Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Notes > NCERT Textbooks & Solutions for Class 8 > NCERT Summary: Mineral & Power Resources
Mineral & Power Resources Summary Class 8 NCERT Summary Chapter 1
Mineral
- A naturally occurring substance that has a definite chemical composition is a mineral.
- Minerals are not equally distributed over space.
- Minerals are formed in different types of geological environments, under varying conditions.
- They are created by natural processes without any human interference.
- They can be identified on the basis of their physical properties such as colour, density, hardness and chemical property such as solubility.
Types of Minerals
- On the basis of composition, minerals are classified mainly as:
- Metallic
- Non-metallic minerals
- Metallic minerals contain metal in raw form.
- Examples: Iron ore, bauxite, manganese ore.
- Metallic minerals may be ferrous or non-ferrous.
- Ferrous minerals contains iron. Examples are iron ore, manganese and chromites.
- Non-ferrous mineral does not contain iron but may contain some other metal such as gold, silver, copper or lead.
- Non-metallic minerals do not contain metals.
- Examples: Limestone, mica and gypsum and mineral fuels like coal and petroleum.
Extraction of Minerals
- Minerals can be extracted by mining, drilling or quarrying.
- The process of taking out minerals from rocks buried under the earth’s surface is called mining.
- Minerals that lie at shallow depths are taken out by removing the surface layer; this is known as open-cast mining.
- The mining in which deep bores, called shafts, have to be made to reach mineral deposits that lie at great depths is called is shaft mining.
- Deep wells are bored to take minerals out is called drilling. Petroleum and natural gas are extracted through drilling method.
- Minerals that lie near the surface are simply dug out, by the process known as quarrying.
Distribution of Minerals
- Minerals occur in different types of rocks such as igneous rocks, metamorphic rocks or sedimentary rocks.
- Generally, metallic minerals are found in igneous and metamorphic rock formations that form large plateaus.
- Metamorphic examples: Iron-ore in north Sweden, copper and nickel deposits in Ontario, Canada, iron, nickel, chromites and platinum in South Africa.
- Sedimentary rock examples: Limestone deposits of Caucasus region of France, manganese deposits of Georgia and Ukraine and phosphate beds of Algeria
Asia
- China and India have large iron ore deposits.
- The continent produces more than half of the world’s tin.
- China, Malaysia and Indonesia are among the world’s leading tin producers.
- China also leads in production of lead, antimony and tungsten.
- Asia also has deposits of manganese, bauxite, nickel, zinc and copper.
Europe
- It is the leading producer of iron-ore in the world.
- Russia, Ukraine, Sweden and France have large deposits of iron ore.
- Minerals deposits of copper, lead, zinc, manganese and nickel are found in eastern Europe and European Russia.
North America
- Mineral deposits in North America are located in three zones:
- The Canadian region north of the Great Lakes: Iron ore, nickel, gold, uranium and copper
- The Appalachian region: Coal
- The mountain ranges of the west: Copper, lead, zinc, gold and silver
South America
- Iron Ore: Brazil
- Copper: Chile and Peru
- Tin: Brazil and Bolivia
- Mineral Oil: Venezuela, Argentina, Chile, Peru and Columbia
- South America also has large deposits of gold, silver, zinc, chromium, manganese, bauxite, mica, platinum, asbestos and diamond.
Africa
- It is the world’s largest producer of diamonds, gold and platinum.
- Gold: South Africa, Zimbabwe and Zaire
- Oil: Nigeria, Libya and Angola.
- Other minerals found in Africa are copper, iron ore, chromium, uranium, cobalt and bauxite.
Australia
- It is the largest producer of bauxite in the world.
- It is a leading producer of gold, diamond, iron ore, tin and nickel.
- It is also rich in copper, lead, zinc and manganese.
- Kalgoorlie and Coolgardie areas of western Australia have the largest deposits of gold.
Antartica
- Deposits of coal in the Transantarctic Mountains and iron near the Prince Charles Mountains of East Antarctica is predicted
- Iron ore, gold, silver and oil are also present in commercial quantities.
Distribution in India
- Iron: Jharkhand, Odisha, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Goa, Maharashtra and Karnataka.
- Bauxite: Jharkhand, Odisha, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu.
- Mica: Jharkhand, Bihar, Andhra Pradesh and Rajasthan.
- India is the largest producer and exporter of mica in the world.
- Copper: Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh.
- Manganese: Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh.
