Producer’s Equilibrium Class 12 Economics
Producer
A producer is an economic agent who produces goods and services for sale with the objective of
→ maximizing profit ; or → minimizing losses
Producer's Equilibrium
It refers to a situation where producer maximizes his profit or minimizes his losses.
⇒ It tells the level of output that producer should undertake to produce to achieve the objectiveof maximizing profit and at this level of output there is no incentive for firm either to increase or decrease output
Conditions of Producer's Equilibrium
A firm maximise profit that is difference between TR and TC at a level of output where two conditions are met
(a) MARGINAL REVENUE(MR) = MARGINAL COST (MC)
(b) MC BECOMES GREATER THAN MR AFTER EQUILIBRIUM LEVEL : In other words Marginal cost (MC) should be rising OR MC should cut MR from below (rising MC means that a firm achieves its profit maximising equil ibrium only in stage of diminishing return)
PRODUCER’S EQUILIBRIUM UNDER PERFECT COMPETITION
{WHEN MORE IS SOLD AT SAME PRICE}
| First condition of MR = MC is satisfied at both 2nd and 4th level of output . But second condition MC > MR after equilibrium level (or MC is rising) is satisfied only at 4th level of output indicating that producing more will lead to decline in profits . Hence producer equilibrium is achieved at 4th level of output |
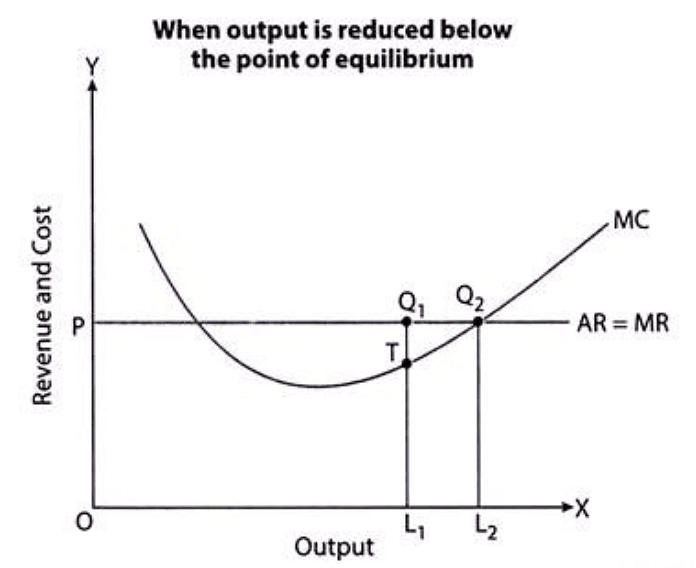
| Accordingly E is equilibrium point and OQ the profit maximising output .Thus the equilibrium point will be at point where MR = AR(Price) = MC. In other words in a perfect competitive market, the market price (P) should be equal to rising part of MC |
PRODUCER’S EQUILIBRIUM IMPERFECT COMPETITION
{WHEN MORE IS SOLD BY LOWERING THE PRICE}
| First condition of MR = MC is satisfied at both 2nd and 4th level of output . But second condition MC > MR after equilibrium level (or MC is rising) is satisfied only at 4th level of output indicating that producing more will lead to decline in profits. Hence producer equilibrium is achieved at 4th level of output |
⇒ Accordingly E is equilibrium point and OQ the profit maximising output.
| SPECIAL POINT :: Thus the equality of MR and MC is a necessary condition for equilibrium but it is not by itself sufficient to attain producers equilibrium. So first condition must be supplemented with the second condition to attain the producer’sequilibrium |
RELATION BETWEEN PRICE AND MC at EQUILIBRIUM
IN THE SHORT-RUN , A FIRM SHOULD PRODUCE IF AND ONLY IF AR (P) > AVC OR TR > TVC
IF a firm exercises the option of closing down and produces nothing , the losses would be equal to its fixed cost. Thus in short run a firm has to compare losses in the two situation -
(A) losses in a situation of shut down (that is loss of fixed cost) and
(B) losses if the firm continues to produce
| (Q1) Do producer always maximise their profit ? (Q2) Producer doesnot always work to maximise their profit ? (Q3) Should a producer stop production when producer means losses to him ? (Q4) Will a profit- maximising firm in a competitive market ever produce a positive level of output in the short run if the market price is less than minimum of AVC ? Give an explanation |
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN B.E.P & SHUT DOWN POINT
| B.O.D | BREAK EVEN POINT | SHUT DOWN POINT |
| Meaning | It refers to a situation when TR = TC or AR (P) = AC | It refers to a situation when TR = TVC or AR (P) = AVC |
| Situation | It i ndicates situation of no profit (abnormal) or no loss. Thus the Firm is able to earn only Normal profit that are included in COP | It i ndicates situat ion whe re firm is recovering only variable cost or the loss is equal to fixed cost |
| Decision | Since normal profit is there, firm carries on production | Producer is indifferent whether to suspend production or not . However in case of further rise in cost or Fall in price , The producer will stop production |
|
476 videos|360 docs
|
FAQs on Producer’s Equilibrium Class 12 Economics
| 1. What is producer's equilibrium? |  |
| 2. How is producer's equilibrium determined? |  |
| 3. What factors can shift a producer's equilibrium? |  |
| 4. What is the relationship between producer's equilibrium and profit maximization? |  |
| 5. Can a producer be in equilibrium without maximizing their profits? |  |




















