but blister copper burns. Hence the order of reactivity of these metals with oxygen is:
Na > Mg > Cu.
Metals react with water to produce a metal oxide and hydrogen gas. Sodium (Na) and potassium (K) react violently with cold water. So the reaction is violent and exothermic. Magnesium (Mg) does not react with cold water. It reacts with hot water. Metals like lead, copper, silver do not react with water at all. The reactivity series of metals towards water is:
Na > Mg > Cu.
Q.13. State two physical properties of gold which are of extreme use to jewellers. (1 Marks)
Ans. Malleability, ductility, lustrous. (Any two)
Q.14. Explain how the following metals are obtained from their compounds by reduction process :
(i) Metal X, which is low in reactivity series.
(ii) Metal Y, which is in the middle of reactivity series.
(iii) Metal Z, which is high in the reactivity series. (3 Marks)
Ans. (i) Metal X is obtained simply by heating their oxides with carbon. e.g., Mercury is obtained from cinnabar.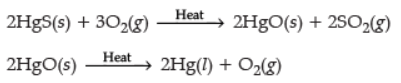
(ii) Metals in the middle of activity series can be obtained by heating with carbon, e.g.,
(iii) Metals that lies high in the reactivity series are obtained by electrolytic reduction of molten ores, e.g., in NaCl
NaCl → Na+ + Cl–
Na + e– →Na (at cathode)
2Cl– → Cl2 + 2e– (at anode)
Q.15. Alloys are homogeneous mixtures of a metal with a metal or non-metal. Which among the following alloys contain non-metal as one of its constituents? (1 Marks)
(a) Brass
(b) Bronze
(c) Amalgam
(d) Steel
Ans. (d)
Solution. Steel is an alloy of basically iron and carbon. Mixing of carbon gives strength to iron.
Q.16. What happens when ZnCO3 is heated in the absence of air? Give the relevant equation. (1 Marks)
Ans. ZnO(s) and CO2(g) are formed.
Q.17. An electrolytic cell consists of (1 Marks)
(i) positively charged cathode
(ii) negatively charged anode
(iii) positively charged anode
(iv) negatively charged cathode
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (iii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Ans. (b)
Solution. Positively charged ions are called cations as it is deposited at a negatively charged pole. Negatively charged ions are called anions as these are deposited at a positively charged pole. That’s why the negatively charged pole is called cathode, and positively charged pole is called anode.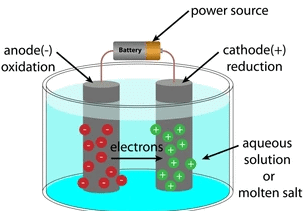 Electrolytic CellQ.18. Why do we apply paint on iron articles? (1 Marks)
Electrolytic CellQ.18. Why do we apply paint on iron articles? (1 Marks)
Ans. Paint forms a protective coating on the surface of iron. So, oxygen and moisture present in the air cannot have direct contact with the metal. Therefore, the surface gets protected against rusting.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Metals and Non-metals - 3 Class 10 Worksheet Science
| 1. What are metals and non-metals? |  |
| 2. What are some examples of metals and non-metals? |  |
| 3. How do metals and non-metals differ in terms of their chemical properties? |  |
| 4. What are some common uses of metals and non-metals? |  |
| 5. Can an element be both a metal and a non-metal? |  |
