- Limestone: Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Rajasthan, Gujarat and Tamil Nadu.
- Gold: Kolar in Karnataka has deposits of gold in India. These mines are among the deepest in the world which makes mining of this ore a very expensive process.
- Salt: It is obtained from seas, lakes and rocks. India is one of the world’s leading producers and exporters of salt.
Uses of Minerals
- Minerals are used in many industries.
- Minerals used in various styles for jewellery.
- Copper is another metal used in everything from coins to pipes.
- Silicon, used in the computer industry is obtained from quartz.
- Aluminum obtained from its ore bauxite is used in automobiles and airplanes, bottling industry, buildings and even in kitchen cookware.
Conservation of Minerals
Why to conserve minerals?
- Minerals are a non-renewable resource.
- It takes thousands of years for the formation and concentration of minerals.
- The rate of formation is much smaller than the rate at which the humans consume these minerals.
How to conserve minerals?
- By reducing wastage in the process of mining.
- Recycling of metals is another way in which the mineral resources can be conserved.
Power Resources
- Power or enrgy is necessary for industry, agriculture, transport, communication and defense.
- Power resources categorised as:
- Conventional resources
- Non-conventional resources
Conventional Sources of Energy
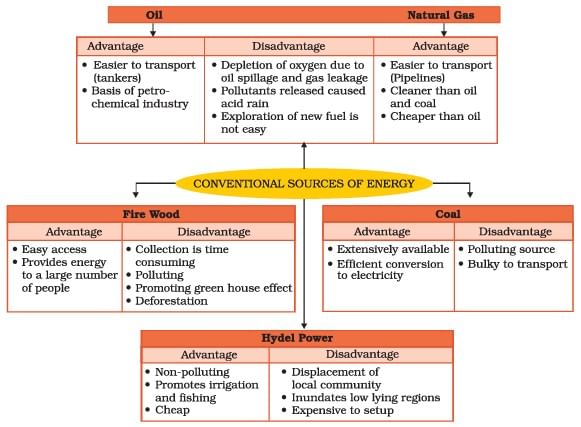
- Those sources which have been in common use for a long time are called Conventionals sources of energy.
- Firewood and fossil fuels are the two main conventional energy sources.
Firewood
- It is widely used for cooking and heating.
- In India, more than fifty per cent of the energy used by villagers comes from fire wood.
Fossil Fuels
- Remains of plants and animals which were buried under the earth for millions of years got converted by the heat and pressure into fossil fuels.
- Coal, petroleum and natural gas are the fossils fuels which are the main sources of conventional energy.
- Fossile fuels are in limited quantities and the rate at which the growing world population is consuming them is far greater than the rate of their formation.
Coal
- Most abundantly found fossil fuel.
- It is used as a domestic fuel, in industries such as iron and steel, steam engines and to generate electricity.
- Electricity from coal is called thermal power.
- The giant ferns and swamps got buried under the layers of earth millions of years ago converted into Coal. Therefore referred to as Buried Sunshine.
- Producers in the world: China, USA, Germany, Russia, South Africa and France.
- Producers in India: Raniganj, Jharia, Dhanbad and Bokaro in Jharkhand.
Petroleum
- Petroleum is a thick black liquid.
- It is found between the layers of rocks and is drilled from oil fields located in off-shore and coastal areas.
- This is then sent to refineries which process the crude oil and produce a variety of products like diesel, petrol, kerosene, wax, plastics and lubricants.
- Petroleum and its derivatives are called Black Gold as they are very valuable.
- Producers in the world: Iran, Iraq, Saudi Arabia and Qatar, USA, Russia, Venezuela, and Algeria.
- Producers in India: Digboi in Assam, Bombay High in Mumbai and the deltas of Krishna and Godavari rivers.
Natural Gas
- Natural gas is found with petroleum deposits and is released when crude oil is brought to the surface.
- It can be used as a domestic and industrial fuel.
- Producers in the world: Russia, Norway, UK and the Netherlands
- Producers in India: Jaisalmer, Krishna Godavari delta, Tripura and some areas off shore in Mumbai.
Why use of Fossile fuels should be checked?
- The sharp increase in our consumption of fossil fuels has led to their depletion at an alarming rate.
- The toxic pollutants released from burning these fuels are also a cause for concern.
Hydel Power
How Hydel Power is generated?
- Rain water or river water stored in dams is made to fall from heights.→ The falling water flows through pipes inside the dam over turbine blades placed at the bottom of the dam.
- The moving blades then turn the generator to produce electricity. which is called hydro electricity.
- The water discharged after the generation of electricity is used for irrigation.
- One fourth of the world’s electricity is produced by hydel power.
- Producers in the world: Paraguay, Norway, Brazil, and China.
- Important hydel power stations in India: Bhakra Nangal, Gandhi Sagar, Nagarjunsagar and Damodar valley projects.
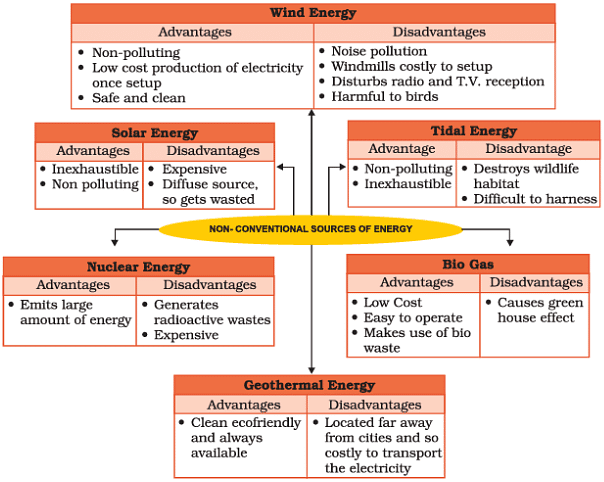
Non-Conventional Sources of Energy
Why we need to use non-conventional sources of energy
- The increasing use of fossil fuels is leading to its shortage.
- It is estimated that if the present rate of consumption continues, the reserves of these fuel will get exhausted.
- Also it causes environmental pollution.
- Therefore, there is need for using non-conventional sources.
- Examples of non-conventional sources: Solar energy, wind energy, tidal energy.
Solar Energy
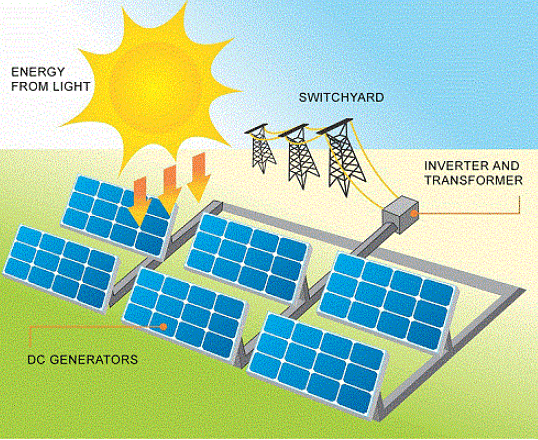
- Solar energy trapped from the sun can be used in solar cells to produce electricity.
- Many of these cells are joined into solar panels to generate power for heating and lighting purpose.
- The technology of utilising solar energy benefits a lot of tropical countries that are blessed with abundant sun shine.
- Solar energy is also used in solar heaters, solar cookers, solar dryers besides being used for community lighting and traffic signals.
Wind Energy
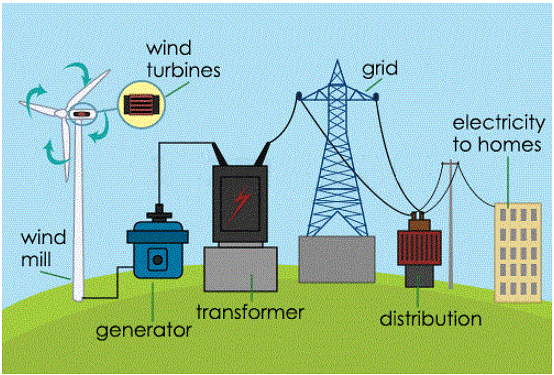
- The high speed winds rotate the wind mill which is connected to a generator to produce electricity.
- Wind farms having clusters of such wind mills are located in coastal regions and in mountain passes where strong and steady winds blow.
- Windfarms are found in Netherlands, Germany, Denmark, UK, USA and Spain.
Nuclear Power
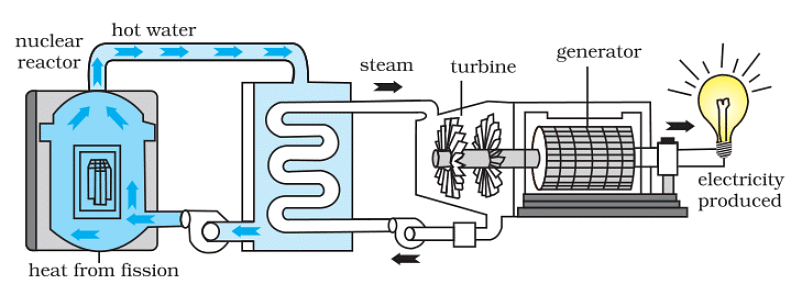
- Nuclear power is obtained from energy stored in the nuclei of atoms of naturally occurring radio active elements like uranium and thorium.
- These fuels undergo nuclear fission in nuclear reactors and emit power.
- Greatest Producers: USA and Europe.
- Uranium deposits in India: Rajasthan and Jharkhand.
- Thorium is found in large quantities in the Monozite sands of Kerala.
- Nuclear power stations in India: Kalpakkam in Tamilnadu, Tarapur in Maharastra, Ranapratap Sagar near Kota in Rajasthan, Narora in Uttar Pradesh and Kaiga in Karnataka.
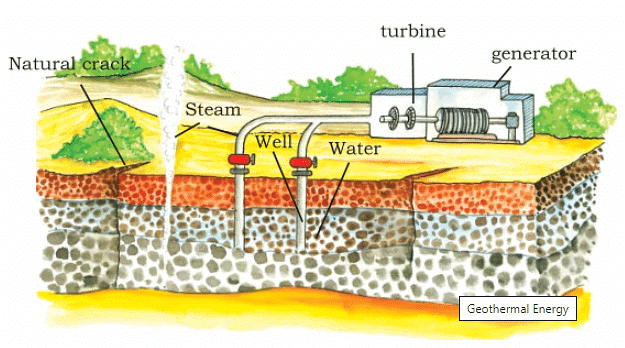
Geothermal Energy
- Heat energy obtained from the earth is called geothermal energy.
- The temperature in the interior of the earth rises steadily as we go deeper.
- Some times this heat energy may surface itself in the form of hot springs.
- This heat energy can be used to generate power.
- Geothermal energy in the form of hot springs has been used for cooking, heating and bathing for several years.
- USA has the world’s largest geothermal power plants followed by New Zealand, Iceland, Philippines and Central America.
- In India, geothermal plants are located in Manikaran in Himachal Pradesh and Puga Valley in Ladakh.
Tidal Energy
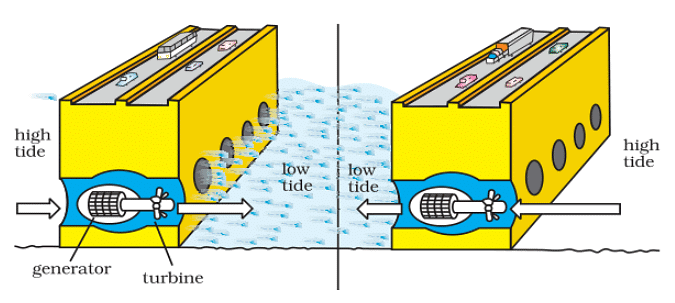
- Energy generated from tides is called tidal energy.
- Tidal energy can be harnessed by building dams at narrow openings of the sea.
- During high tide the energy of the tides is used to turn the turbine installed in the dam to produce electricity.
- Producers in the world: Russia, France and the Gulf of Kachchh in India have huge tidal mill farms.
Bio Gas
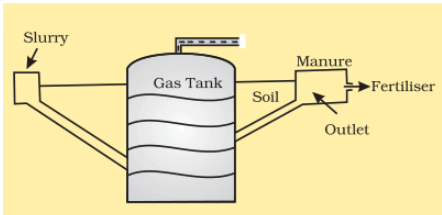
- Organic waste such as dead plant and animal material, animal dung and kitchen waste can be converted into a gaseous fuel called biogas.
- The organic waste is decomposed by bacteria in biogas digesters to emit biogas which is essentially a mixture of methane and carbon dioxide.
- Biogas is an excellent fuel for cooking and lighting and produces huge amount of organic manure each year.
The document Mineral & Power Resources Summary Class 8 NCERT Summary Chapter 1 is a part of the Class 8 Course NCERT Textbooks & Solutions for Class 8.
All you need of Class 8 at this link: Class 8
FAQs on Mineral & Power Resources Summary Class 8 NCERT Summary Chapter 1
The underlying connection was closed: An unexpected error occurred on a receive.
Related Searches